The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has transformed the natural language processing (NLP) landscape. The introduction of transformative architecture marked a turning point and ushered in a new era in NLP. While a universal definition for LLMs is lacking, they are generally understood as versatile machine learning models adept at simultaneously handling multiple natural language processing tasks, showing the rapid evolution and impact of these models in the field.
Four essential tasks in LLMs are natural language understanding, natural language generation, knowledge-intensive tasks, and reasoning ability. The evolving landscape includes various architectural strategies, such as models that employ encoders and decoders, encoder-only models like BERT, and decoder-only models like GPT-4. GPT-4's decoder-only approach excels at natural language generation tasks. Despite GPT-4 Turbo's improved performance, its 1.7 trillion parameters raise concerns about substantial energy consumption, emphasizing the need for sustainable ai solutions.
Researchers at McGill University have proposed the Pythia 70M model, a pioneering approach to improve the efficiency of prior LLM training by championing Knowledge distillation for transfer between architectures. Inspired by the efficient Hyena mechanism, the method replaces attention heads in transformer models with Hyena, providing a cost-effective alternative to conventional pre-training. This approach effectively addresses the intrinsic challenge of processing extensive contextual information in quadratic attention mechanisms, offering a promising avenue for more efficient and scalable LLMs.
The researchers use the efficient Hyena mechanism, replacing attention heads in transformer models with Hyena. This innovative approach improves inference speed and outperforms traditional pre-training in accuracy and efficiency. The method specifically addresses the challenge of processing long contextual information inherent to quadratic attention mechanisms, striving to balance computational power and environmental impact, showing a cost-effective and environmentally conscious alternative to conventional pre-training methods.
The studies present perplexity scores for different models, including Pythia-70M, the pre-trained Hyena model, the Hyena student model distilled with MSE loss, and the Hyena student model fine-tuned after distillation. The pre-trained Hyena model shows improved perplexity compared to Pythia-70M. Distillation further improves performance, with the lowest perplexity achieved by the Hyena student model through adjustments. In language assessment tasks using the Language Model Assessment Harness, Hyena-based models demonstrate competitive performance on several natural language tasks compared to the attention-based Pythia-70M teacher model.
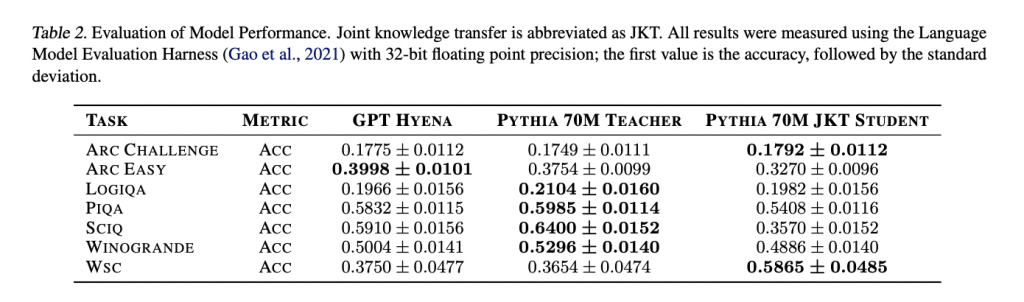
To conclude, researchers at McGill University have proposed the Pythia 70M model. Employing joint knowledge transfer with Hyena operators as a substitute for attention improves the computational efficiency of LLMs during training. When evaluating perplexity scores on the OpenWebText and WikiText data sets, the Pythia 70M Hyena Model, in the process of progressive knowledge transfer, surpasses its previously trained counterpart. Fine-tuning post-knowledge transfer further reduces perplexity, indicating better model performance. Although the Hyena student model shows slightly lower accuracy on natural language tasks compared to the teacher model, the results suggest that joint knowledge transfer with Hyena offers a promising alternative to form more computationally efficient LLMs.
Review the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on Twitter and Google news. Join our 36k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook community, Discord channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Telegram channel
![]()
Asjad is an internal consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing B.tech in Mechanical Engineering at Indian Institute of technology, Kharagpur. Asjad is a machine learning and deep learning enthusiast who is always researching applications of machine learning in healthcare.
<!– ai CONTENT END 2 –>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





