Introduction
Conditional formatting in Excel is more than just a feature—it’s a powerful tool that transforms the way you interact with data. Whether you’re managing a simple budget or analyzing complex data sets, conditional formatting helps you highlight important trends, patterns, and outliers with just a few clicks. In this article, we’ll explore how you can use this feature to make your data more visually appealing and informative.
General description
- Learn how conditional formatting in Excel turns raw data into visual insights, highlighting trends and outliers.
- Learn how to use Excel's conditional formatting rules to automatically highlight critical data points with colors, icons, and data bars.
- Explore applying custom conditional formatting using Excel formulas for more nuanced data analysis.
- Use conditional formatting to quickly detect highest or lowest results and duplicate entries in large data sets.
- Get practical tips to maximize the impact of conditional formatting without cluttering your spreadsheets.
- Master conditional formatting to create visually appealing and informative spreadsheets that effectively communicate data stories.
Conditional Formatting: An Overview
Essentially, conditional formatting allows you to apply specific formatting (such as colors, icons, or data bars) to cells based on the values they contain. This automatic formatting is triggered by rules you define, making it easy to spot trends or critical data points without having to manually sift through the numbers.
Read also: Microsoft Excel for data analysis
Highlight cells based on value
One of the simplest and most effective uses of conditional formatting is to highlight cells based on their value. For example, if you want to quickly identify which sales figures exceed a certain threshold, conditional formatting can help. Here's how:
Here's how you can highlight cells based on their values:
- Select the range
Select the cells you want to format.
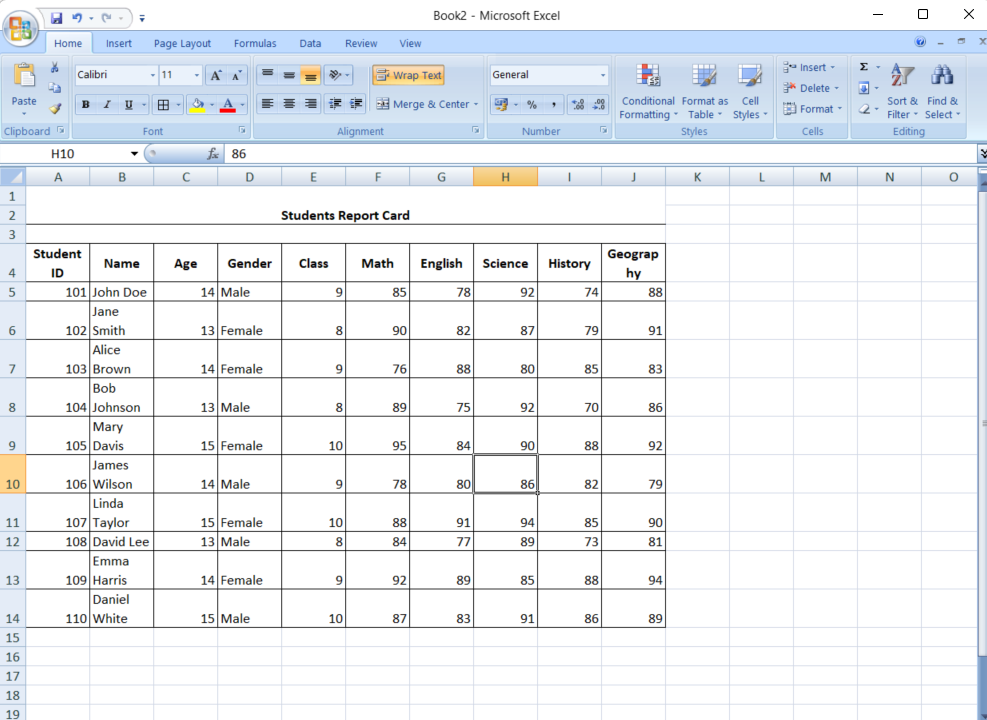
- Navigate to Conditional Formatting
Find the Conditional Formatting option on the Home tab, in the Styles group.
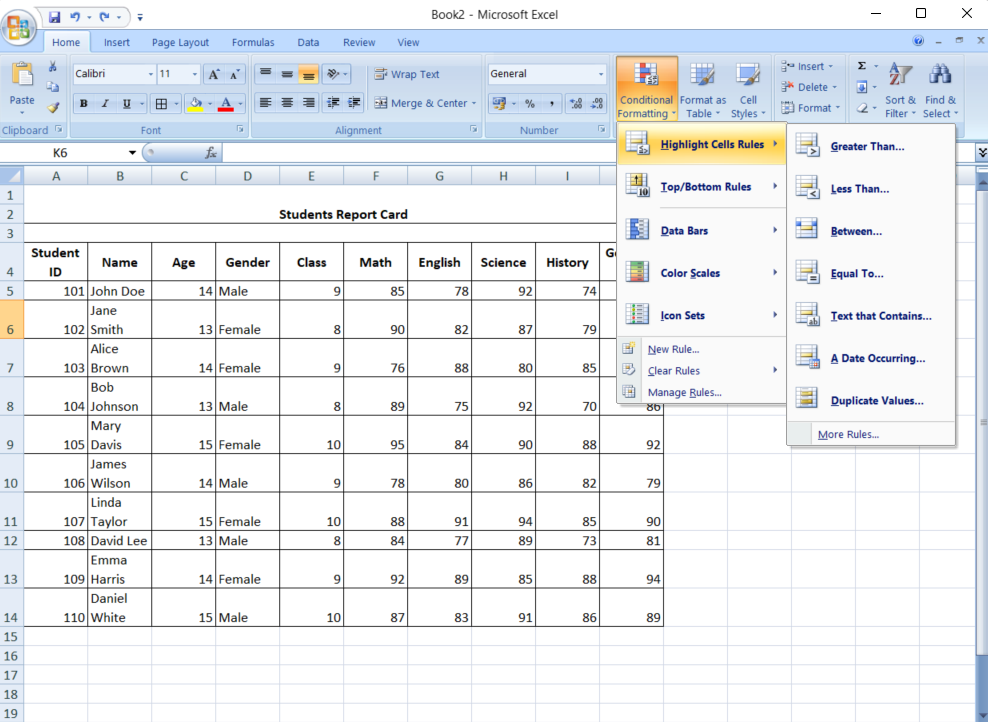
- Choose your rule
Select “Highlight Cells Rules” and then “Greater Than.” Then enter the threshold value and choose the formatting style you want.
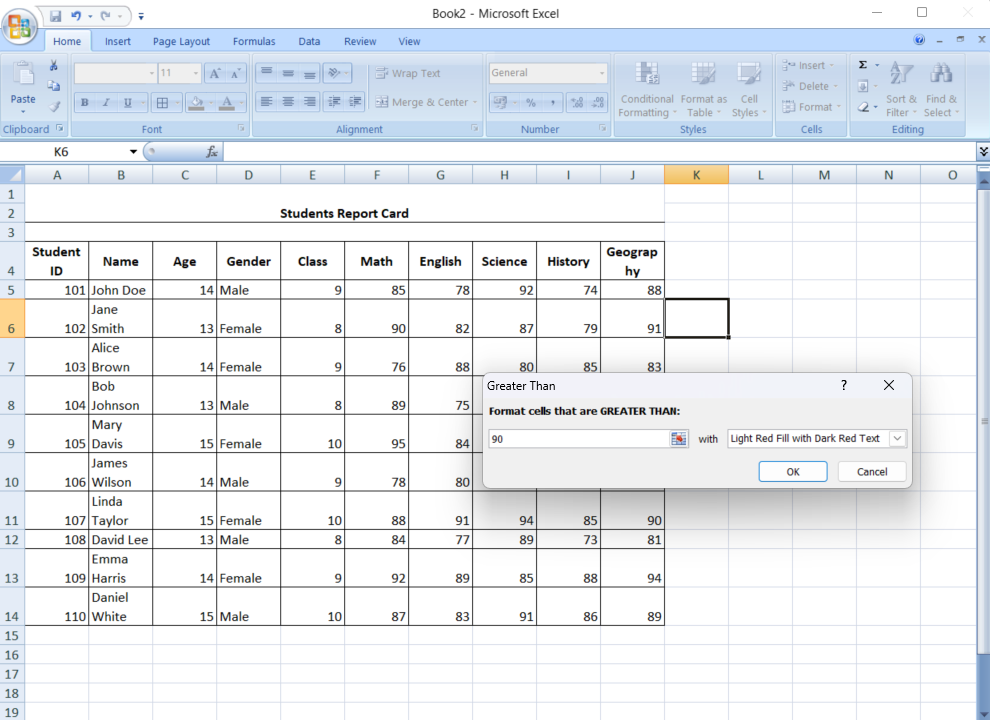
- Apply the format
Click OK and Excel will highlight the cells that meet your criteria.
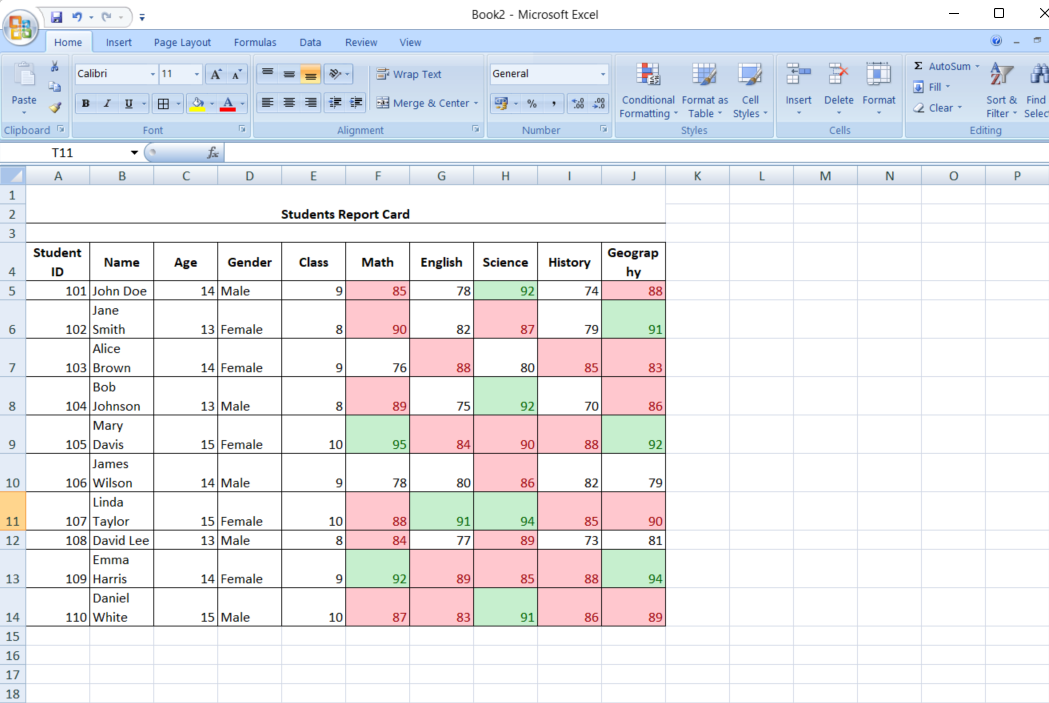
Using formulas for custom formatting
Excel's flexibility shines when using formulas to apply Conditional formatThis allows for more nuanced and customized rules. For example, you might want to highlight cells based on a condition other than simply a comparison to a static value, such as flagging sales that are above the previous month's average.
- Select your range: Highlight the cells you want to format.
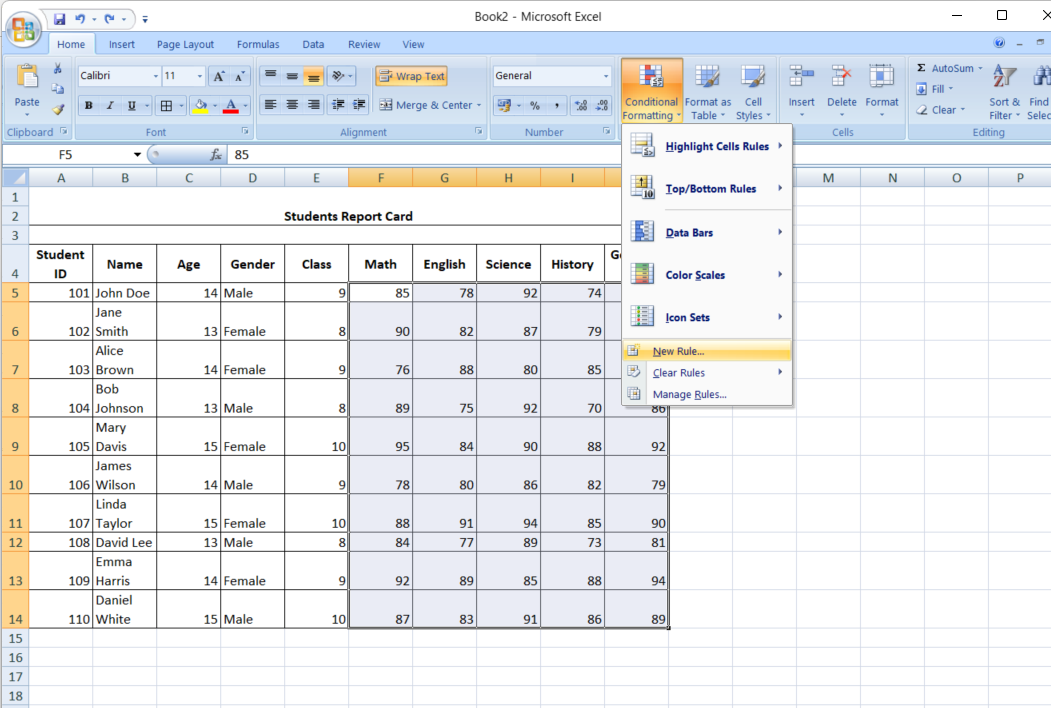
- Create a new rule: From the Conditional Formatting menu, select “New Rule” and choose “Use a formula to determine which cells to format.”
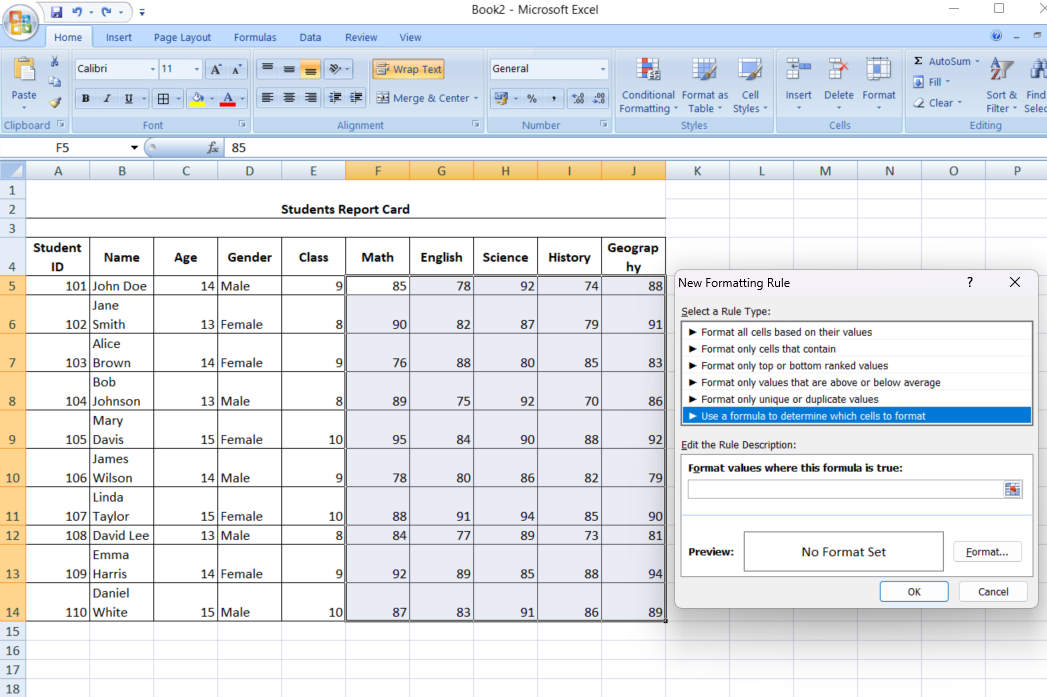
- Enter the formula: Enter your formula, which should return a TRUE or FALSE result.
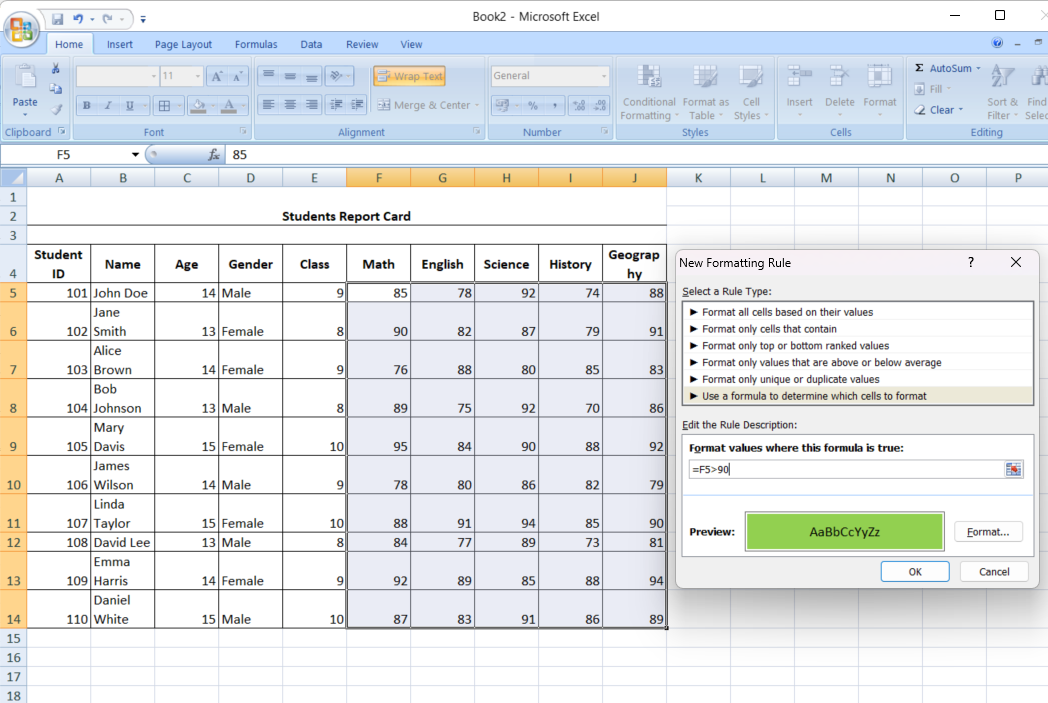
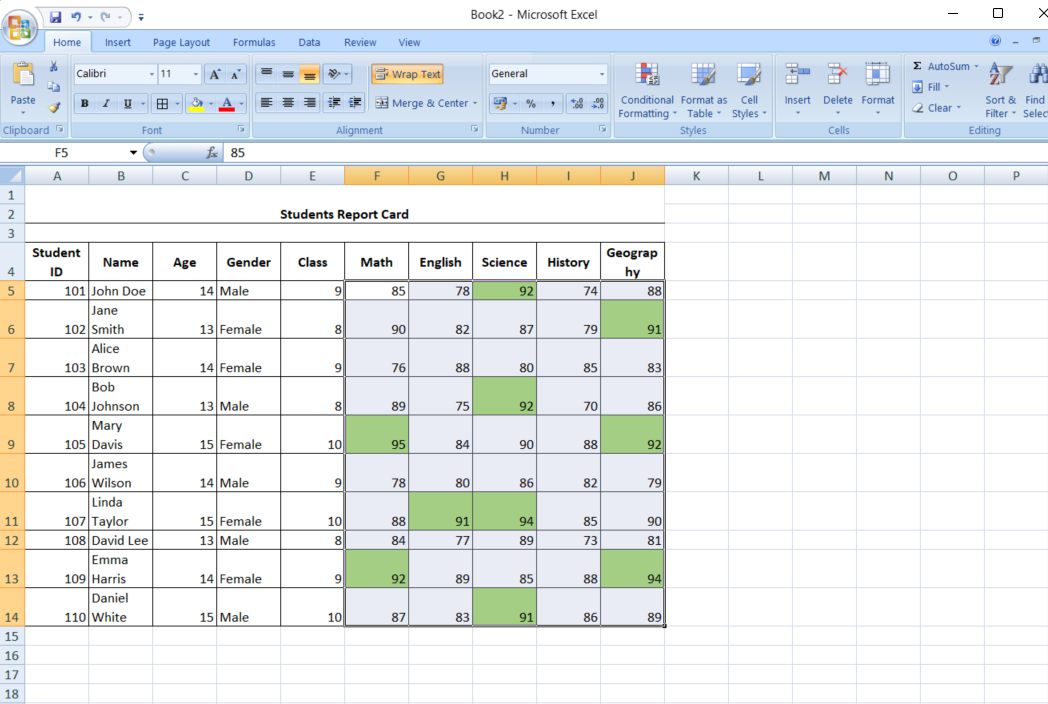
- Select a format: Choose how you want the cells to appear if the condition is met.
- Apply: Click OK to see the changes in your spreadsheet.
Also Read: A Complete Guide to Advanced Microsoft Excel for Data Analysis.
Highlighting the extremes: top/bottom rules
Conditional formatting can also help you focus on the highest and lowest values in a data set, such as identifying the top 10 performers or the lowest 5 sales figures.
- Select your data range: Highlight the relevant cells.
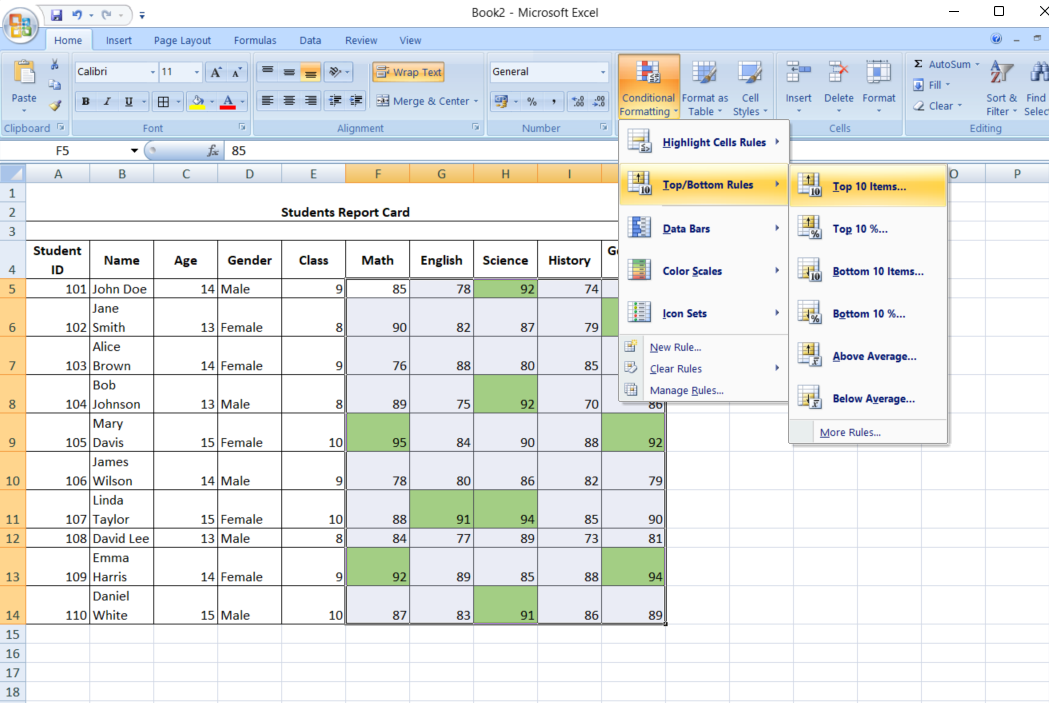
- Accessing conditional formatting: Go to Conditional Formatting > Top/Bottom Rules.
- Set the parameters: Select whether to highlight top or bottom values and specify the number of items.
- Finalize the format: Select the desired formatting style and apply the rule.
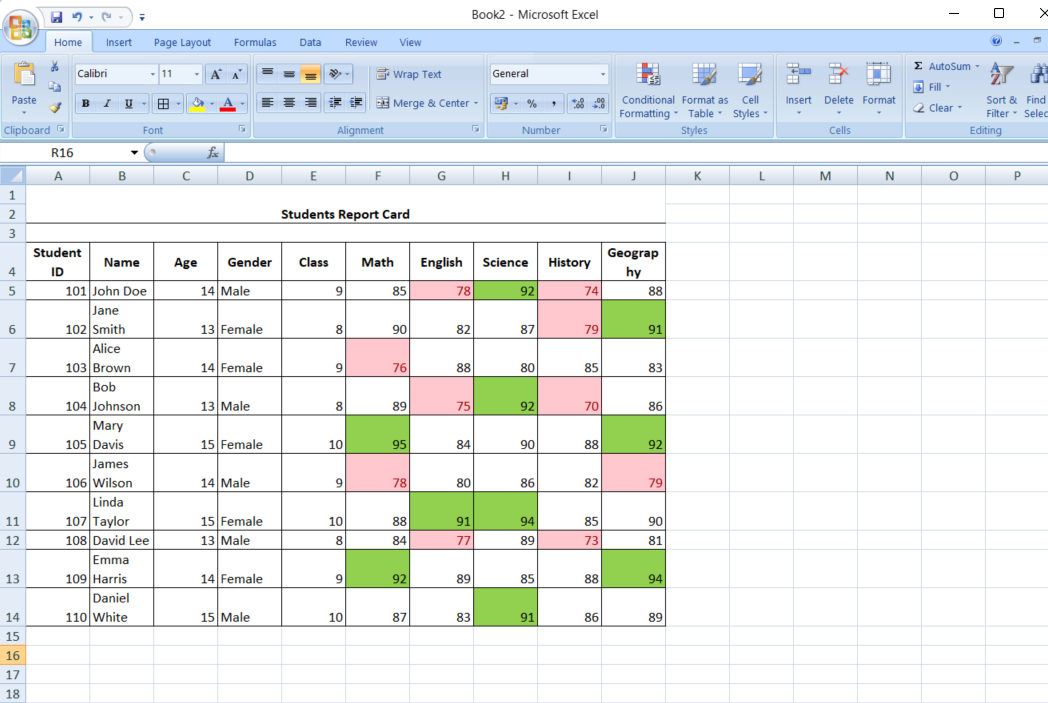
Similarly, identifying duplicate entries is crucial in large data sets. Conditional formatting can quickly highlight duplicates, helping you maintain data accuracy.
- Select range: Select the cells you want to check for duplicates.
- Choose duplicate values rule: From the Conditional Formatting menu, select “Highlight Cells Rules” and “Duplicate Values.”
- Format: Select the formatting style and click OK.
Tips for effective use of conditional formatting in Excel
Here are the tips:
- Get started simply: Start with basic rules like highlighting values greater than or less than a specific number. This will help you get familiar with how conditional formatting works.
- Use cell references for added flexibility: Instead of using static values in conditional formatting rules, reference another cell. This allows you to change the criteria by simply updating the reference cell.
- Leverage formulas for custom rules: Excel's formula-based conditional formatting allows you to create highly customized rules. Make sure your formula returns a TRUE or FALSE value to apply formatting correctly.
- Combining multiple rules: Feel free to apply multiple conditional formatting rules to the same range of cells. For example, you can use both color scales and icon sets to provide different layers of information about your data.
- Review and manage rules periodically: As you add more conditional formats, check and manage your rules to avoid conflicts or overly complex settings. Use the “Manage Rules” option to edit or delete rules as needed.
- Prioritize rules: When applying multiple rules, remember that Excel prioritizes them in the order they appear in the list. You can change the priority by moving rules up or down in the Manage Rules dialog box.
- Use the preview to your advantage: Before you apply conditional formatting, use the preview feature to see how your data will look. This will help you adjust your settings to get the best visual result.
- Avoid overloading with formatting: While conditional formatting is powerful, too much of it can clutter your spreadsheet and make it difficult to read. Use formatting sparingly to ensure clarity.
- Experiment with custom formats: Excel allows you to create custom formatting styles (for example, specific colors or font styles) in Conditional Formatting. This is particularly useful for maintaining a consistent look across all of your spreadsheets.
- Clear formatting when necessary: If your data changes significantly, delete old formatting rules to start over. This prevents outdated rules from being incorrectly applied to new data.
Conclusion
Conditional formatting in Standing out It’s not just a handy feature, but it’s a game-changer for anyone working with data. By leveraging this tool, you can turn a simple spreadsheet into a dynamic, visually appealing report that highlights key insights and trends at a glance. Whether you’re a data newbie or a seasoned analyst, mastering conditional formatting will improve your ability to communicate data-driven stories effectively. So, next time you’re in Excel, don’t just look at the numbers — let conditional formatting help you see the bigger picture.
Frequent questions
Answer: Conditional formatting in Excel allows you to apply specific formatting to cells based on their values, such as highlighting, color scales, or icon sets.
Answer: Select the cells, go to the “Home” tab, click “Conditional Formatting”, choose a rule and configure it as needed.
Answer: Yes, you can use formulas to create custom conditional formatting rules by selecting “Use a formula to determine which cells to format.”
Answer: Select the cells, go to “Conditional Formatting” on the “Home” tab and choose “Clear Rules” to remove the formatting.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





