Large language models (LLMs) have gained ground for their exceptional performance on various tasks. Recent research aims to improve its feasibility by integrating external resources, including structured data and free text. However, many data sources, such as patient records and financial databases, contain a combination of both types of information. “Can you find me an Italian restaurant with a romantic atmosphere?”, an agent needs to combine structured cooking attributes and free-text attribute reviews.
Previous chat systems typically employ classifiers to direct queries to specialized modules for handling structured data, unstructured data, or chats. However, this method is not sufficient for questions that require structured and free text data. Another approach involves converting structured data to free text, limiting the use of SQL for database queries and the effectiveness of free text retrievers. The need for hybrid data queries is underscored by datasets such as HybridQA, which contain questions that require information from both structured and free-text sources. Previous efforts to base question answering systems on hybrid data operate on small data sets, sacrifice the richness of structured data queries, or support limited combinations of structured and unstructured knowledge queries.
Stanford researchers present an approach to connecting conversational agents in hybrid data sources, using structured data queries and free text retrieval techniques. It empirically demonstrates that users frequently ask questions spanning structured and unstructured data in real-life conversations, and more than 49% of queries require knowledge of both types. To enhance expressiveness and precision, they propose SUQL (Structured and Unstructured Query Language)a formal language that augments SQL with primitives for processing free text, allowing a combination of commercially available retrieval models and LLM with SQL semantics and operators.
The design of the SUQL aims to Expressiveness, precision and efficiency.. SUQL extends SQL with NLP operators such as SUMMARY and ANSWER, facilitating full-spectrum queries over hybrid knowledge sources. LLMs competently translate complex text into SQL queries, allowing SUQL to perform complex queries. Although SUQL queries can be executed in standard SQL compilers, a simple implementation may be inefficient. Describe SUQL free text primitives, highlighting their distinction from retrieval-based methods by expressing queries end-to-end.

The researchers evaluate SUQL through two experiments: one with HybridQA, a question-and-answer dataset, and another with real restaurant data from Yelp.com. The HybridQA experiment uses LLM and SUQL to achieve an exact match (EM) of 59.3% and an F1 score of 68.3%. SUQL outperforms existing models by 8.9% EM and 7.1% F1 on the test set. In real-life restaurant experiments, SUQL demonstrates a turn accuracy of 93.8% and 90.3% on single-turn and conversational queries respectively, outperforming linearization-based methods by up to 36.8%. and 26.9%.
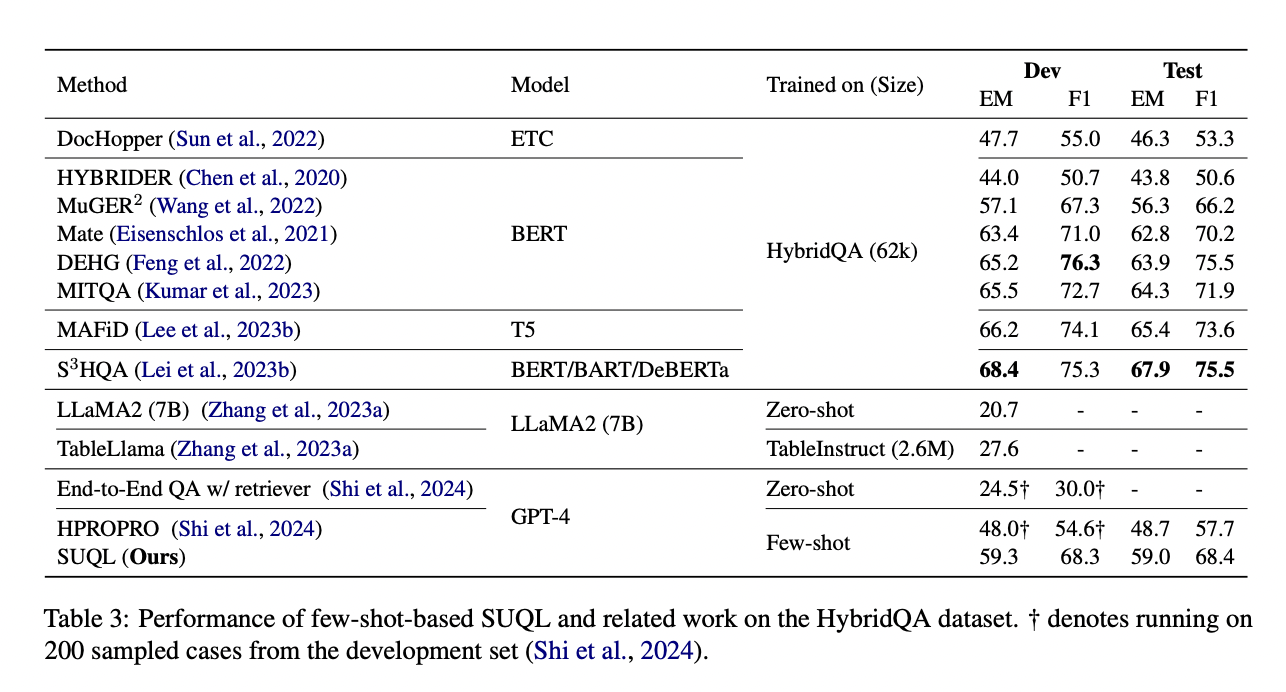
To conclude, this article introduces SUQL as the inaugural formal query language for hybrid knowledge corpora, spanning structured and unstructured data. Its innovation lies in the integration of free text primitives into a precise and concise query framework. In-context learning applied to HybridQA achieves results within 8.9% of SOTA, trainable on 62,000 samples. Unlike previous methods, SUQL supports large databases and free text corpora. Experiments using Yelp data demonstrate the effectiveness of SUQL, with a 90.3% success rate in satisfying user queries compared to 63.4% for linearization baselines.
Review the Paper, GitHuband Manifestation. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on twitter.com/Marktechpost”>twitter. Join our Telegram channel, Discord Channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our 41k+ ML SubReddit
![]()
Asjad is an internal consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing B.tech in Mechanical Engineering at Indian Institute of technology, Kharagpur. Asjad is a machine learning and deep learning enthusiast who is always researching applications of machine learning in healthcare.
<script async src="//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js” charset=”utf-8″>






