Large language models (LLMs) have become powerful tools in the field of ai, transforming several industries through their ability to understand and generate human-like text. From natural language understanding to text generation, LLMs such as GPT (generative pre-trained transformer) models have revolutionized various fields and promise greater efficiency and innovation. However, in medicine, few fields require more precision or more data than radiation oncology. Patients' lives depend on receiving appropriate treatment in this specialized setting.
Mayo Clinic has developed a robust LLM called RadOnc-GPT, which uses Meta Llama 2 technology. This model has the potential to improve the overall efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of radiotherapy decision making. It was trained using a substantial data set composed of patient records from the radiation oncology department at Mayo Clinic in Arizona. Importantly, patient data was handled securely within the clinic network and the model was tuned locally using a GPU server powered by Llama 2. All research involving this model is conducted with approval of an institutional review board.
“Properly optimized, open-source LLMs have immense potential to revolutionize radiation oncology and other highly specialized healthcare domains,” says Dr. Wei Liu, Professor of Radiation Oncology and Research Director of the Division of Medical Physics at Mayo Clinic in Arizona.
The initial clinical application of RadOnc-GPT focuses on patient monitoring. Liu's team intends to create a chatbot that can address common queries patients may have after undergoing radiation therapy. This initiative aims to reduce the burden on nurses and doctors, allowing them to spend more time on higher priority tasks.
Potential future advancements may involve expanding the capabilities of RadOnc-GPT to encompass various clinical responsibilities, such as developing models to predict patient outcomes in radiation oncology. Additionally, Liu mentions that the team is considering using the more sophisticated and recently released Llama 3 model to improve its effectiveness.
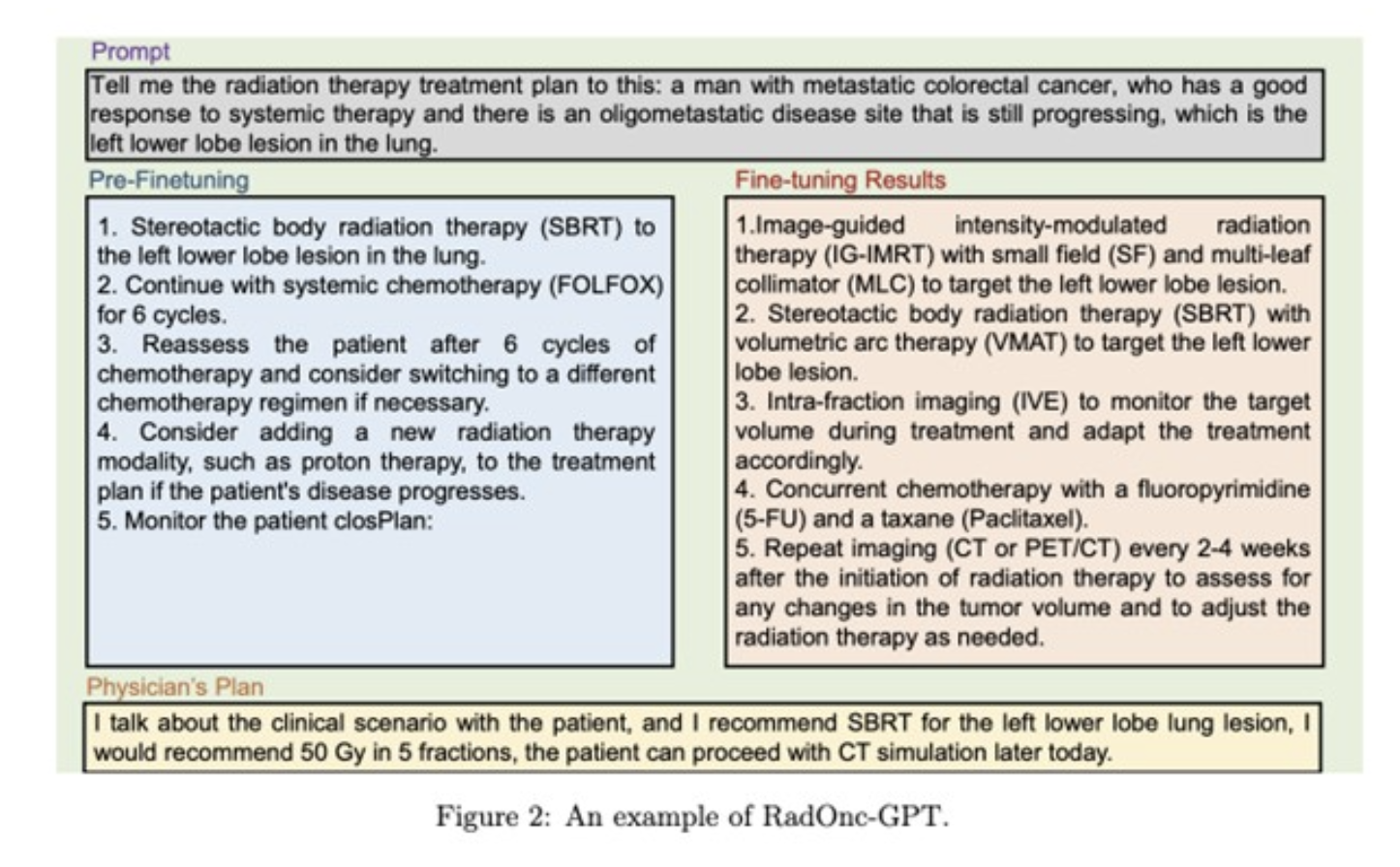
ai-powered tools streamline tasks, quickly analyze complex data sets, and uncover patterns that may elude human observation, allowing healthcare providers to focus on critical tasks like direct patient care. The Mayo Clinic team collaborated with the University of Georgia on natural language processing in healthcare and chose Llama 2 as the basis for RadOnc-GPT. This model is optimized for tasks including generating treatment regimens, selecting radiation modalities, and providing diagnostic descriptions and International Statistical Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes based on patient data, improving specificity and clinical relevance. . Extensive manual processing was performed to prepare the radiation oncology dataset, overcoming the challenges of data curation and extraction.
ai.meta.com/blog/radonc-gpt-meta-llama-2-mayo-clinic/” target=”_blank” rel=”noreferrer noopener”>According to Liu, making advanced ai models open source allows Mayo Clinic to use cutting-edge models directly in its research, speeding up the development process. This not only improves patient care but also expands the reach of the initiative beyond precision in therapeutic interventions. Open source ai systems are crucial to democratizing innovation, particularly for smaller companies and institutions. They facilitate the collective advancement of medical science by providing access to LLM, even for organizations with limited resources to develop customized models.
In conclusion, the integration of LLM such as RadOnc-GPT in radiation oncology represents a transformative leap in the role of ai in healthcare. Mayo Clinic's development of RadOnc-GPT, which uses Meta Llama 2 technology, promises greater accuracy and efficiency in treatment decision-making. Collaborative efforts with institutions like the University of Georgia highlight the potential of ai-powered tools to optimize patient care while democratizing innovation. By using open source models and advancing research, Mayo Clinic is at the forefront of shaping a future where ai optimizes treatment outcomes.
![]()
Asjad is an internal consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing B.tech in Mechanical Engineering at Indian Institute of technology, Kharagpur. Asjad is a machine learning and deep learning enthusiast who is always researching applications of machine learning in healthcare.
(Recommended Reading) GCX by Rightsify: Your go-to source for high-quality, ethically sourced, copyright-cleared ai music training datasets with rich metadata
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER




