Existing web agents face limitations that arise from the fact that these agents often rely on a single input modality and are tested in controlled environments, such as web simulators or static snapshots, which do not accurately reflect the complexity and dynamic nature of the applications. real-world web interactions. . This significantly restricts its applicability and effectiveness in real-world scenarios where dynamic interactions with web content are required. This creates a gap in their practical usefulness as they cannot effectively navigate and interact with the diverse and constantly evolving content found on real websites.
Previous work on web agents has focused on autonomous navigation and interaction with web environments. Key developments include WebGPT and WebAgent, which leverage the GPT-3 and T5 models for text-based web browsing and HTML fragment extraction. There is also growing interest in multimodal web agents, such as WebGUM that combines T5 with Vision Transformers and PIX2ACT that uses web screenshots. These efforts contrast previous simplified or single-modal web environment approaches, moving toward more realistic and dynamic web interactions. At the same time, large multimodal models (LMMs) such as GPT-4V have demonstrated strong multimodal understanding, laying the foundation for more sophisticated web agents.
Researchers from Zhejiang University, Tencent ai Lab, and Westlake University have proposed the development of WebVoyager, an LMM-powered web agent that can complete end-to-end user instructions by interacting with real-world websites. They have proposed a new evaluation protocol that leverages the strong multimodal understanding capabilities of GPT-4V and includes a real-world task benchmark from 15 widely used websites. The agent's interaction with the Apple website is demonstrated step by step, showing an optimal path without redundant actions.

The evaluation set is constructed using a combination of self-instruction and human verification methods. Assignments are sampled and rewritten from various websites, ensuring high quality and relevance. Human validation is performed to verify the generated tasks and ensure that the answers can be found on the corresponding websites. Human evaluation is the primary metric, where expert annotators judge the success of the task based on the agent's interaction with the web. Interestingly, it uses GPT-4V for automatic evaluation, aiming to reduce reliance on human evaluators and experiment costs.
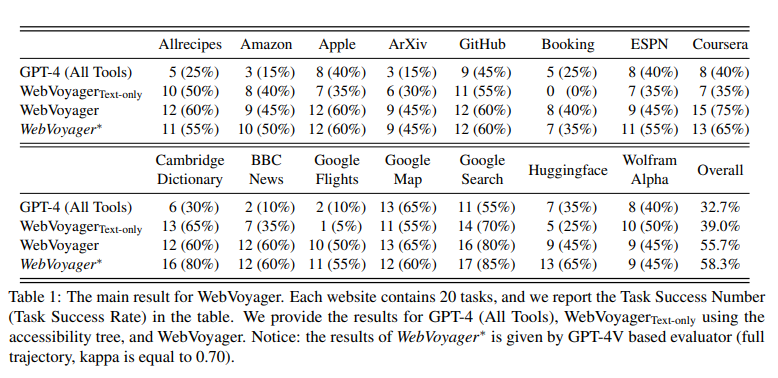
WebVoyager achieved a task success rate of 55.7%, outperforming GPT-4 and its text-only variant. The automated assessment protocol using GPT-4V closely aligned with human judgment and showed an agreement rate of 85.3%. Despite performing well on most website tasks, WebVoyager encountered challenges with text-heavy sites like Cambridge Dictionary and Wolfram Alpha. Agent consistency improved with more information, reaching a Kappa score of 0.7, matching levels of human agreement and highlighting the potential of GPT-4V for efficient, large-scale evaluations of web agents.
In conclusion, WebVoyager is an LMM-powered web agent designed for end-to-end web task resolution, with a task success rate of 55.7%. Still, there is room for improvement, as indicated by the extensive bug analysis provided in the document. The researchers allude that future work should focus on better methods of integrating visual and textual information and exploring the creation of multimodal web agents using open source LMMs.
Review the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our 36k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook community, Discord Channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Telegram channel
![]()
Nikhil is an internal consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing an integrated double degree in Materials at the Indian Institute of technology Kharagpur. Nikhil is an ai/ML enthusiast who is always researching applications in fields like biomaterials and biomedical science. With a strong background in materials science, he is exploring new advances and creating opportunities to contribute.
<!– ai CONTENT END 2 –>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER




