Amazon Q is a new ai-powered generative app that helps users get their work done. Amazon Q can become your personalized business expert, allowing you to discover content, exchange ideas, or create summaries using your business data securely. You can use Amazon Q to have conversations, solve problems, generate content, get insights, and take action by connecting to your company's repositories of information, code, data, and business systems. For more information, see Introducing Amazon Q, a new ai-powered generative assistant (preview).
In this post, we show you how to bring Amazon Q, your business expert, to Slack users.
You'll be able to chat with Amazon Q using Slack direct messages (DMs) to ask questions and get answers based on company data, get help creating new content such as email drafts, summarizing file attachments, and completing tasks.
You can also invite Amazon Q to participate in your team's channels. In a channel, users can ask you questions in a new message or tag you in an existing thread at any time, to provide additional data points, resolve a debate, or summarize the conversation and capture next steps.
Solution Overview
Amazon Q is incredibly powerful. Watch the demo below – seeing is believing!
In the demo, our Amazon Q app includes a set of AWS technical documents. You can populate your own Amazon Q business expert application with documents and articles from your own company's knowledge base, so you can answer your questions.
Everything you need is provided as open source in our GitHub repository.
In this post, we'll walk you through the process of deploying Amazon Q to your AWS account and adding it to your Slack workspace. When you're done, you'll wonder how you ever managed without it!
The following are some of the things you can do:
- Reply to messages – In DM respond to all messages. In channels, reply only to @mentions and reply in a conversation thread.
- Represent responses containing markdowns – This includes titles, lists, bold, italics, tables and more.
- Sentiment Tracking – Provides thumbs up and thumbs up buttons to track user feedback.
- Provide source attribution – Provides references and hyperlinks to sources used by Amazon Q.
- Understand the context of the conversation – Follow the conversation and respond according to the context.
- Stay on top of multiple users – When tagged in a thread, you know who said what and when, so you can contribute context and accurately summarize the thread when prompted.
- Process attachments – You can process up to five attachments to answer questions about documents, summaries, and more.
- Start new conversations – You can reset and start new conversations in DM channels using
/new_conversation.
In the following sections, we show how to deploy the project to your own AWS account and Slack workspace, and start experimenting!
Previous requirements
You must have an AWS account and an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user and role with permissions to create and manage the resources and components required for this application. If you don't have an AWS account, see How do I create and activate a new Amazon Web Services account?
You also need to have an existing and running Amazon Q Business Expert app. If you haven't set one up yet, see Creating an Amazon Q app.
Lastly, you need a Slack account and access to create and publish apps to your Slack organization. If you don't have one, see if your company can create a Slack sandbox organization so you can experiment or go to slack.com to create a free Slack account and workspace.
Deploy solution resources
We provide pre-built AWS CloudFormation templates that implement everything you need in your AWS account.
If you are a developer and want to build, deploy, or publish your solution from code, see the Developer readme.
Complete the following steps to start the CloudFormation stack:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- Choose one of the following launch stack buttons for the desired AWS Region to open the AWS CloudFormation console and create a new stack.
| Region | launch stack |
|---|---|
Northern Virginia (us-east-1) |
 |
Oregon (us-west-2) |
 |
- For First nameEnter a name for your app (for example,
AMAZON-Q-SLACK-GATEWAY). - For AmazonQAppIdenter your existing Amazon Q App ID (e.g.
80xxxxx9-7xx3-4xx0-bxx4-5baxxxxx2af5). You can copy it from the Amazon Q console. - For AmazonQRegionChoose the region where you created your Amazon Q app (us-east-1 or us-west-2).
- For AmazonQUserIdEnter an Amazon Q user ID email address (leave blank to use a Slack user email as the user ID).
- For ContextDaysToLiveEnter the time period to keep conversation metadata cached in Amazon DynamoDB (you can leave it as the default).
When the status of your CloudFormation stack is CREATE_COMPLETEchoose the Departures and keep it open; you will need it in later steps.
Create your application
Now you can create your app in Slack. Complete the following steps:
- Create a Slack app on https://api.slack.com/apps from the generated manifest: copy and paste from the stack output:
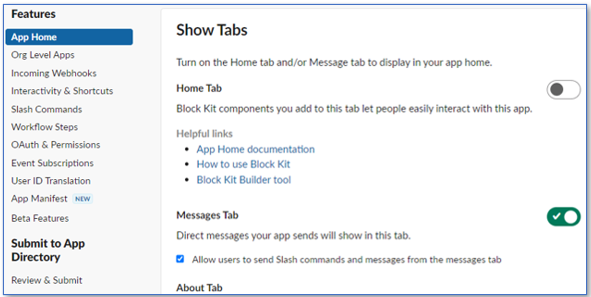
SlackAppManifest. - Choose Application start in the navigation pane and scroll down to the section Show tabs.
- Allow Messages tab.
- Select Allow users to send slash commands and messages from the messages tab.
This is a necessary step to allow your user to send messages to your application.
Add your app to your workspace
Now you can add your app to your workspace. This is necessary to generate the bot user's OAuth token value needed in the next step.
- Gonna OAuth and permissions (in https://api.slack.com) and choose Install to workspace to generate the OAuth token.
- In Slack, go to your workspace.
- Choose the name of your workspace, Configuration and administrationand Manage applications.
- Choose your newly created application.
- In the right panel, choose Open in applications directory.
- Choose Open in Slack.
Set up Slack secrets in AWS Secrets Manager
Let's set up your Slack secrets to verify the signature of every request and post on behalf of your Amazon Q bot.
In this example, we don't enable Slack token rotation. You can enable it for a production application by implementing rotation through AWS Secrets Manager. Create an issue (or better yet, a pull request) in the GitHub repository if you want to add this feature to a future version.
Complete the following steps to set up a secret in Secrets Manager:
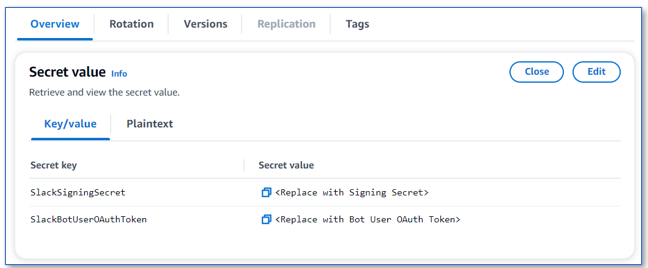
- In the AWS CloudFormation console, navigate to your stack Departures tab and choose the link to
SlackSecretConsoleUrlto be redirected to the Secrets Manager console. - Choose Retrieve secret value.
- Choose Edit.
- Replace the values of
SlackSigningSecretandSlackBotUserOAuthTokenusing the values in the Slack app settings in Basic information and OAuth and permissions.
Be careful not to accidentally copy Client secret rather Signature secret.
Start using Amazon Q
Complete the following steps to start using Amazon Q in Slack:
- Open your Slack workspace.
- Low Applications, Manageadd your new Amazon Q app.
- Optionally, add your Amazon Q app to team channels.
- In the app's DM channel, enter
Hello.
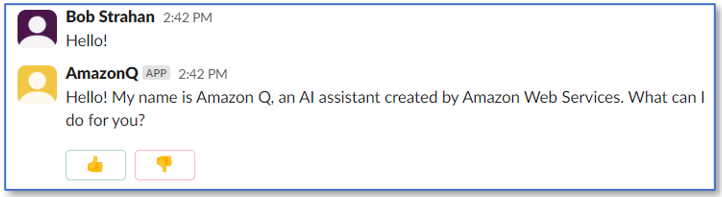
Now you've implemented a powerful new ai assistant in your Slack sandbox environment.
Play around with it, try all the features discussed in this post, and copy the things you saw in the demo video. Most importantly, you can ask about topics related to the documents you've ingested into your own Amazon Q business expert app. But don't stop there. You may find additional ways to make it useful, and when you do, please let us know by posting a comment.
Once you're convinced how useful it is, talk to your Slack admins (and show them this post) and work with them to implement it in your company's Slack workspaces. Your coworkers will thank you!
Clean
When you're done experimenting with this solution, delete your app in Slack (https://api.slack.com/apps) and clean up your AWS resources by opening the AWS CloudFormation console and deleting the AMAZON-Q-SLACK-GATEWAY stack you implemented. This deletes the resources that you created when you deployed the solution.
Conclusions
This sample Amazon Q Slack app discussed in this post is provided as open source; You can use it as a starting point for your own solution and help us improve it by contributing fixes and features through GitHub pull requests. Explore the code, choose Look in it GitHub repository to receive notifications about new releases and check the latest updates. We'd also love to hear your suggestions for improvements and features.
For more information about Amazon Q, see What is Amazon Q (for business use)?
About the authors
 Gary Benattar is a senior software development manager at AWS HR. Gary started at Amazon in 2012 as an intern and focused on building real-time, scalable outlier detection systems. He worked in Seattle and Luxembourg and now resides in Tel Aviv, Israel, where he dedicates his time to creating software to revolutionize the future of Human Resources. He co-founded a startup, Zengo, focused on making digital wallets secure through multi-party computing. He received his Master's degree in Software Engineering from the Sorbonne University in Paris.
Gary Benattar is a senior software development manager at AWS HR. Gary started at Amazon in 2012 as an intern and focused on building real-time, scalable outlier detection systems. He worked in Seattle and Luxembourg and now resides in Tel Aviv, Israel, where he dedicates his time to creating software to revolutionize the future of Human Resources. He co-founded a startup, Zengo, focused on making digital wallets secure through multi-party computing. He received his Master's degree in Software Engineering from the Sorbonne University in Paris.

Bob Strahan is a Principal Solutions Architect on the AWS Linguistics ai Services team.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER




