In the world of business, keeping track of money matters is crucial, and that’s where General Ledger Codes, or GL Codes, come into play. Think of these codes as the secret sauce that helps businesses organize their finances, making sure every dollar spent or earned is tracked accurately. GL Codes are not just about keeping things neat; they’re about making smarter financial decisions, simplifying tax time, and ensuring your business runs smoothly. In this guide, we’ll break down what GL Codes are, why they’re so important for your company, and how to use them effectively. We’ll also discuss how to set up efficient GL coding processes in your team, and explore GL coding automation software.
What are GL Codes?
General Ledger Codes, or GL Codes, are unique alphanumeric strings that classify and record financial transactions within a company’s general ledger. These codes serve as the fundamental building blocks of a business’s financial structure, enabling the categorization of transactions into distinct accounts for revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. For instance, a GL code for office supplies expense helps ensure that all expenditures related to office supplies are grouped together, facilitating easier tracking and analysis.
The General Ledger Explained: At the heart of a company’s financial record-keeping lies the General Ledger (GL) – a comprehensive repository that records every financial transaction conducted by the business. Think of it as the financial backbone of a company, supporting the structure of its economic activities. Each transaction entered into the GL is tagged with a GL code, acting as a marker that categorizes every inflow and outflow into its appropriate GL account.
Why use GL Codes?
Through their systematic organization, GL codes empower businesses to –
- Enhance Financial Accuracy and Compliance with Financial Standards: GL Codes allow for the precise categorization of financial transactions, which is crucial for producing accurate financial reports. For example, a business can assign a specific GL code to utility expenses. This ensures that payments for electricity, water, and internet services are accurately recorded under utility expenses, enabling the company to produce financial statements that truly reflect its operational costs. Similarly, a retail business that uses separate GL codes for inventory purchases and sales is able to accurately calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS), a critical figure for both financial analysis and tax calculations.
- Simplify Tax Preparation and Maximize Deductions: Utilizing GL Codes makes tax time less daunting. By having expenses properly categorized, you can easily identify tax-deductible expenses and ensure you’re claiming all entitled deductions. For instance, a GL Code dedicated to travel expenses can help you quickly compile all travel-related expenditures, ensuring you don’t miss out on claiming these deductions. Similarly, by reviewing expenses recorded under a GL code for equipment purchases, a business might realize it can take advantage of accelerated depreciation methods or Section 179 deductions, thereby reducing its taxable income. This kind of organization can lead to significant tax savings and reduce the risk of errors in tax filings.
- Improve Budget Management: With GL Codes, businesses can compare actual spending against budgets at a granular level. For instance, assigning a GL code to marketing expenses allows a business to track its marketing budget performance closely. If a digital marketing agency notices that its expenses in the GL-coded marketing category are consistently over budget, it can take targeted actions to adjust its marketing strategies or budget allocations.
- Enhance Spend Visibility and Decision Making: By allocating a unique GL code to every transaction, an organization can meticulously monitor spending across different departments, the size of each transaction, and detailed expenditure data at the line item level. Businesses can thus generate detailed financial reports that provide insights into spending patterns, profitability, and financial health. A manufacturing company might use GL codes to track costs associated with different production lines. Analyzing these costs can help identify inefficiencies or areas for improvement, leading to better strategic decisions about where to allocate resources for maximum return.
- Increase Efficiency of Month-End Close: Accurate GL coding directly contributes to increased efficiency within a company’s financial processes, especially during critical periods like month-end close. By ensuring each financial transaction is assigned to the appropriate GL code from the outset, businesses significantly reduce the likelihood of errors that require time-consuming corrections. This precision allows for the automatic consolidation of expenses, minimizing manual adjustments and reclassifications that slow down financial reporting. The result is a faster, more efficient close process that also saves up your time which can be better spent elsewhere.
- Reduce Risk of Fraud and Achieve Audit-Readiness: The granularity provided by GL codes offers an invaluable layer of security for businesses. With each transaction meticulously categorized, it becomes easier to spot anomalies or patterns indicative of issues such as fraud or mismanagement. For example, if a company assigns a unique GL code to employee reimbursements, it can easily review these transactions for any that are unusually high or inconsistent with established policies. Furthermore, in the case of an audit, the detailed organization of transactions by GL code simplifies the process of providing necessary documentation and explanations, reducing the risk of penalties or fines for non-compliance. This approach ensures that businesses not only safeguard their financial resources but also maintain their reputation and integrity in the marketplace.
How to Assign GL Codes?
In the world of business, where every penny counts and every transaction matters, the setup of your General Ledger (GL) codes isn’t just a task—it’s an art. The importance of laying a strong foundation for your accounting system cannot be stressed enough. And at the heart of this system? A well-planned GL code structure. Let’s dive into how you can master the art of GL code organization and assignment.
Before you even begin to assign numbers or names to your GL codes, take a step back. Why? Because planning your GL code structure is akin to drafting the blueprints for a building. You wouldn’t start construction without a clear plan, would you? Similarly, setting up GL codes without a strategy is a recipe for confusion, inefficiencies, and financial reporting nightmares down the line.
1. Start with the Big Picture: Begin by defining the main categories of your financial transactions. Typically, these include
- Assets: These are resources owned by a business that have economic value. Examples include cash, inventory, and equipment.
- Liabilities: These represent what a business owes to others, such as loans and accounts payable.
- Equity: Equity represents the owner’s claim after all liabilities have been subtracted from assets. This includes retained earnings and stock.
- Revenues: Revenues are the income earned from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are subtracted.
- Expenses: Expenses are the costs incurred in the process of earning revenue, such as rent, utilities, and salaries.
These categories form the backbone of your GL code system and help ensure that every transaction can be accurately classified.
2. Embrace Detail, But Avoid Overcomplication: Within each main category, create subcategories that reflect the nuances of your business operations. Below is an example of a framework with potential subcategories. Click on each category and subcategory to explore further.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Prepaid Expenses
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E)
Intangible Assets
stocks, bonds, or real estate
Accounts Payable
Accrued Expenses
Short-term Loans
Long-term Loans
Deferred Tax Liabilities
Bonds Payable
Capital
Retained Earnings
Common Stock
Preferred Stock
Sales Revenue
Service Revenue
Interest Income
Rental Income
Dividend Income
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Payroll
Rent
Utilities
Marketing and Advertising
Insurance
Depreciation and Amortization
Interest Expense
Losses from Asset Sales
By embracing detail within each main category, you create a robust system that accurately reflects your business operations. However, remember the principle of avoiding overcomplication: tailor your subcategories to match the specific needs and scale of your business, ensuring that your GL code system remains both useful and manageable.
3. Create the GL Codes: Use a consistent logic for numbering your codes. This could mean using certain ranges for specific categories (e.g., 1000 series for assets, 2000 for liabilities). When designing your GL codes, consider the following:
- Level of Detail: Determine the granularity of information you need. While detail is valuable, too much can overwhelm your system and users.
- Departmental Level Codes: If your business spans multiple departments or locations, consider incorporating these distinctions into your codes for more detailed tracking and reporting.
- Project Level Codes: For businesses that operate on a project basis, project-specific codes can help in tracking costs and revenues accurately.
4. Establish a Comprehensive Chart of Accounts: Once your categories, subcategories and GL codes are set up, you have effectively built your chart of accounts. Here’s an snippet of what a Chart of Accounts might eventually look like.
XYZ Manufacturing Co.
Chart of Accounts
| ID | Name | ID | Name | Type | Side |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1010 | Sales – Consumer Electronics | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1020 | Sales – Home Appliances | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1030 | Sales – Office Equipment | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1040 | Sales – Mobile Devices | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1050 | Sales – IT Solutions | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1060 | Sales – Wearable tech | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1070 | Sales – Software Solutions | 11 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1080 | Sales – Service Contracts | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 1090 | Sales – Technical Support | 10 | Sales | Income | Cr |
| 2000 | Interest Received | 15 | Interest | Income | Cr |
| 2010 | Consulting Income | 16 | Services | Income | Cr |
| 2020 | Miscellaneous Income | 17 | Other Income | Income | Cr |
| 2030 | Dividend Income | 17 | Other Income | Income | Cr |
| 2040 | Gain on Investment Sale | 17 | Other Income | Income | Cr |
| 3000 | COGS – Consumer Electronics | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3010 | COGS – Home Appliances | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3020 | COGS – Office Equipment | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3030 | COGS – Mobile Devices | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3040 | COGS – IT Solutions | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3050 | COGS – Wearable tech | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3060 | COGS – Software Solutions | 21 | Direct Costs | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3070 | COGS – Service Contracts | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 3080 | COGS – Technical Support | 20 | Cost of Sales | Cost of Goods | Dr |
| 4000 | Wages – Production Staff | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
| 4010 | Wages – Sales Team | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
| 4020 | Wages – Administrative Staff | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
| 4030 | Wages – Research & Development | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
| 4040 | Wages – IT Support Staff | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
| 4050 | Wages – Executive Salaries | 22 | Wages | Other Costs | Dr |
A well-thought-out GL code system enables you to track every financial transaction with precision, facilitates seamless audits, and provides actionable insights to guide your business decisions. It’s not just about keeping your books in order; it’s about gaining a strategic advantage through superior financial intelligence.
Consulting with an Accounting Professional: Even with the best plans, the complexities of financial accounting can sometimes be daunting. This is where a seasoned accounting professional becomes invaluable. They can provide expert guidance on setting up your GL code system, ensuring it aligns with industry standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices. Moreover, they can offer insights tailored to your specific business needs, helping you avoid common pitfalls and capitalize on opportunities for financial optimization.
Setting Up GL Codes in Accounting Software
When it comes to integrating GL codes into your accounting software, think of it as programming the DNA of your financial system. Most modern accounting software offers a user-friendly interface to simplify this process. Here’s how to go about it:
- Access the Chart of Accounts Feature: Begin by navigating to the chart of accounts section of your software. This is typically found within the settings or system setup menu. Here, you’ll be able to view, add, edit, or delete accounts and their corresponding GL codes.
- Add New GL Codes: Depending on the structure you’ve planned, start adding new GL codes. Ensure that each code is unique and aligns with the numbering logic you’ve decided upon. For example, all asset accounts might start with the number 1 (e.g., 1010 for Cash, 1020 for Accounts Receivable, etc.).
- Input Descriptions: For each GL code, provide a clear and concise description. This description should reflect the nature of the transactions that the code will represent. This step is vital for ensuring clarity and consistency across your financial team.
- Assign Account Types: Correctly categorize each GL code according to the main account types (assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses). This classification is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis.
- Test Your Setup: Before going live, perform a test by entering a few transactions and ensuring they are accurately reflected in the correct GL accounts. This step helps identify any issues in your GL code setup, allowing you to make necessary adjustments.
Assigning GL Codes to Transactions
Once your GL codes are set up in your accounting software, the next step is to assign these codes to transactions as they occur. This process is at the core of maintaining an organized and efficient accounting system. Here’s how to ensure accuracy and consistency in this task:
- Educate Your Team: Ensure that all team members involved in financial transactions understand the importance of GL codes and how to use them. This might involve training sessions or creating a reference guide.
- Review Source Documents: For every transaction, review the source document (invoices, receipts, bank statements, etc.) to determine the appropriate GL code. The nature of the transaction will guide which GL code to use.
- Input Transactions: When entering transactions into your accounting software, select the appropriate GL code from the drop-down menu or enter it manually, depending on your system’s setup. Ensure that the details of the transaction align with the GL code’s description.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of transactions to ensure GL codes are being used correctly. This can help identify errors or inconsistencies early, making them easier to rectify.
GL Code Assignment Workflow
Let’s illustrate the workflow with a real-world example to bring it all together:
- Transaction Identification: Your business purchases $5,000 worth of office supplies on credit.
- Review Source Document: You receive an invoice in your mail inbox from the supplier detailing the purchase.
- Determine Appropriate GL Code: Based on your GL code structure, you identify that office supplies should be recorded under the GL code for office expenses (e.g., 5060 – Office Supplies Expense).
- Enter Transaction in Accounting Software:
- Access the transaction entry page in your software.
- Input the transaction date, the amount ($5,000), and the supplier’s details.
- Select or input the GL code 5060 for Office Supplies Expense.
- Since the purchase was made on credit, also select the GL code for Accounts Payable (e.g., 2010 – Accounts Payable) to represent the liability created by this transaction.
- Review and Confirm: Double-check the transaction details and GL codes for accuracy, then confirm or save the transaction in the system.
- Regular Reconciliation: At month-end, reconcile the accounts payable to ensure that all purchases, including the office supplies, are accurately accounted for and that the payment liabilities are clear.
Automate GL Coding with Nanonets
In the digital age, automation is key to enhancing efficiency and accuracy in financial processes. By leveraging a tool like Nanonets for automating the General Ledger (GL) code assignment workflow, businesses can significantly reduce manual effort and minimize errors & delays.
Let’s revisit the office supplies purchase example in an automated workflow:
- Invoice Receipt and Capture: Upon receiving the electronic invoice for the $5,000 office supplies purchase in your mail inbox, Nanonets automatically captures the document from the email.
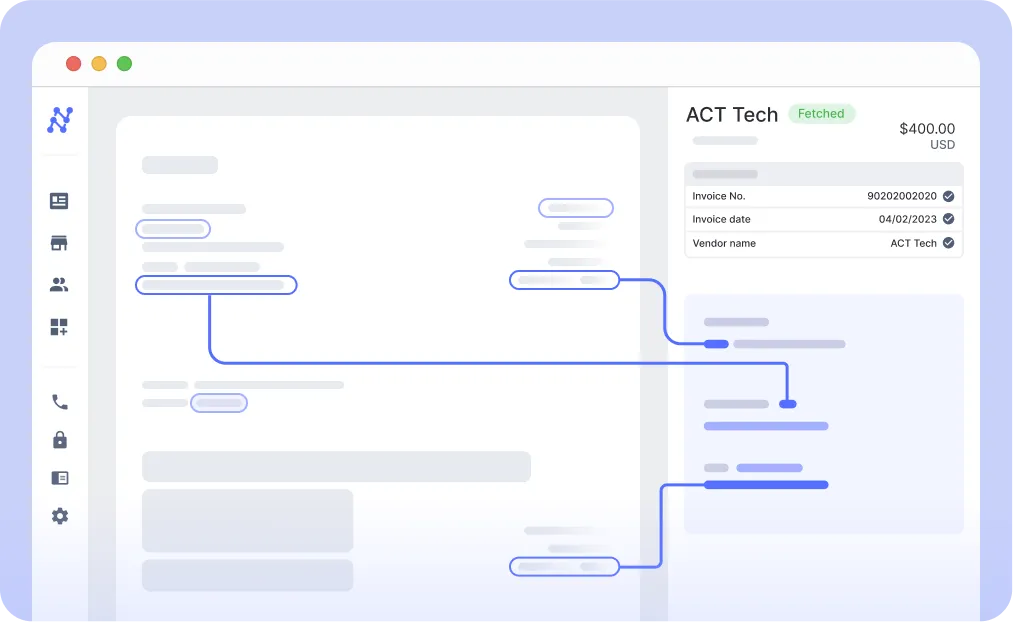
- Data Extraction: Using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and ai, Nanonets extracts relevant transaction details from the invoice.
- GL Code Assignment: GL code assignment can be effectively executed by –
- Training on past data: With Nanonets, you can train a machine learning model to recognize and categorize financial transactions. This involves uploading historical financial documents and transactions tagged with historically correct GL codes. The model learns from these examples to accurately predict GL codes for new transactions.
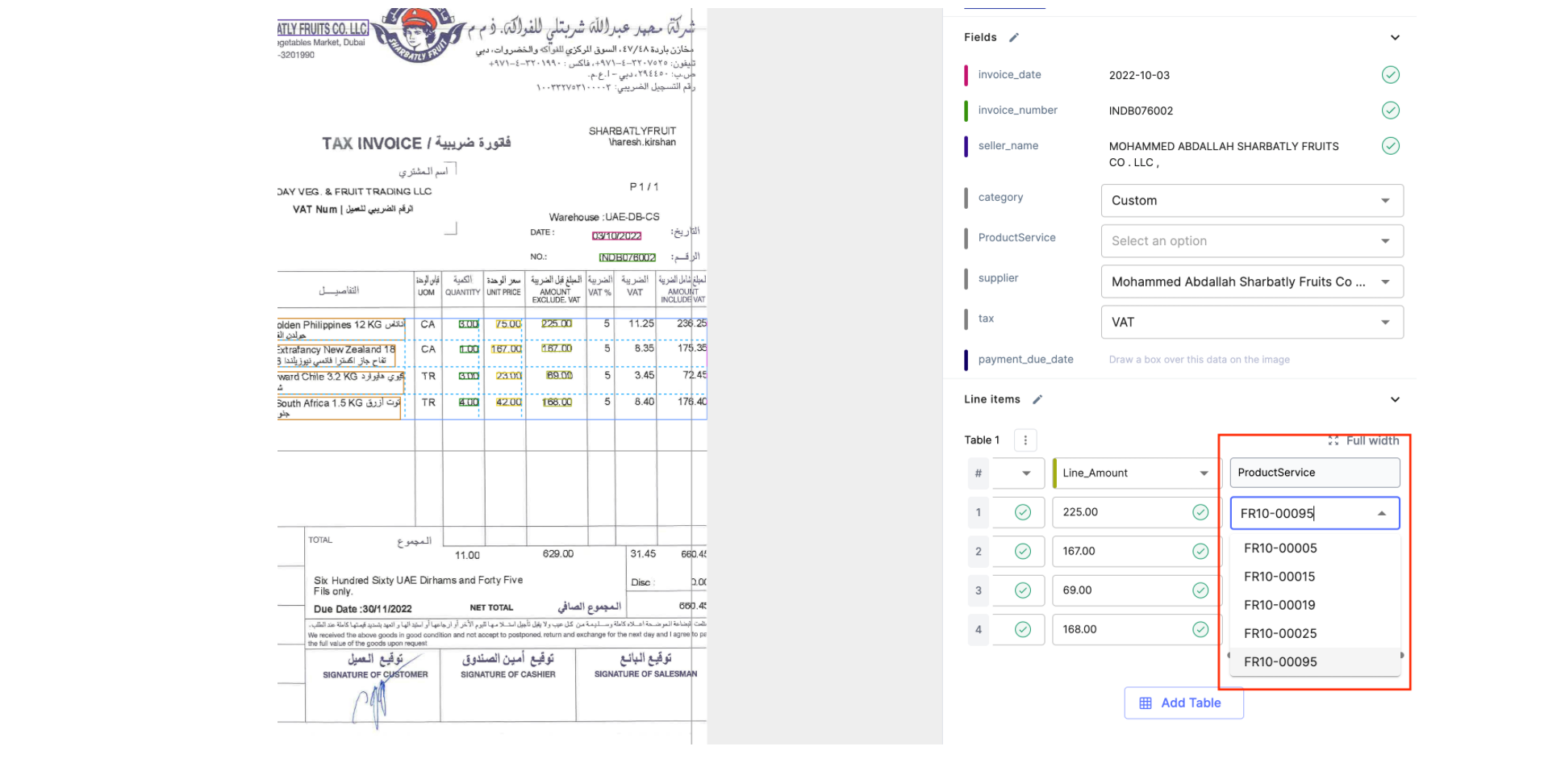
- Out of the Box Gen ai: By using Nanonets GenAI, our software can interpret the text on financial documents in a way that mimics human understanding. This allows it to extract relevant information, context and semantics in order to apply complex reasoning to assign GL codes accurately, even in cases where transaction details are ambiguous or sparse.
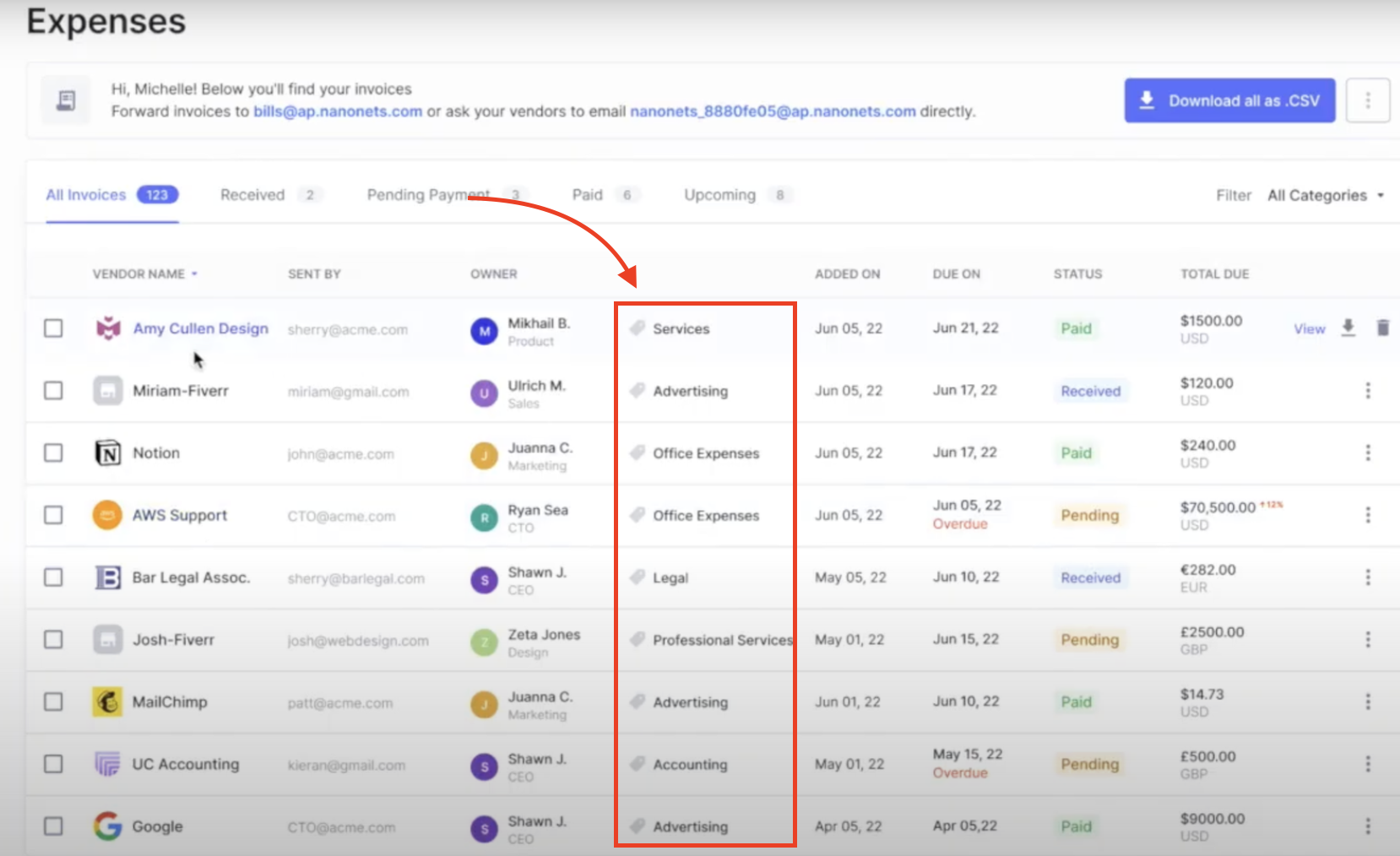
- Review and Validation: The transaction is flagged for a quick review because the amount exceeds a predefined threshold. After verifying the details, the finance team approves the GL code assignment.
- Posting to Accounting Software and Syncing Data with other apps: The validated transaction, complete with assigned GL codes, is automatically uploaded to the accounting software. The accounts payable and office supplies expense accounts are updated accordingly without manual data entry.

- Automated Reconciliation: Integrate Nanonets with your bank statements and General Ledger data to instantly match your books and identify discrepancies, and reduce the time taken to close your books at month-end by 90%.

Conclusion
In the intricate dance of business finance, General Ledger Codes (GL Codes) emerge not just as a methodical step but as a transformative leap towards financial clarity and strategic insight. These alphanumeric keys unlock the potential for businesses to navigate the complexities of financial transactions with precision, ensuring that every penny’s journey is tracked, categorized, and analyzed for the betterment of the company’s financial health.
The essence of GL Codes transcends mere organization; it’s about embedding a layer of intelligence into the financial fabric of a business. By meticulously assigning these codes to every transaction, companies can illuminate the path to enhanced financial accuracy, streamlined tax preparation, and robust budget management. This clarity fosters an environment where strategic decisions are informed by data, not guesswork, enabling businesses to pivot with agility in the face of financial challenges and opportunities.
Moreover, the integration of GL Codes into accounting software, complemented by the power of automation tools like Nanonets, represents a leap towards a future where financial processes are not only efficient but resilient. This digital transformation reduces the manual strain on teams, allowing them to focus on strategic tasks that propel the business forward, while also safeguarding against errors and fraud.
Ready to revolutionize your financial processes with unparalleled efficiency and accuracy? Embrace the future of finance with Nanonets. Our cutting-edge automation platform transforms the way you handle General Ledger (GL) coding along with streamlining your financial workflows like never before.
Schedule a Call Here






