Understanding the world from a first-person perspective is essential in Augmented Reality (AR), as it introduces unique challenges and significant visual transformations compared to third-person views. While synthetic data has greatly benefited vision models in third-person views, their utilization in tasks involving embodied egocentric perception still needs to be explored. A major hurdle in this area is the accurate simulation of natural human movements and behaviors, crucial for directing the built-in cameras to capture faithful egocentric representations of the 3D environment.
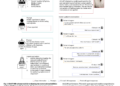
In response to this challenge, researchers from eth Zurich and Microsoft present EgoGen, a novel synthetic data generator designed to produce accurate and comprehensive field training data for egocentric perception tasks. At the core of EgoGen is a pioneering human motion synthesis model that directly uses egocentric visual inputs from a virtual human to perceive the surrounding 3D environment.
This model is complemented by collision avoidance motion primitives and employs a two-stage reinforcement learning strategy, thus providing a closed-loop solution where embodied perception and virtual human motion are seamlessly integrated. Unlike previous approaches, their model eliminates the need for a predefined global path and applies directly to dynamic environments.
With EgoGen, existing real-world egocentric datasets can be seamlessly augmented with synthetic images. Their quantitative evaluations show significant performance improvements of state-of-the-art algorithms in various tasks, including mapping and localization of helmet-mounted cameras, tracking egocentric cameras, and retrieving human meshes from egocentric views. These results underscore the effectiveness of EgoGen in improving the capabilities of existing algorithms and highlight its potential to advance research in egocentric computer vision.
EgoGen is complemented by a scalable and easy-to-use data generation pipeline, showing its effectiveness in three key tasks: mapping and localization for helmet-mounted cameras, egocentric camera tracking, and human mesh recovery from egocentric views. By making EgoGen completely open source, the researchers aim to provide a practical solution for creating realistic egocentric training data and serve as a valuable resource for egocentric computer vision research.
Furthermore, EgoGen's versatility and adaptability make it a promising tool for various applications beyond tasks such as human-computer interaction, virtual reality, and robotics. With its release as an open source tool, researchers anticipate that EgoGen will foster innovation and advances in the field of egocentric perception and contribute to the broader landscape of computer vision research.
Review the Paper and Code. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on Twitter and Google news. Join our 36k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook community, Discord channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Telegram channel
Arshad is an intern at MarktechPost. He is currently pursuing his international career. Master's degree in Physics from the Indian Institute of technology Kharagpur. Understanding things down to the fundamental level leads to new discoveries that lead to the advancement of technology. He is passionate about understanding nature fundamentally with the help of tools such as mathematical models, machine learning models, and artificial intelligence.
<!– ai CONTENT END 2 –>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER