Managing multiple lease agreements in the real estate world can be overwhelming. These documents are often lengthy—sometimes running over 100 pages—making it challenging to grasp the key points quickly. Not just that, they are filled with legal jargon and clauses requiring specialised knowledge, making manual data extraction time-consuming, error-prone and generally inefficient. That’s where lease abstraction comes in.
Lease abstraction is a critical process in the real estate and property management industries, involving the extraction of key information from lengthy and complex lease documents. This process has become increasingly important as businesses and organisations seek to streamline their lease management, ensure compliance with accounting standards (ASC 842, IFRS 16, or GASB 87), and make data-driven decisions about their property portfolios.
Use-cases for lease abstraction are diverse and span various industries. As technology advances, many organisations are turning to artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions to automate the lease abstraction process.
If you are reading the blog, chances are you are struggling with lease abstraction. Through the following sections, we will dive deeper into what lease abstraction is, the various techniques one can use to automate lease abstraction and the various benefits of using ai-based document processing tools over these techniques.
Lease Abstract: An Overview
A lease abstract takes complicated lease contracts and breaks them down into an easy-to-read summary. It serves as a quick reference document that allows stakeholders to access essential lease information without having to go through the entire lease document.
Essentially, it breaks down a complex legal document into a digestible format that can be easily understood and utilized by various departments within an organization, including finance, operations, and facilities management.
Not just that, it also serves as a navigation tool which directs you to detailed sections whenever necessary
The importance of lease abstracts cannot be overstated in today’s business environment. With the introduction of new lease accounting standards such as ASC 842 and IFRS 16, organizations are required to report lease obligations on their balance sheets, making accurate and comprehensive lease data more crucial than ever. Lease abstracts provide the foundation for this compliance by ensuring that all relevant financial information is captured and readily available.
Moreover, lease abstracts play a vital role in other areas as well:
1. Stay on top of important dates like rent reviews, break options, and lease expirations.
2. Improve how you budget and forecast property-related expenses.
For a clearer understanding of lease abstracts, here is a general overview of the key components extracted from leases:
- Property Information: Details about the leased property, including its address, size, and specific features.
- Lease Parties: The names and contact information of the landlord and tenant involved in the lease agreement.
- Lease Term: The duration of the lease, including the start and end dates and any options for renewal.
- Rent: The base rent amount the tenant must pay, along with the payment schedule (e.g., monthly, quarterly).
- Additional Rent: Any extra payments the tenant must make, such as property taxes, utilities, or common area maintenance fees.
- Tenant Improvement Allowance: Funds the landlord provides for the tenant to customize or improve the leased space.
- Maintenance and Repairs: The landlord and tenant are responsible for maintaining and repairing the property, including who covers the costs.
- Parking: Terms related to parking facilities, including the number of spaces provided, fees, and any specific conditions.
- Use of Premises: The tenant’s permitted use of the property, including any restrictions on activities or business operations.
- Assignment and Subletting: Conditions under which the tenant can transfer the lease or sublet the property to another party.
- Default and Remedies: The actions considered a breach of the lease and the remedies available to the landlord, such as penalties or lease termination.
- Insurance and Indemnification: There are insurance requirements for both parties and provisions for indemnification in case of damages or legal claims.
- Additional Clauses: Any other specific terms or conditions that are important to the lease, such as options for expansion, early termination rights, or unique tenant obligations.
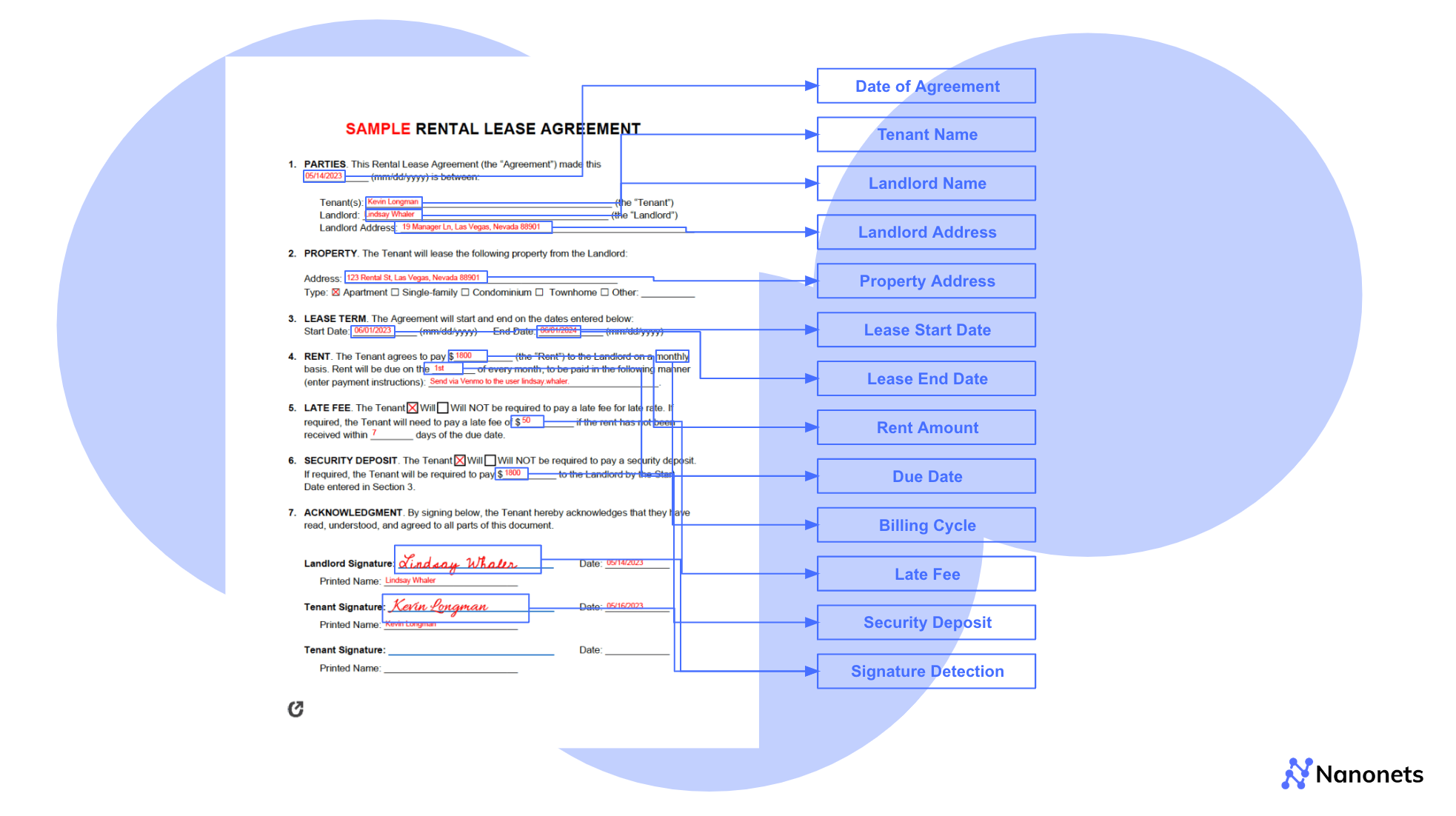
The specific data points extracted may vary depending on the type of property, industry, and the organization’s particular needs. However, the goal remains the same: to create a comprehensive yet concise summary that captures all critical information necessary for effective lease management.
| Use-case | Industry | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Portfolio Optimization | Real estate advisory firms | Advisory firms use lease abstraction to analyze lease terms across portfolios, helping property owners identify opportunities to optimize assets. |
| Rent Collection Management | Property management companies | Property managers abstract leases to automate rent collection processes, ensuring that property owners receive payments on time and in full. |
| Compliance Monitoring | REITs | REITs leverage lease abstraction to ensure lease terms and tenant obligations are followed, reducing legal risks for property owners. |
| Budgeting and Forecasting | Real estate advisory firms | By abstracting rent schedules and expense clauses, advisors help property owners accurately budget and forecast revenue from their assets. |
| Lease Renewal Negotiations | Property management companies | Lease abstraction enables managers to prepare for renewal negotiations, helping property owners secure better lease terms with current tenants. |
Techniques for Lease Abstraction
While many small organisations still rely on manual processes involving emails and spreadsheets, the game has changed. Thanks to the rise of lease abstraction software and ai-based or automated document processing tools, what once took hours can now be done in just a few clicks. Let’s take a look at a few techniques that can be used for Lease Abstraction but before we jump into each one in detail, here’s a quick summary of the methods we will be discussing today:
| Method | Short Description | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Using Lease Abstraction Software | Pre-built templates for extracting data from standard leases, commonly used by companies for efficiency. | 1. Struggles with non-standard leases 2. Time-consuming setup 3. Limited adaptability 4. Inconsistent accuracy 5. Heavy human oversight |
| Using Large Language Models (LLMs) | Utilizes machine learning models like GPT to summarize or extract data from leases with prompts. | 1. Requires coding proficiency 2. Needs prompt engineering 3. Prone to hallucinations 4. Black-box nature 5. Data security concerns |
| ai-based-intelligent-document-processing-systems-for-lease-abstraction”>ai-based Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) | Automates lease abstraction using ai for any document type, with high accuracy and workflow automation. | 1. High initial setup cost 2. Requires technical expertise 3. Limited customization without platform-specific tools |
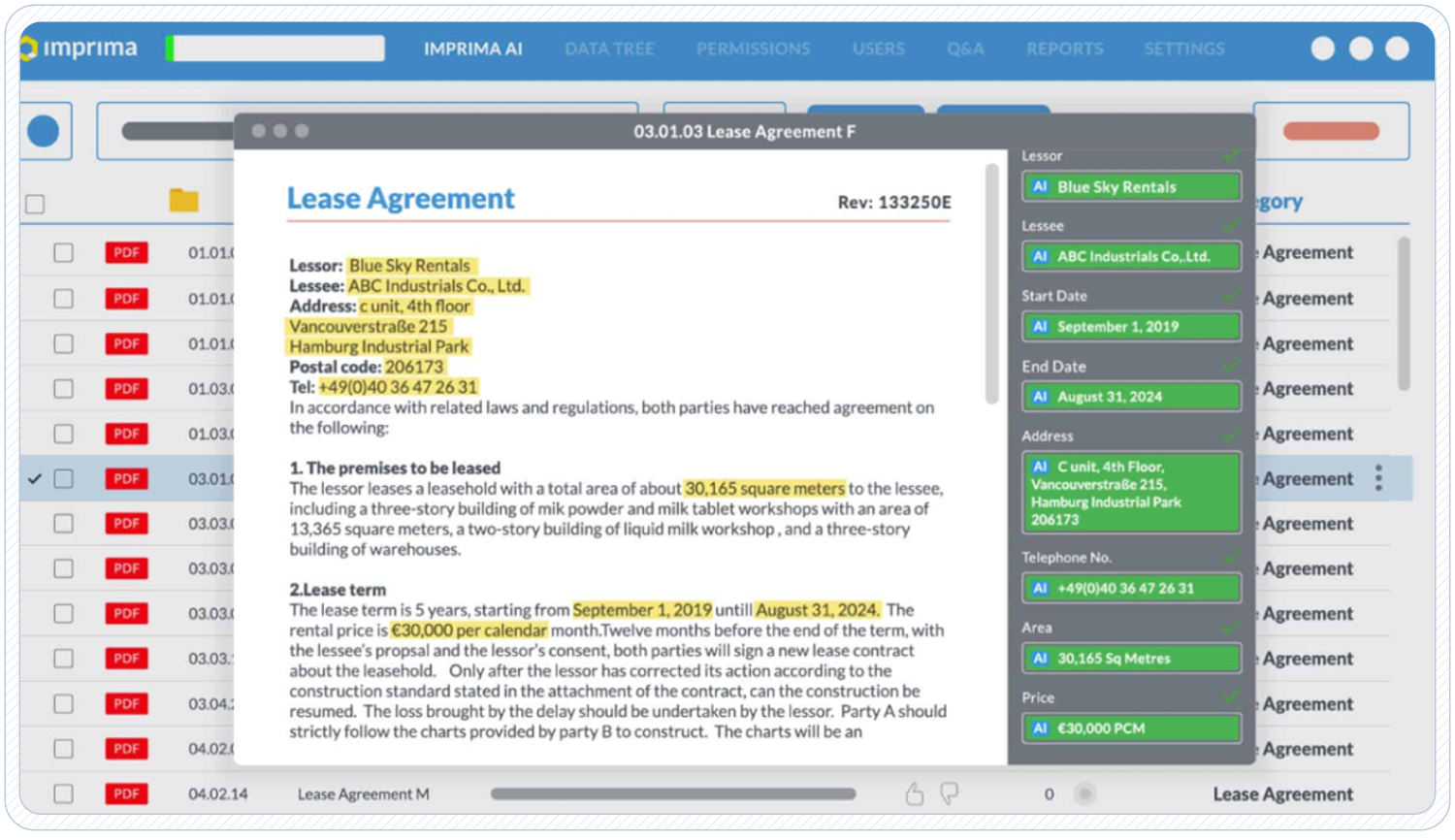
1. Using Lease abstraction software
This method has been a go-to solution for many companies looking to streamline their lease management processes. These specialized tools offer pre-built templates and extraction rules tailored to common lease formats. Common examples include Imprima, LeaseLens and MRI Software. However, they often fall short when dealing with non-standard leases or company-specific clauses.
The rigidity of these systems can lead to missed critical information, and they typically require significant manual setup and ongoing maintenance. Many users find themselves still relying heavily on human review to ensure accuracy, somewhat defeating the purpose of automation.
1. Rigidity: These systems often struggle with non-standard lease formats or unique clauses, potentially missing crucial information that doesn’t fit their predefined templates.
2. Setup time: Configuring templates for different lease types can be time-consuming, requiring significant upfront investment.
3. Limited adaptability: They may not easily accommodate changes in accounting standards or company-specific reporting requirements without extensive reconfiguration.
4. Inconsistent accuracy: Performance can vary widely depending on how closely a lease matches the template, leading to unreliable results across a diverse portfolio.
5. Over-reliance on human review: To ensure accuracy, many organisations still need substantial human oversight, reducing the efficiency gains.
2. Using LLMs for lease abstraction
LLMs or Large Language Models are machine learning algorithms that are trained on large data sets and can respond to queries the same way a human would. So, this method essentially involves using an LLM to summarise leases.
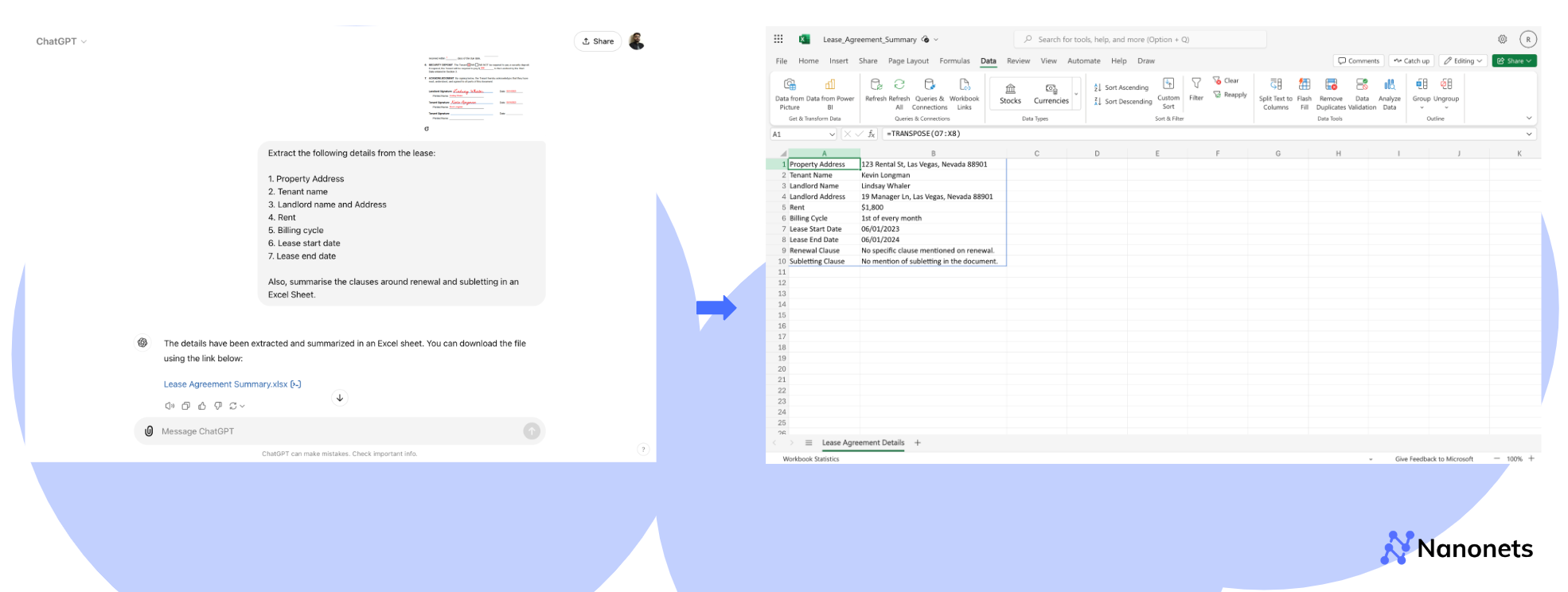
We will leverage the GPT-4o user interface to summarise a lease. Alternatively, one can request extraction of specific data points from the lease. This requires some level of prompt engineering. We tried out the following two prompts which worked for us.
Prompt 1: “Summarise this lease contract.”
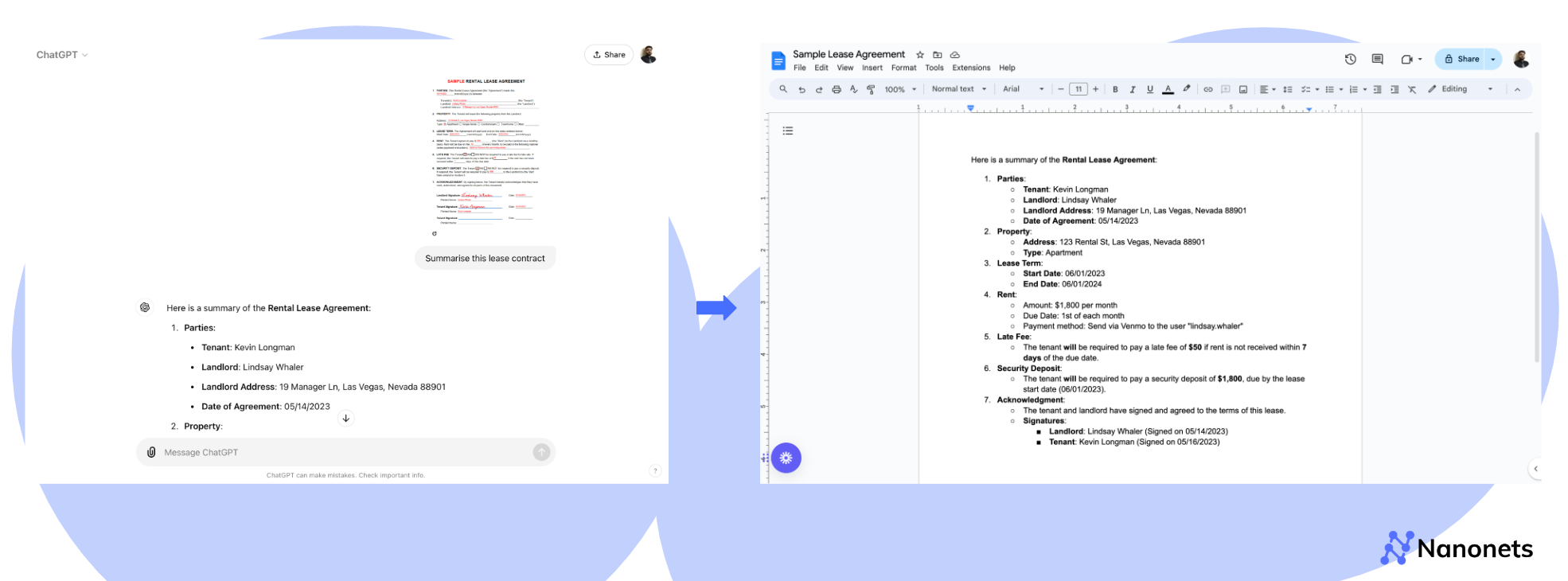
1. Property Address
2. Tenant name
3. Landlord name and Address
4. Rent
5. Billing cycle
6. Lease start date
7. Lease end date
Also, summarise the clauses around renewal and subletting in an Excel Sheet.”
1. Coding Proficiency: Requires coding proficiency for API access, maintenance and debugging.
2. Prompt engineering: Requires specialised prompt engineering experience.
3. Prone to Hallucinations: Prone to hallucinations, requires manual verification.
4. Manual post-processing: Post-processing effort after vague prompts, ends up requiring more resources than manual conversion.
5. Black-box functionality: LLMs are a “black box” which essentially means, you cannot trace the errors and fix them. It isn’t an ideal method as you scale your operations.
6. Data security: Privacy issues when using third-party LLMs for sensitive lease abstraction.
<h3 id="3-using-ai-based-intelligent-document-processing-idp-systems-for-lease-abstraction”>3. Using ai-based Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) systems for lease abstraction
Using ai-based Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) systems represent the cutting edge in lease abstraction technology. These solutions combine the power of data extraction with workflow automation to automate the entire lease abstraction workflows end-to-end.
ai-based IDPs are specialized for data extraction from any document type and format. Since they are powered by artificial intelligence, they can understand data points and infer from context. Their accuracy is high, surpassing humans with specialised legal knowledge. They also have validation features, built-in which offer the capability of human review should the need arise. With automated import and export and high security standards, IDPs are the ultimate solution for automating lease abstraction.
Nanonets is one such example. We will take a look at how we can automate lease abstraction using the zero-training extractor from Nanonets. Let’s get started.
Step 1: Log into the Nanonets application (app.nanonets.com)
Step 2: Click on “New Workflow” on the left panel > Zero-training Extractor.
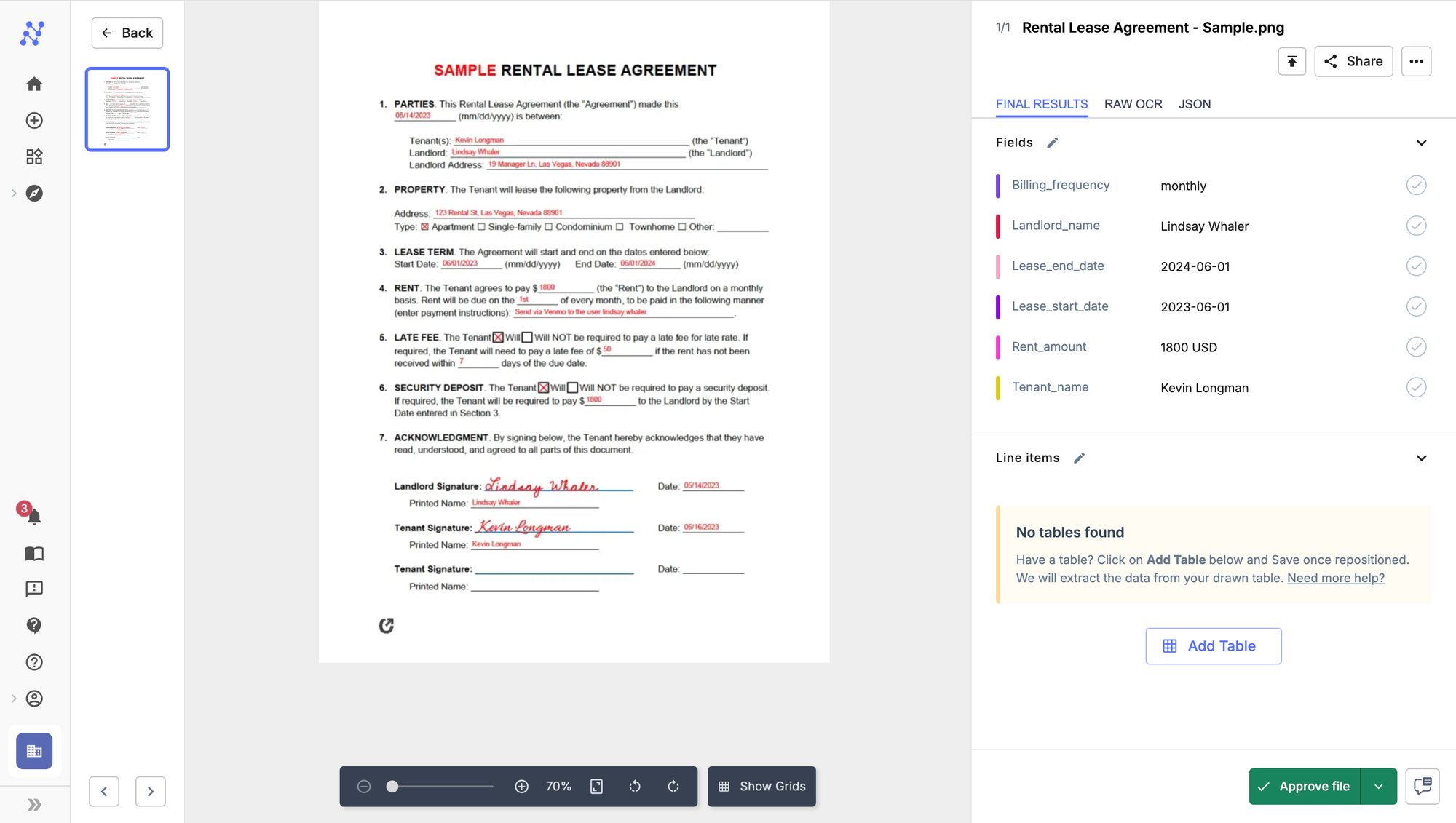
Step 3: Enter the fields you want extracted from the lease, for instance:
- Landlord name
- Tenant name
- Rent amount
- Billing frequency
- Lease start date
- Lease end date
Step 4: Click on continue. Upload the file, and allow some time for processing.
<h2 id="benefits-of-using-ai-based-idps-nanonets-for-lease-abstraction”>Benefits of using ai-based IDPs (Nanonets) for Lease abstraction
1. Format agnostic
Nanonets offers a zero-training extractor, completely powered by generative ai. It doesn’t require any manual training and can be deployed in seconds. It infers text from context and extracts it without any manual or template-based training. You just need to enter the data points you want to extract and click “Continue.”
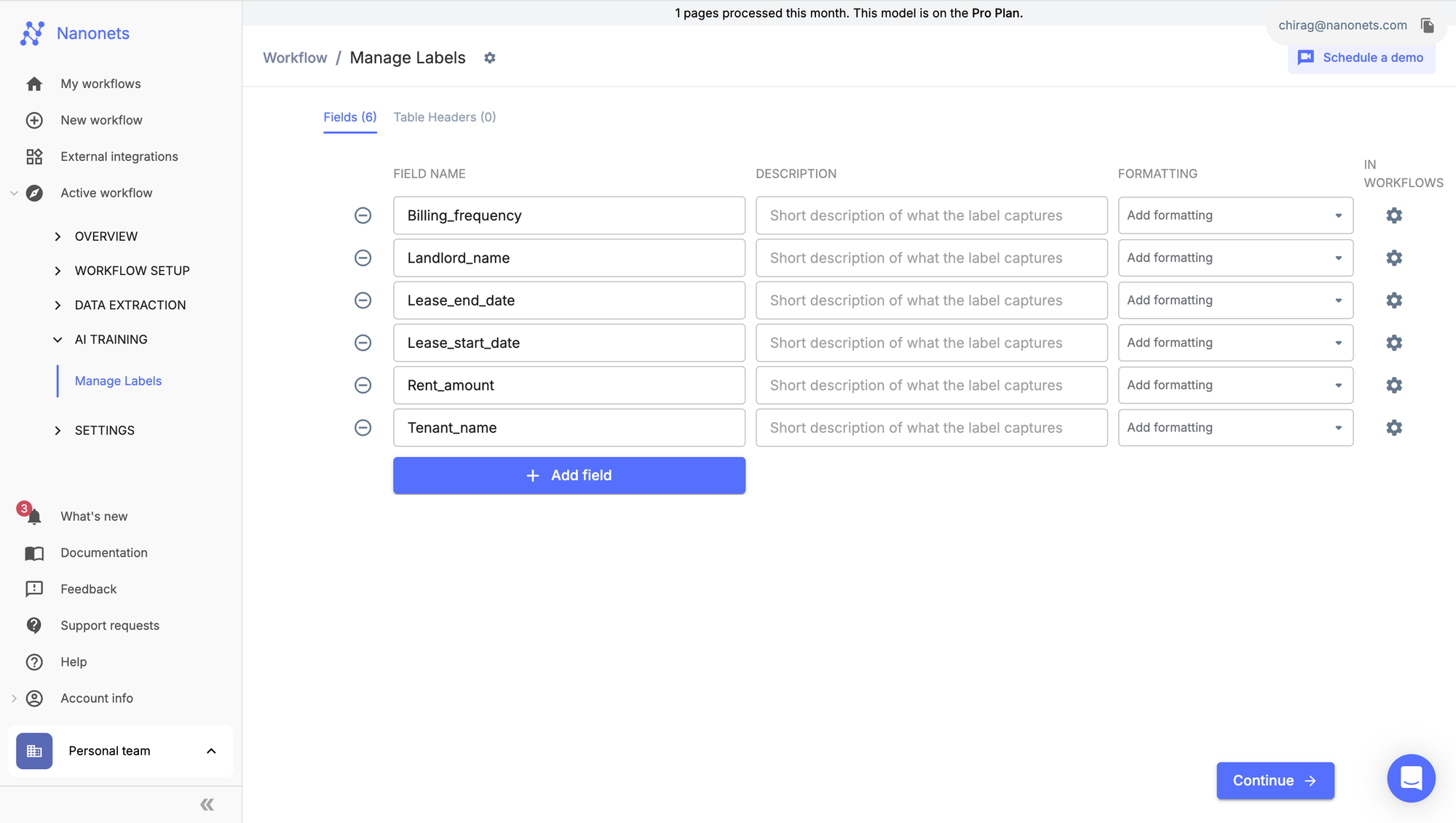
This ensures scalability regardless of the layout and requires no maintenance or “re-training” for different templates.
2. Data Validation and Approval
There’s a dedicated section on data validation that can flag files based on custom logic, for instance, the lease is missing “lease start date”, or lease start date + tenure doesn’t equal lease end date.
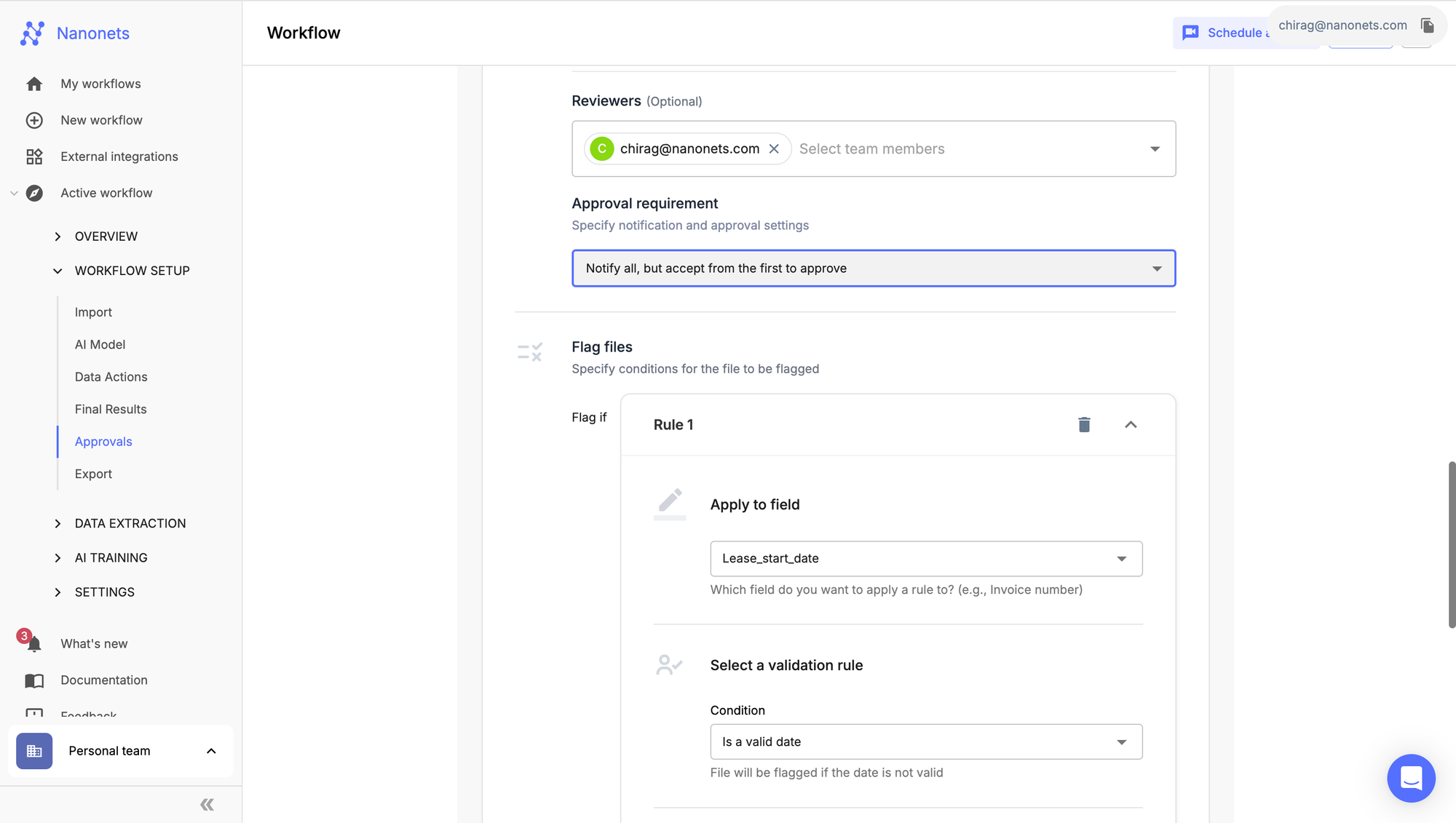
This ensures that no critical data points are missed out and facilitates human review for specified sections only. The export section can be triggered once the files have been manually reviewed and approved. Moreover, since this is ai-powered the model learns from its mistakes and improves over time by carefully analysing the “approved files”.
3. Custom Data actions
There is a dedicated section on “custom data actions” which powers all kinds of formatting actions in-house, such as lookup against external databases, finding and replacing characters, etc. There is a section powered by LLMs, where you can summarize entire sections within leases, ask questions based on lease sections, etc. This comes in handy when preparing comprehensive lease abstracts and cuts down the time taken by over 80%.
For instance, let’s say we have monthly rent (US$ 1800), we can calculate annual rent using the “Data Actions” section powered by LLMs. Not just simple mathematical calculations, but more advanced and complicated questions.
4. Automated Import and Export options
Nanonets offers the capability to import leases from a host of different places. Popular options include email inboxes (auto-forwarding option available), cloud storages, like, G-Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, Sharepoint or even databases, like amazon S3. There’s always an option of importing leases from API endpoints.
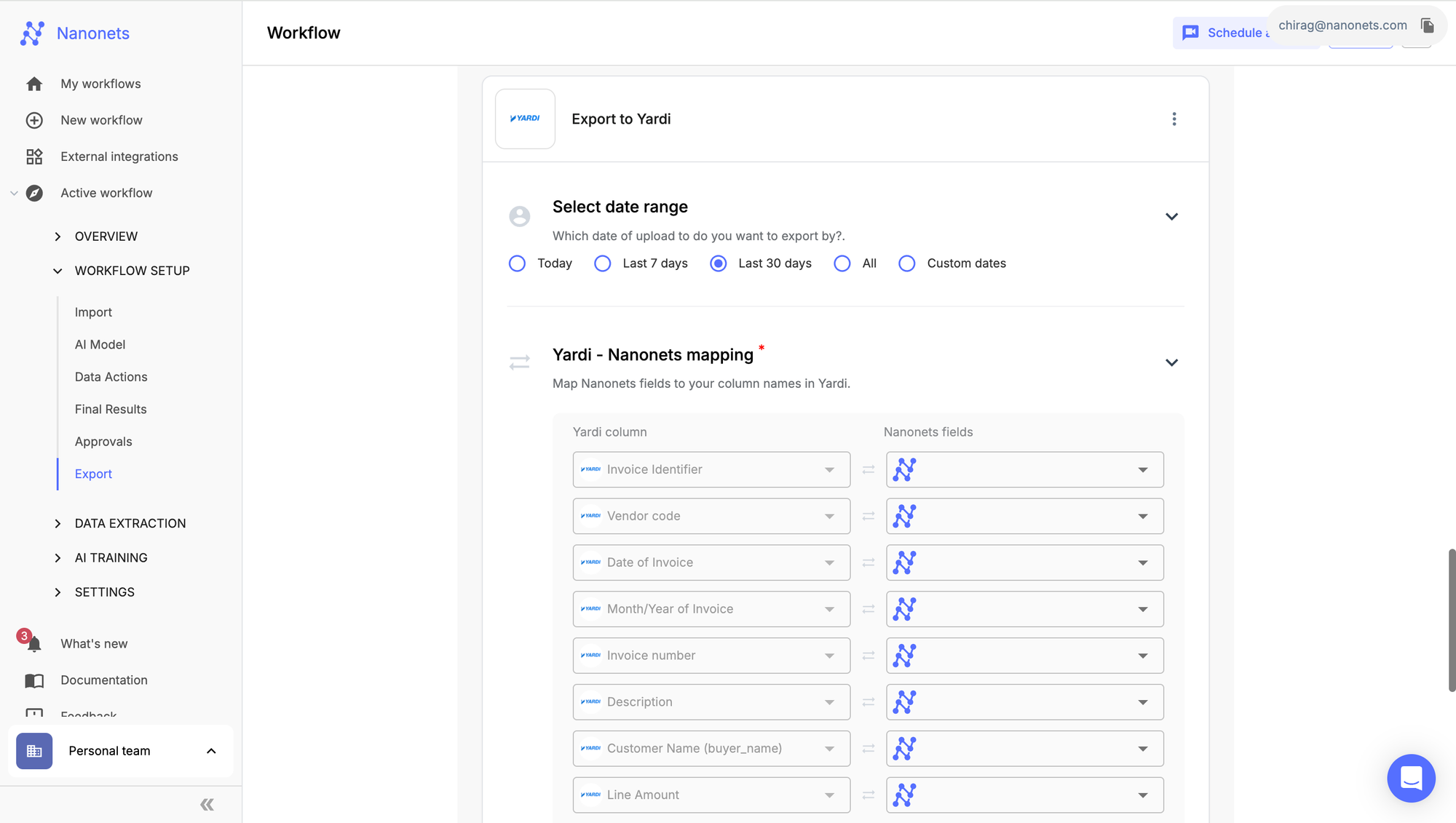
Similarly, there are plenty of export options available as well. The default options include Excel, CSVs, XML and JSON files. There are one-click integrations with third-party ERP software, like, Google Docs, Salesforce, Airtable, or Hubspot as well as the option to export to databases, like, MsSQL, PostgresSQL, Yardi, etc. You can always export the output in JSON format via API endpoints.
Summary
So, as we saw, Lease abstraction is a critical process in real estate and property management that involves extracting key information from complex lease documents. It has become increasingly important as organizations seek to streamline lease management, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and make data-driven decisions about their property portfolios.
Lease abstracts provide a concise summary of essential terms and conditions, allowing stakeholders to quickly access important information without having to go through entire lease documents. The process is crucial for various industries, from retail companies managing multiple locations to real estate investment trusts evaluating potential acquisitions.
We discussed three main techniques for lease abstraction: using Large Language Models (LLMs), template-based lease abstraction software, and ai-based Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) systems.
While LLMs and template-based software have their applications, they come with limitations such as potential inaccuracies, rigidity, and the need for significant manual oversight.
ai-based IDPs, particularly Nanonets, are the most advanced and efficient solution for lease abstraction. These systems offer benefits such as format-agnostic processing, data validation and approval features, custom data actions, and automated import and export options, making them highly scalable and adaptable to various lease structures and organizational needs.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER