In the field of biotechnology, the intersection of machine learning and genomics has generated a revolutionary paradigm, particularly in DNA sequence modeling. This interdisciplinary approach addresses the intricate challenges posed by genomic data, including understanding long-range interactions within the genome, the bidirectional influence of genomic regions, and the unique property of DNA known as reverse complementarity (RC). Recent advances in this field have led to the development of innovative methods and tools to improve the accuracy and efficiency of genomic sequence modeling.
One of the persistent problems in genomics research is the complexity of accurately modeling long-range interactions within DNA sequences. Traditional approaches often need to capture extensive and nuanced relationships across the vast expanse of the genome. This limitation has urged researchers to explore new methodologies that can skillfully handle these long-range dependencies while taking into account the bidirectional nature of genetic influence and the RC characteristic of DNA strands.
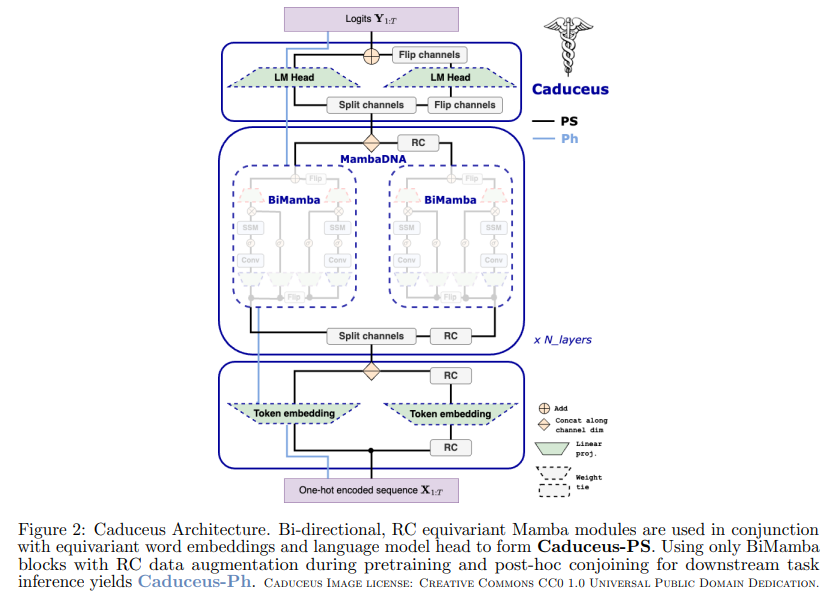
In response to these challenges, a new approach has emerged thanks to a collaborative effort between researchers at Cornell University, Princeton University, and Carnegie Mellon University. This innovative method introduces a novel architecture designed to effectively address the complexities of genomic sequence modeling. The basis for this approach is the development of the “Mamba” block, which has been further enhanced to support bidirectionality through the “BiMamba” component and incorporate RC equivariance with the “MambaDNA” block.
The MambaDNA block serves as the cornerstone of the “Caduceus” models, a pioneering family of bidirectional, RC-equivalent DNA sequence models. These models have been meticulously constructed not only to understand conventional aspects of genomic sequences but also to interpret complex reverse complementarity and bidirectional influences. By leveraging this advanced architecture, Caduceus models have shown promise and have demonstrated superior performance over previous long-range models in several downstream benchmarks, especially in predicting the effects of genetic variants, a task known for its dependence on understanding long-range genomic interactions.
They outperform significantly larger models, but require a more sophisticated understanding of bidirectionality and equivariance. This achievement underscores the effectiveness of the approach in capturing essential features of genomic sequences, critical for various applications in biology and medicine. By introducing a novel pre-training and tuning strategy, these models set a new standard in the field and promise to accelerate progress in genomics research.
In conclusion, the development of Caduceus models represents an important milestone in the integration of machine learning with genomics. This research not only addresses long-standing challenges in modeling DNA sequences, but also opens new avenues for exploring the genetic basis of life. The implications of this work are enormous for our understanding of diseases, genetic disorders, and the intricate mechanisms that govern biological systems. As the field continues to evolve, the contributions of this research will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping the future of genomics.
Review the Paper, Projectand GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on Twitter and Google news. Join our 38k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook community, Discord Channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Telegram channel
You may also like our FREE ai Courses….
![]()
Sana Hassan, a consulting intern at Marktechpost and a dual degree student at IIT Madras, is passionate about applying technology and artificial intelligence to address real-world challenges. With a strong interest in solving practical problems, she brings a new perspective to the intersection of ai and real-life solutions.
<!– ai CONTENT END 2 –>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER