Large Language Models (LLM) are the driving force behind the ai revolution, but the game just took a major plot twist. Databricks DBRX, an innovative open source LLM, is here to challenge the status quo. Outperforming established models and going head-to-head with industry leaders, DBRX boasts superior performance and efficiency. Dive into the world of LLMs and explore how DBRX is rewriting the rulebook, offering a glimpse into the exciting future of natural language processing.
Understanding LLMs and Open Source LLMs
Large Language Models (LLM) are advanced natural language processing models that can understand and generate human-like text. These models have become increasingly important in various applications, such as language understanding, programming, and mathematics.
Open source LLMs play a crucial role in the development and advancement of natural language processing technology. They provide the open community and enterprises with access to cutting-edge language models, allowing them to create and customize their models for specific applications and use cases.
What is Databricks DBRX?
Databricks DBRX is an open, general-purpose large language model (LLM) developed by Databricks. It has established a new state of the art for established open LLMs, surpassing GPT-3.5 and rivaling Gemini 1.0 Pro. DBRX excels in several benchmarks, including language understanding, programming and mathematics. It is trained using next token prediction with a detailed Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, resulting in significant improvements in training and inference performance.
The model is available to Databricks customers via API and can be pre-trained or tuned. Its efficiency is highlighted by training and inference performance, outperforming other established models and being approximately 40% the size of similar models. DBRX is a critical component of Databricks' next generation of GenAI products, designed to empower businesses and the open community.
The Databricks DBRX MoE Architecture
Databricks' DBRX stands out as an open source, general-purpose large language model (LLM) with a unique architecture for efficiency. Here's a breakdown of its key features:
- Detailed Mix of Experts (MoE): This innovative architecture uses 132 billion total parameters, with only 36 billion active per entry. This focus on active parameters significantly improves efficiency compared to other models.
- Expert power: DBRX employs 16 experts and selects 4 for each task, offering a staggering 65 times more possible expert combinations, leading to superior model quality.
- Advanced techniques: The model leverages cutting-edge techniques such as Rotary Position Encodings (RoPE), Gated Linear Units (GLU), and Grouped Query Attention (GQA), further improving its performance.
- Efficiency Champion: DBRX features inference speeds up to two times faster than LLaMA2-70B. Additionally, it features a compact size, being approximately 40% smaller than Grok-1 in total and active parameter counts.
- Real world performance: When hosted on Mosaic ai Model Serving, DBRX offers text generation speeds of up to 150 tokens per second per user.
- Training Efficiency Leader: The training process for DBRX demonstrates significant improvements in computing efficiency. It requires about half the FLOPs (floating point operations) compared to training dense models to obtain the same level of final quality.
DBRX Training
Training a powerful LLM like DBRX is not without obstacles. Here's a closer look at the training process:
- Challenges: The development of expert mixture models such as DBRX presented significant scientific and performance obstacles. Databricks needed to overcome these challenges to create a robust pipeline capable of efficiently training DBRX class models.
- Advance in efficiency: The training process for DBRX has achieved notable improvements in computing efficiency. Take for example DBRX MoE-B, a smaller model in the DBRX family, which required 1.7 times less FLOP (floating point operations) to achieve a score of 45.5% on Databricks LLM Gauntlet compared to other models.
- Efficiency Leader: This achievement highlights the effectiveness of the DBRX training process. It positions DBRX as a leader among open source models and even rivals the GPT-3.5 Turbo in RAG tasks, while boasting superior efficiency.
DBRX vs. other LLMs
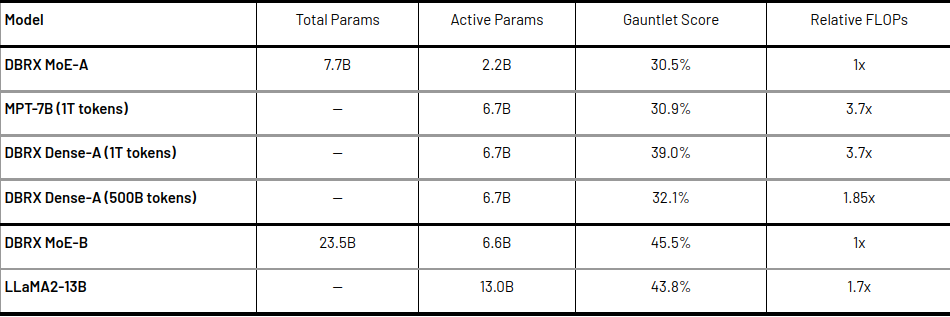
Metrics and results
- DBRX has been measured against established open source models in language comprehension tasks.
- It has outperformed GPT-3.5 and is competitive with Gemini 1.0 Pro.
- The model has demonstrated its capabilities on various benchmarks, including composite benchmarks, programming, mathematics, and MMLU.
- It has outperformed all lean chat or instruction models on standard benchmarks, scoring highest on composite benchmarks such as Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard and Databricks Model Gauntlet.
- Additionally, DBRX Instruct has demonstrated superior performance on long context and RAG tasks, outperforming GPT-3.5 Turbo at all context lengths and in all parts of the sequence.
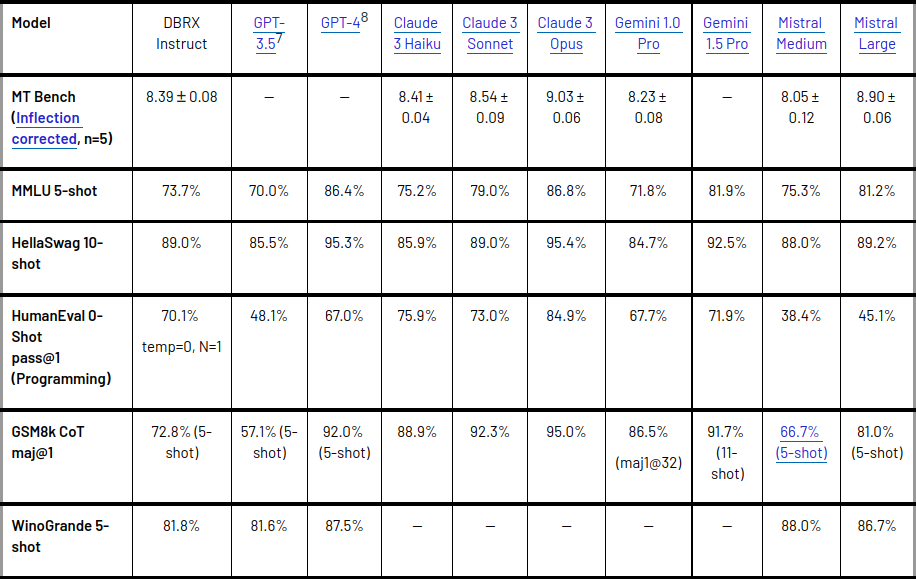
Strengths and weaknesses compared to other models
DBRX Instruct has proven its strength in programming and mathematics, scoring higher than other open models in benchmarks such as HumanEval and GSM8k. It has also shown competitive performance with Gemini 1.0 Pro and Mistral Medium, outperforming Gemini 1.0 Pro in several benchmarks. However, it is important to note that model quality and inference efficiency are often in tension, and while DBRX excels in quality, smaller models are more efficient for inference. Despite this, DBRX has been shown to achieve better trade-offs between model quality and inference efficiency than dense models typically achieve.
Key innovations in DBRX
DBRX, developed by Databricks, introduces several key innovations that differentiate it from existing proprietary and open source models. The model uses a detailed Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture with 132 B of total parameters, of which 36 B are active on any input.
This architecture allows DBRX to provide a robust and efficient training process, outperforming GPT-3.5 Turbo and challenging GPT-4 Turbo in applications such as SQL. Furthermore, DBRX employs 16 experts and chooses 4, providing 65 times more possible combinations of experts, resulting in better model quality.
The model also incorporates rotary position encodings (RoPE), gated linear units (GLU), and clustered query attention (GQA), contributing to its exceptional performance.
Advantages of DBRX over existing proprietary and open source models
DBRX offers several advantages over existing proprietary and open source models. It outperforms GPT-3.5 and is competitive with Gemini 1.0 Pro, demonstrating its capabilities in various benchmarks including composite benchmarks, programming, math, and MMLU.
- Additionally, DBRX Instruct, a variant of DBRX, outperforms GPT-3.5 in general knowledge, common sense reasoning, programming, and mathematical reasoning.
- It also excels at long context tasks, outperforming GPT-3.5 Turbo at all context lengths and in all parts of the sequence.
- Additionally, DBRX Instruct is competitive with Gemini 1.0 Pro and Mistral Medium, outperforming Gemini 1.0 Pro in several benchmarks.
The efficiency of the model is highlighted by its training and inference performance, outperforming other established models and being approximately 40% the size of similar models. DBRX's detailed MoE architecture and training process have demonstrated substantial improvements in computational efficiency, making it approximately 2x more FLOP efficient than dense model training for the same final model quality.
Also Read: Claude vs GPT: Which is a better LLM?
Conclusion
Databricks DBRX, with its innovative expert combination architecture, eclipses GPT-3.5 and competes with Gemini 1.0 Pro in language understanding. Its detailed MoE, advanced techniques, and superior computational efficiency make it an attractive solution for enterprises and the open community, promising groundbreaking advances in natural language processing. The future of LLMs is brighter with DBRX at the helm.
Follow us Google news to stay up to date with the latest innovations in the world of ai, data science and GenAI.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





