Large linguistic models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities across a number of domains. But do they also possess metacognitive knowledge – an understanding of their thought processes? This intriguing question is explored in a new paper investigating the metacognitive capabilities of LLMs, specifically in the context of mathematical problem solving. A team of researchers from Mila, the University of Montreal, Princeton University, the University of Cambridge, and Google DeepMind develops an innovative approach to extract and leverage LLMs’ implicit knowledge of mathematical skills and concepts, with promising results for improving mathematical reasoning.
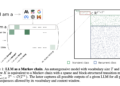
Current methods for improving the performance of master’s students in mathematics often rely on generic priming techniques such as chain-of-thought reasoning. While effective, these approaches do not tap into any potential metacognitive knowledge within the models. The researchers propose a novel method for leveraging the latent understanding of master’s students’ mathematics skills. Their approach involves using a powerful LLM such as GPT-4 to assign fine-grained skill labels to mathematics questions, followed by semantic clustering to obtain broader skill categories. This results in a “Skill Example Repository” – a curated set of questions labeled with interpretable skill labels.
The key innovation is the use of this repository during inference on new mathematical problems. When presented with a question, the MSc student is first asked to identify the most relevant skill from the repository. Example questions/answers associated with that skill are then given as examples in context before attempting the solution. This skill-based prompting approach was evaluated on challenging datasets such as GSM8K and MATH, which cover various mathematical difficulties. On the MATH dataset, it achieved an impressive 11.6% improvement over standard chain-of-thought prompting. The method also improved performance when integrated with program-assisted language (PAL) models that generate code-based solutions.
Importantly, the researchers demonstrated that the skill knowledge extracted by a powerful model such as GPT-4 effectively transfers to improve the performance of weaker LLM students. The approach also showed strong generalization, improving results when applied to several other math problem datasets in addition to those used to create the skill repository. This study provides compelling evidence that LLM students possess significant metacognitive knowledge about math problem solving. By developing techniques to extract and put this knowledge into practice, the researchers have opened up exciting new avenues for improving the mathematical reasoning capabilities of LLM students.
The skill-based approach offers several key advantages: it allows for more specific and relevant contextualized examples, can be seamlessly integrated with existing stimulus methods, and demonstrates high transferability across models and datasets. While there is room for improvement, particularly in handling problems requiring multiple skills, this work represents a significant step towards more sophisticated mathematical reasoning in ai systems. Beyond mathematics, the presented methodology could be adapted to uncover and leverage metacognitive knowledge in other domains. As such, this research advances our understanding of LLMs’ cognitive processes and points towards promising new directions for improving their general capabilities through metacognitive bootstrapping.
Take a look at the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on twitter.com/Marktechpost”>twitter and LinkedInJoin our Telegram Channel.
If you like our work, you will love our fact sheet..
Don't forget to join our SubReddit of over 50,000 ml
Shreya Maji is a Consulting Intern at MarktechPost. She pursued her Bachelors from the Indian Institute of technology (IIT) in Bhubaneswar. She is an ai enthusiast and enjoys keeping herself updated about the latest advancements. Shreya is particularly interested in real-life applications of cutting-edge technology, especially in the field of data science.
<script async src="//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js” charset=”utf-8″>