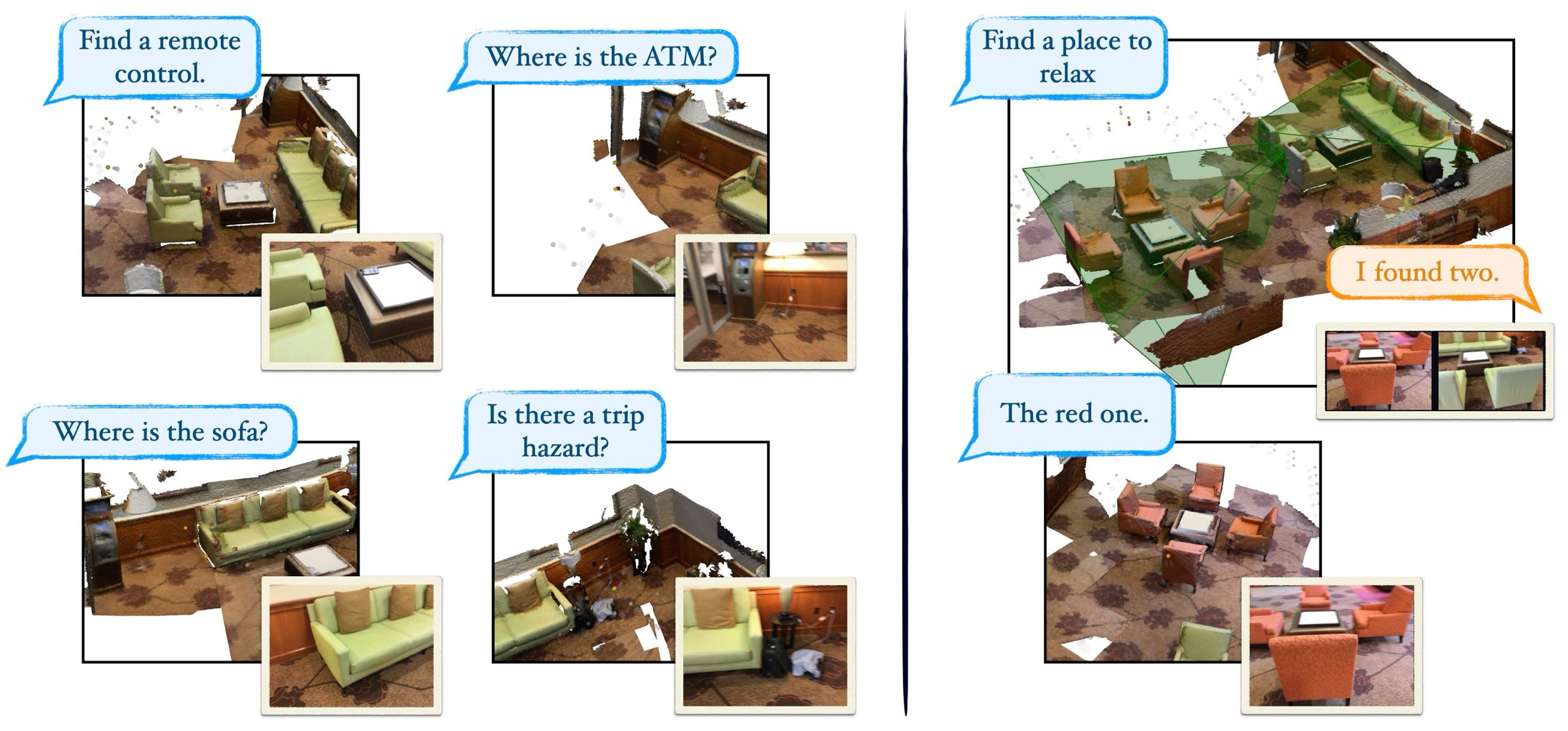
This paper presents Embedding Pose Graph (EPG), an innovative method that combines the strengths of basic models with a simple 3D representation suitable for robotics applications. To address the need for efficient spatial understanding in robotics, EPG provides a compact yet powerful approach by attaching features of the basic model to the nodes of a pose graph. Unlike traditional methods that rely on bulky data formats such as voxel grids or point clouds, EPG is lightweight and scalable. It facilitates a variety of robotic tasks, including open vocabulary queries, disambiguation, image-based queries, language-driven navigation, and relocalization in 3D environments. We show the effectiveness of EPG in handling these tasks, demonstrating its ability to improve the way robots interact and navigate through complex spaces. Through both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we illustrate EPG's strong performance and its ability to outperform existing methods in offshoring. Our work presents a crucial step forward in enabling robots to understand and operate efficiently within large-scale 3D spaces.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER