In the last decade, the data-driven method using deep neural networks has boosted the success of ai in various challenging applications across different fields. These advancements address multiple problems; however, existing methodologies face the challenge in data science applications, especially in fields such as biology, healthcare, and business due to the requirement of high expertise and advanced coding skills. Moreover, a major barrier in this field is the lack of communication between domain experts and advanced ai models.
In recent years, the rapid progress of large language models (LLMs) has opened up many possibilities in the field of artificial intelligence. Some of the most well-known LLMs are GPT-3, GPT-4, PaLM, LLaMA, and Qwen. These models have great potential for understanding, generating, and applying natural language. These advances have created a medium for LLM-driven agents that are now being developed to solve problems in search engines, software engineering, games, recommendation systems, and scientific experiments. These agents are typically guided by a chain of thought (CoT) such as ReAct and can use tools such as APIs, code interpreters, and retrievers. Methods discussed in this paper include (a) augmenting LLMs with function calls and (b) augmenting LLMs using code interpreters.
A team of researchers from the Hong Kong Polytechnic University has unveiled LAMBDA, a novel open-source, no-code multi-agent data analytics system developed to overcome the lack of effective communication between domain experts and advanced ai models. LAMBDA provides an essential medium that enables seamless interaction between domain knowledge and ai capabilities in data science. This method solves numerous problems such as removing coding barriers, integrating human intelligence with ai, and reshaping data science education, promising reliability and portability. Reliability means that LAMBDA can tackle data analytics tasks stably and correctly. Portability means that it is compatible with multiple LLMs, allowing it to be enhanced with the latest cutting-edge models.
The proposed method, LAMBDA, a multi-agent data analysis system, contains two agents that work together to solve data analysis tasks using natural language. The process starts with writing code based on user instructions and then executing that code. LAMBDA’s two main roles are “programmer” and “inspector.” The programmer writes code according to the user instructions and the data set. This code is then executed on the host system. If the code encounters any errors during execution, the inspector serves the role of suggesting improvements. The programmer uses these suggestions to correct the code and submit it for re-evaluation.
The experiment results show that LAMBDA performs well on machine learning tasks. It achieved the highest accuracy rates of 89.67%, 100%, 98.07%, and 98.89% for AIDS, NHANES, Breast Cancer, and Wine datasets, respectively, for classification tasks. For regression tasks, it achieved the lowest MSE (mean square error) of 0.2749, 0.0315, 0.4542, and 0.2528, respectively. These results highlight its effectiveness in handling various data science application models. Moreover, LAMBDA successfully overcame the coding barrier without any human involvement in the whole process of these experiments and connected data science with human experts who lack coding skills.
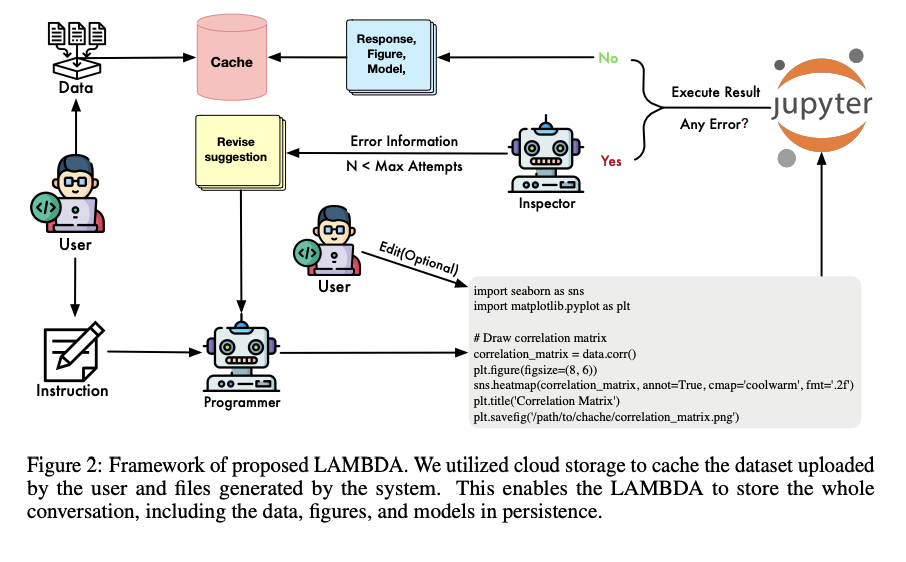
In this paper, a team of researchers from the Hong Kong Polytechnic University has proposed a novel open-source, no-code, multi-agent data analysis system called LAMBDA, which combines human intelligence with ai. Experimental results show that it performs well on data analysis tasks. In the future, it can be enhanced with planning and reasoning techniques. It has bridged the gap between data science and humans without coding skills, successfully connecting them without human involvement. By bridging the gap between human expertise and ai capabilities, LAMBDA aims to make data science and analytics more accessible, fostering more innovation and discovery in the future.
Review the Paper, Projectand GitHubAll credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on twitter.com/Marktechpost”>twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn GrAbove!. If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Over 47,000 ML subscribers on Reddit
Find upcoming ai webinars here

Sajjad Ansari is a final year student from IIT Kharagpur. As a technology enthusiast, he delves into practical applications of ai, focusing on understanding the impact of ai technologies and their real-world implications. He aims to articulate complex ai concepts in a clear and accessible manner.
<script async src="//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js” charset=”utf-8″>






