The purpose of data visualization is to present complex data in a way that is clear to understand and engages the audience. Visualizations make it easy to convey an overall message, highlight key ideas, and can be very persuasive in terms of guiding the audience toward a conclusion.
In this article, we will consider how to present complex information effectively with data visualization in a simple five-step guide, also discuss its benefits and provide some use case examples.
Data visualization represents data and information in a graphical way that is easy to understand. Visualizations can include charts, maps, graphs, infographics, and other elements that help simplify data. This makes it easy to identify patterns and trends, detect inconsistencies and outliers, and help the audience conclude the data being presented.
Picture of infogram
Data visualizations are also very effective when it comes to presenting complex and potentially confusing data to a company’s non-technical staff. This can help key decision makers when it comes to approving new projects or allocating more budget to a certain department, for example.
As humans, our eyes are immediately drawn to patterns, colors and shapes and we can instantly differentiate between certain elements. Branding and logos of large companies. They are excellent examples From this, almost everyone in the world is able to identify a big yellow ‘M’ or the outline of that famous apple.
Data visualizations build on these human insights, capturing the audience’s interest and keeping them focused on the message. If used effectively, data visualization can be an incredible storytelling tool, taking your audience on a journey in an engaging and persuasive way.
As discussed above, data visualization is very effective at turning complex and confusing data into something more digestible and easier to understand, especially if presented to non-technical people or an audience that is unfamiliar with the topic.
Visualizations also make it possible to analyze big datadata that is so large, complex and
at such a rapid pace that it is impossible to process it by traditional means. This presents new opportunities for companies, allowing the discovery of new knowledge and trends and providing a competitive advantage.
Other key uses of data visualization include visualizing relationships and patterns between two elements, sharing key information quickly, and exploring new business opportunities interactively.
To fully understand data visualization we cannot focus solely on the advantages, but must also look at its limitations to determine when and where it can be used.
One drawback that is more of a user error than a technology failure is the possibility of making inaccurate assumptions when there are a large number of different data points. Inexperienced users may also choose a poor or incorrect design, displaying data in a way that confuses the audience or implements too much bias.
Another problem to avoid is automatically believing that any correlation can be linked to a cause. Of course, in many cases, the correlation represents a valuable idea or trend, but coincidences do not always occur.
Finally, it can sometimes be easy to get caught up in fancy graphs and interactive charts, losing sight of the key message and overall goal of the visualization. Like any type of presentation and reporting technique, focus is crucial to conveying the key message effectively.
Now that we understand what data visualization is, its benefits, and what to avoid when designing and delivering a report, let’s consider how it can be applied with some common use cases.
- Data visualization can provide advanced marketing analytics to help drive decision making, discover new trends and niches, while improving current campaigns. The data could include website traffic and page performance, which would help fine-tune web content to drive more conversions.
- Risk management can also rely on data visualization to quickly highlight any issues within business operations or cybersecurity, for example. By analyzing historical data and presenting it in an engaging way, risks can be easily identified and mitigated before they cause any disruption.
- In sales, CRM tools allow companies to present data in a visually appealing way, simplifying understanding for both internal teams and customers. Additionally, there are specialized CRM tools designed for very specific industries. For example, roofing contractors You can take advantage of roofing CRM software instead of generic options. This tailored approach ensures that data visualization is accessible and applicable to a wide range of businesses.
Effective use of data visualization can be relatively simple if you follow best practices and are clear about the purpose of data analysis and to whom it is presented.
Here are five steps on how to present complex data effectively with data visualization.
1. Determine who the audience is
The first step when creating a data visualization is to fully determine who the audience is, their level of knowledge, and their technical expertise. If you know people well, you will also be able to understand their general attention span and interest in the topic.
For a data visualization to be effective, you must fully understand your audience’s expectations and goals and deliver the data in a format and design that suits their needs.
2. Eliminate unnecessary complexity
When designing a data visualization, simplicity is key, removing any unnecessary elements that could distract or confuse the audience. The overall message should be very clear and uncomplicated. To achieve this, implement a bold and consistent color scheme, clear and appropriately sized fonts, and use white space, grids, and margins to organize the page layout. Large titles, captions, and labels can also help explain content more clearly.
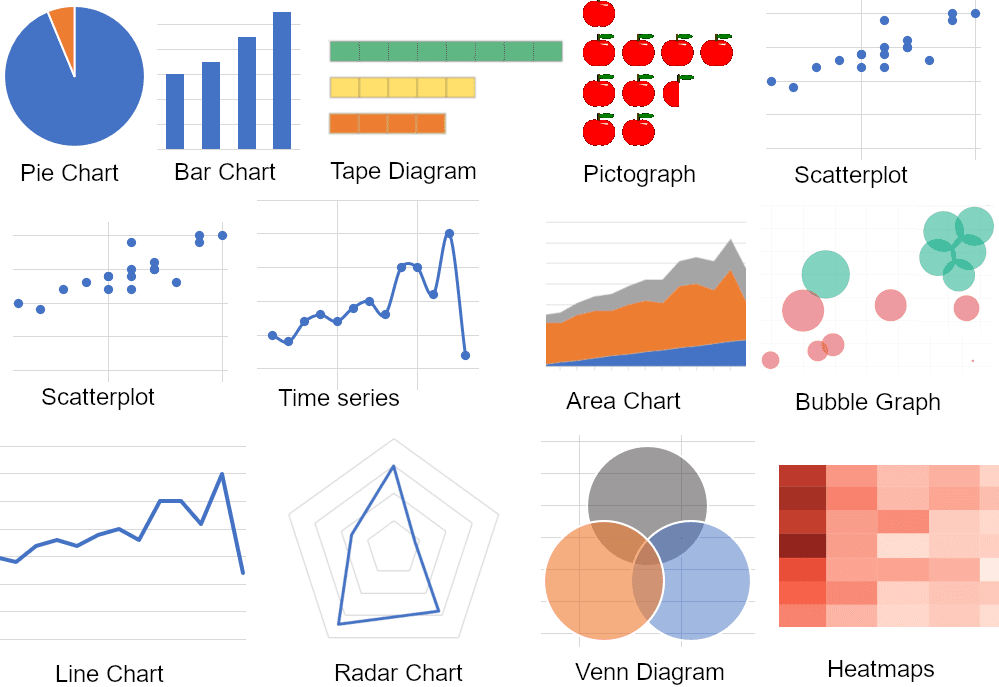
3. Use relevant graphics

Picture of search for polymers
Relevance is crucial for efficient data visualizations, therefore it is recommended Use the correct graphics. and graphs to display any data. For example, a line chart is the recommended way to show trends, and scatter charts show relationships and correlations, while a pie or donut chart can show percentages.
4. Create a story
Data visualization should be more than just cold, hard numbers: it should have a clear story that keeps the audience interested and gradually reaches a conclusion. Be sure to include any relevant background information before delving into the figures, and highlight key points to ensure they are understood.
5. Test your data visualization
The last step is to test the data visualization so it can be optimized before presenting it to an audience. Make sure key points are evident, data is accurate, and charts and graphs are easy to follow. Having a colleague check the visualization is one of the best ways to find errors, typos or inconsistencies, plus they can also provide honest feedback on whether the design and content are attractive.
Data visualization has become essential in terms of presenting big data and uncovering new insights and trends, especially in the sales and marketing sectors. By presenting data in this way, the audience is engaged and complex information can be displayed in a way that is easy to digest.
This can result in a better understanding of big data and analytics across an organization, resulting in better decision making and a boost to operations.
Nahla Davies is a software developer and technology writer. Before dedicating her full-time job to technical writing, she managed, among other interesting things, to work as a lead programmer at an Inc. 5,000 experiential brand organization whose clients include Samsung, Time Warner, Netflix, and Sony.