Introduction
Understanding Python coding interview questions is crucial as they serve as a gateway to opportunities in software development and data science careers. Mastering these questions not only demonstrates problem-solving ability and mastery of Python, but also improves overall programming skills. By becoming familiar with common challenges and honing problem-solving strategies, candidates can confidently approach technical interviews, demonstrating their readiness for various roles in the tech industry. In this article we will explore Python coding interview questions for beginners that can help you prepare for your interviews.
Python Coding Interview Questions for Beginners
Let's now look at the top 30 Python coding interview questions for beginners.
You can also sign up for our free Python course today.
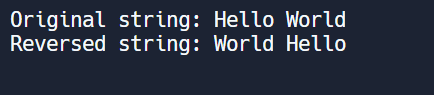
Question 1: Write a Python program to reverse a string?
Solution:
With indexing:
def reverse_string(s):
return s(::-1)
# Example usage
input_string = "Hello, World!"
reversed_string = reverse_string(input_string)
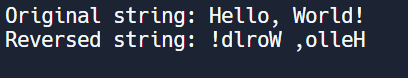
print("Original string:", input_string)
print("Reversed string:", reversed_string)Production:
Without indexing:
def reverse_string(s):
reversed_str = ""
for char in s:
reversed_str = char + reversed_str
return reversed_str
# Example usage
input_string = "Hello, World!"
reversed_string = reverse_string(input_string)
print("Original string:", input_string)
print("Reversed string:", reversed_string)
Production:
Question 2: Write a Python program to check Palindrome?
Solution:
For chain:
def is_palindrome(s):
# Remove spaces and convert to lowercase for case-insensitive comparison
s = s.replace(" ", "").lower()
return s == s(::-1)
# Example usage
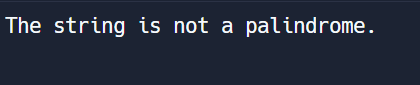
input_string = "A man, a plan, a canal, Panama"
if is_palindrome(input_string):
print("The string is a palindrome.")
else:
print("The string is not a palindrome.")
Production:
For number:
def is_palindrome(number):
# Convert number to string for easy manipulation
num_str = str(number)
return num_str == num_str(::-1)
# Example usage
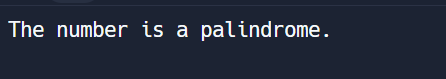
input_number = 12321
if is_palindrome(input_number):
print("The number is a palindrome.")
else:
print("The number is not a palindrome.")
Production:
Question 3: Write a Python program to count vowels in a string?
Solution:
def count_vowels(s):
# Define vowels
vowels = "aeiouAEIOU"
# Initialize count
count = 0
# Count vowels
for char in s:
if char in vowels:
count += 1
return count
# Example usage
input_string = "Hello, World!"
vowel_count = count_vowels(input_string)
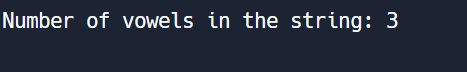
print("Number of vowels in the string:", vowel_count)
Production:
Question 4: Write a Python program to find factorial with recursion?
Solution:
With function:
def factorial(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial(n - 1)
# Example usage
number = 5
result = factorial(number)
print("Factorial of", number, "is", result)
Production:

Functionless:
number = 5
factorial = 1
if number < 0:
print("Factorial is not defined for negative numbers.")
elif number == 0:
print("Factorial of 0 is 1")
else:
for i in range(1, number + 1):
factorial *= i
print("Factorial of", number, "is", factorial)
Production:

Question 5: Write a Python program to find the Fibonacci sequence?
Solution:
def fibonacci(n):
fib_sequence = (0, 1) # Initialize the sequence with the first two terms
for i in range(2, n):
next_term = fib_sequence(-1) + fib_sequence(-2)
fib_sequence.append(next_term)
return fib_sequence
# Example usage
num_terms = 10
fib_sequence = fibonacci(num_terms)
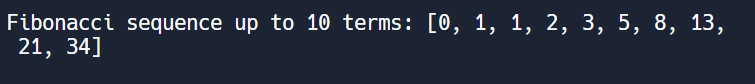
print("Fibonacci sequence up to", num_terms, "terms:", fib_sequence)
Production:
Question 6: Write a Python program to find the maximum element in a list?
Solution:
Using the built-in function:
# Example list
my_list = (10, 23, 45, 67, 12, 89, 34)
# Find maximum element
max_element = max(my_list)
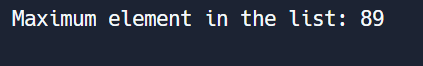
print("Maximum element in the list:", max_element)
Production:
Using user defined function:
def find_max_element(lst):
if not lst: # If the list is empty
return None # Return None since there is no maximum element
max_element = lst(0) # Initialize max_element with the first element of the list
for num in lst:
if num > max_element:
max_element = num
return max_element
# Example usage
my_list = (10, 23, 45, 67, 12, 89, 34)
max_element = find_max_element(my_list)
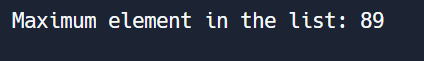
print("Maximum element in the list:", max_element)
Production:
Question 7: Write a Python program to find Anagram Check?
Solution:
def is_anagram(str1, str2):
# Remove spaces and convert to lowercase for case-insensitive comparison
str1 = str1.replace(" ", "").lower()
str2 = str2.replace(" ", "").lower()
# Check if the sorted forms of both strings are equal
return sorted(str1) == sorted(str2)
# Example usage
string1 = "listen"
string2 = "silent"
if is_anagram(string1, string2):
print(f"'{string1}' and '{string2}' are anagrams.")
else:
print(f"'{string1}' and '{string2}' are not anagrams.")
Production:

Question 8: Write a Python program to find prime numbers?
Solution:
def is_prime(num):
if num <= 1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(num ** 0.5) + 1):
if num % i == 0:
return False
return True
def find_primes(start, end):
primes = ()
for num in range(start, end + 1):
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
return primes
# Example usage
start_range = 1
end_range = 50
prime_numbers = find_primes(start_range, end_range)
print("Prime numbers between", start_range, "and", end_range, "are:", prime_numbers)
Production:

Question 9: Write a Python program to check Pangram?
Solution:
import string
def is_pangram(sentence):
# Convert sentence to lowercase for case-insensitive comparison
sentence = sentence.lower()
# Create a set of unique characters in the sentence
unique_chars = set(sentence)
# Remove non-alphabetic characters and spaces
unique_chars.discard(" ")
unique_chars.difference_update(set(string.punctuation))
# Check if all letters of the alphabet are present
return len(unique_chars) == 26
# Example usage
input_sentence = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
if is_pangram(input_sentence):
print("The sentence is a pangram.")
else:
print("The sentence is not a pangram.")
Production:

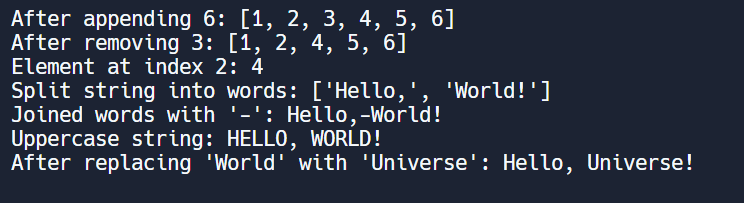
Question 10: Write a Python program for basic data structure operations (e.g. list manipulation, string manipulation)?
Solution:
# List manipulation
my_list = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
# Append an element to the list
my_list.append(6)
print("After appending 6:", my_list)
# Remove an element from the list
my_list.remove(3)
print("After removing 3:", my_list)
# Access elements by index
print("Element at index 2:", my_list(2))
# String manipulation
my_string = "Hello, World!"
# Split the string into a list of words
words = my_string.split()
print("Split string into words:", words)
# Join elements of a list into a single string
new_string = "-".join(words)
print("Joined words with '-':", new_string)
# Convert string to uppercase
upper_string = my_string.upper()
print("Uppercase string:", upper_string)
# Replace a substring
replaced_string = my_string.replace("World", "Universe")
print("After replacing 'World' with 'Universe':", replaced_string)
Production:
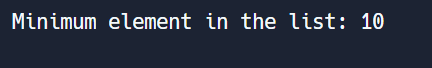
Question 11: Write a Python program to find the minimum element in a list?
Solution:
Using user defined:
def find_min_element(lst):
if not lst: # If the list is empty
return None # Return None since there is no minimum element
min_element = lst(0) # Initialize min_element with the first element of the list
for num in lst:
if num < min_element:
min_element = num
return min_element
# Example usage
my_list = (10, 23, 45, 67, 12, 89, 34)
min_element = find_min_element(my_list)
print("Minimum element in the list:", min_element)
Production:

Using the built-in function:
my_list = (10, 23, 45, 67, 12, 89, 34)
min_element = min(my_list)
print("Minimum element in the list:", min_element)
Production:
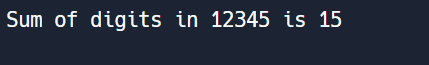
Question 12: Write a Python program to calculate the sum of digits of a number?
Solution:
def sum_of_digits(number):
# Convert number to string to iterate through its digits
num_str = str(number)
# Initialize sum
digit_sum = 0
# Iterate through each digit and add it to the sum
for digit in num_str:
digit_sum += int(digit)
return digit_sum
# Example usage
input_number = 12345
result = sum_of_digits(input_number)
print("Sum of digits in", input_number, "is", result)
Production:
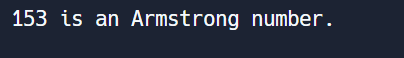
Question 13: Write a Python program to check Armstrong number?
Solution:
def is_armstrong(number):
# Convert number to string to get its length
num_str = str(number)
# Get the number of digits
num_digits = len(num_str)
# Initialize sum
armstrong_sum = 0
# Calculate the sum of digits raised to the power of the number of digits
for digit in num_str:
armstrong_sum += int(digit) ** num_digits
# Check if the sum is equal to the original number
return armstrong_sum == number
# Example usage
input_number = 153
if is_armstrong(input_number):
print(input_number, "is an Armstrong number.")
else:
print(input_number, "is not an Armstrong number.")
Production:
Question 14: Write a Python program to check leap year?
Solution:
def is_leap_year(year):
if (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0) or (year % 400 == 0):
return True
else:
return False
# Example usage
input_year = 2024
if is_leap_year(input_year):
print(input_year, "is a leap year.")
else:
print(input_year, "is not a leap year.")
Production:

Question 15: Write a Python program to calculate factorial without recursion?
Solution:
def factorial(n):
result = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
result *= i
return result
# Example usage
number = 5
result = factorial(number)
print("Factorial of", number, "is", result)
Production:
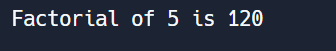
Question 16: Write a Python program to find the average of numbers in a list?
Solution:
def find_average(numbers):
if not numbers: # If the list is empty
return None # Return None since there are no numbers to average
total = sum(numbers) # Calculate the sum of numbers in the list
average = total / len(numbers) # Calculate the average
return average
# Example usage
number_list = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
average = find_average(number_list)
if average is not None:
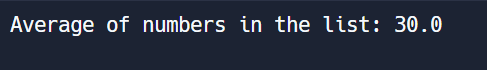
print("Average of numbers in the list:", average)
else:
print("The list is empty.")
Production:
Question 17: Write a Python program to merge two sorted lists?
Solution:
def merge_sorted_lists(list1, list2):
merged_list = ()
i = j = 0
while i < len(list1) and j < len(list2):
if list1(i) < list2(j):
merged_list.append(list1(i))
i += 1
else:
merged_list.append(list2(j))
j += 1
# Append remaining elements from list1, if any
while i < len(list1):
merged_list.append(list1(i))
i += 1
# Append remaining elements from list2, if any
while j < len(list2):
merged_list.append(list2(j))
j += 1
return merged_list
# Example usage
list1 = (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
list2 = (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
merged_list = merge_sorted_lists(list1, list2)
print("Merged sorted list:", merged_list)
Production:

Question 18: Write a Python program to remove duplicates from a string?
Solution:
def remove_duplicates(input_string):
# Initialize an empty set to store unique characters
unique_chars = set()
# Initialize an empty string to store the result
result = ""
# Iterate through each character in the input string
for char in input_string:
# Add the character to the result string if it's not already in the set
if char not in unique_chars:
result += char
unique_chars.add(char)
return result
# Example usage
input_string = "hello world"
result = remove_duplicates(input_string)
print("String with duplicates removed:", result)
Production:

Question 19: Write a Python program to check the perfect number?
Solution:
def is_perfect_number(number):
if number <= 0:
return False
divisor_sum = 0
# Find proper divisors and sum them up
for i in range(1, number):
if number % i == 0:
divisor_sum += i
# Check if the sum of proper divisors equals the number
return divisor_sum == number
# Example usage
input_number = 28
if is_perfect_number(input_number):
print(input_number, "is a perfect number.")
else:
print(input_number, "is not a perfect number.")
Production:

Question 20: Write a Python program to find the maximum difference between two elements in a list?
Solution:
def max_difference(nums):
if len(nums) < 2:
return None # If the list has less than two elements, return None
min_element = float('inf') # Initialize min_element to positive infinity
max_difference = float('-inf') # Initialize max_difference to negative infinity
for num in nums:
min_element = min(min_element, num)
max_difference = max(max_difference, num - min_element)
return max_difference
# Example usage
numbers = (7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4)
result = max_difference(numbers)
if result is not None:
print("Maximum difference between two elements in the list:", result)
else:
print("The list has less than two elements.")
Production:

Question 21: Write a Python program to check if a number is even or odd?
Solution:
With user defined function:
def check_even_odd(number):
if number % 2 == 0:
return "Even"
else:
return "Odd"
# Example usage
input_number = 7
result = check_even_odd(input_number)
print(input_number, "is", result)
Production:

Functionless:
number = 7
if number % 2 == 0:
print(number, "is Even")
else:
print(number, "is Odd")
Production:

Question 22: Write a Python program to count words in a sentence?
Solution:
def count_words(sentence):
# Split the sentence into words using whitespace as the delimiter
words = sentence.split()
# Count the number of words
return len(words)
# Example usage
input_sentence = "This is a sample sentence."
word_count = count_words(input_sentence)
print("Number of words in the sentence:", word_count)Production:

With built-in function:
sentence = "This is a sample sentence."
word_count = len(sentence.split())
print("Number of words in the sentence:", word_count)
Production:

No built-in function:
sentence = "This is a sample sentence."
word_count = 0
# Flag to indicate if the current character is part of a word
in_word = False
# Iterate through each character in the sentence
for char in sentence:
# If the character is not a space and we are not already in a word
if char != ' ' and not in_word:
# Increment word count and set the flag to indicate we are in a word
word_count += 1
in_word = True
# If the character is a space and we are in a word
elif char == ' ' and in_word:
# Set the flag to indicate we are not in a word
in_word = False
print("Number of words in the sentence:", word_count)
Production:

Question 24: Write a Python program to convert decimal to binary?
Solution:
def decimal_to_binary(decimal):
binary = ""
quotient = decimal
while quotient > 0:
remainder = quotient % 2
binary = str(remainder) + binary
quotient //= 2
return binary
# Example usage
decimal_number = 10
binary_number = decimal_to_binary(decimal_number)
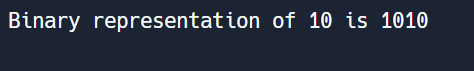
print("Binary representation of", decimal_number, "is", binary_number)
Production:
Question 25: Write a Python program to find the second largest element in a list?
Solution:
def second_largest(nums):
if len(nums) < 2:
return None # If the list has less than two elements, return None
sorted_nums = sorted(nums, reverse=True) # Sort the list in descending order
return sorted_nums(1) # Return the second element (index 1)
# Example usage
numbers = (10, 30, 20, 40, 50)
result = second_largest(numbers)
if result is not None:
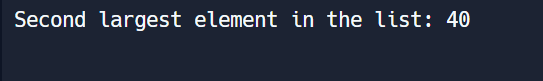
print("Second largest element in the list:", result)
else:
print("The list has less than two elements.")
Production:
Question 26: Write a Python program to reverse words in a string?
Solution:
def reverse_words(input_string):
# Split the string into words
words = input_string.split()
# Reverse the order of words
reversed_words = words(::-1)
# Join the reversed words back into a string
reversed_string = " ".join(reversed_words)
return reversed_string
# Example usage
input_string = "Hello World"
reversed_string = reverse_words(input_string)
print("Original string:", input_string)
print("Reversed string:", reversed_string)
Production:
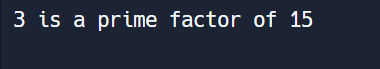
Question 27: Write a Python program to check if a number is a prime factor?
Solution:
def is_prime_factor(number, potential_factor):
if number <= 1 or potential_factor <= 1:
return False # Numbers less than or equal to 1 are not considered prime factors
return number % potential_factor == 0
# Example usage
number = 15
potential_factor = 3
if is_prime_factor(number, potential_factor):
print(potential_factor, "is a prime factor of", number)
else:
print(potential_factor, "is not a prime factor of", number)
Production:
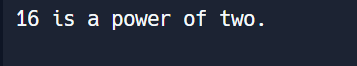
Question 28: Write a Python program to check if a number is a power of two?
Solution:
def is_power_of_two(number):
if number <= 0:
return False # Numbers less than or equal to 0 are not powers of two
while number > 1:
if number % 2 != 0:
return False # If the number is not divisible by 2, it's not a power of two
number //= 2
return True
# Example usage
number = 16
if is_power_of_two(number):
print(number, "is a power of two.")
else:
print(number, "is not a power of two.")
Production:
Question 29: Write a Python program to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
Solution:
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius):
fahrenheit = (celsius * 9/5) + 32
return fahrenheit
# Example usage
celsius_temperature = 25
fahrenheit_temperature = celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius_temperature)
print("Celsius:", celsius_temperature, "Fahrenheit:", fahrenheit_temperature)
Production:

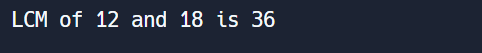
Question 30: Write a Python program to calculate the LCM (least common multiple) of two numbers?
Solution:
import math
def lcm(a, b):
return abs(a * b) // math.gcd(a, b)
# Example usage
num1 = 12
num2 = 18
result = lcm(num1, num2)
print("LCM of", num1, "and", num2, "is", result)
Production:
Conclusion
Completing practice with Python coding interview questions is essential for those who want to succeed in software development and data science positions. This extensive compilation addresses a wide range of basic ideas, from arithmetic operations and list manipulation to string manipulation. There are detailed answers to each query, complete with concise justifications and useful code examples. Candidates who actively engage in these questions not only demonstrate their proficiency in Python, but also develop critical thinking skills that are necessary to succeed in technical interviews and land a variety of jobs in the tech sector.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER