Author's image | Midjourney and Canva
KDnuggets' sister site, StatologyKDnuggets has a wide range of statistics-related content available written by experts, content that has been accumulated over a few years. We have decided to help our readers become familiar with this great resource of statistics, mathematics, data science, and programming content by organizing and sharing some of its fantastic tutorials with the KDnuggets community.
Learning statistics can be difficult, frustrating, and most of all, confusing. That's why Statology It's here to help.
This latest collection of tutorials focuses on data visualization. No statistical or data analysis is complete without data visualization. There are a variety of tools that allow us to better understand our data through visualization, and these tutorials will help us do just that. Learn these different techniques, and then continue reading the Statology archives to learn more.
Box plots
A box plot (sometimes called a box-and-whisker plot) is a graph that shows a five-number summary of a set of data.
The five-issue summary includes:
- The minimum
- The first quartile
- The median
- The third quartile
- The maximum
A box plot allows us to easily visualize the distribution of values in a data set using a simple graph.
Stem and Leaf Plots: Definition and Examples
A stem-and-leaf plot displays data by dividing each value in a data set into a “stem” and a “leaf.”
This tutorial explains how to create and interpret stem and leaf plots.
Scatter plot
Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables.
Suppose we have the following data set showing the weight and height of players on a basketball team:
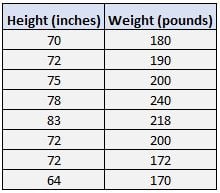
The two variables in this data set are height and weight.
To make a scatter plot, we plot height on the x-axis and weight on the y-axis. Each player is then represented as a point on the scatter plot:
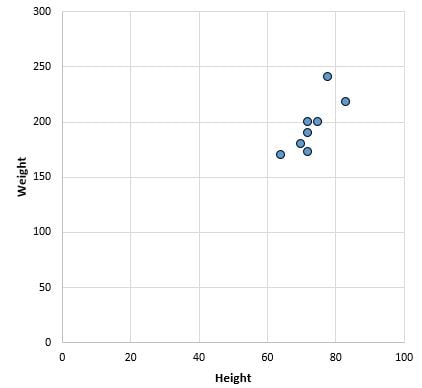
Scatter plots help us see the relationships between two variables. In this case, we see that height and weight have a positive relationship. As height increases, weight tends to increase as well.
Relative Frequency Histogram: Definition and Example
In statistics, you often find tables that show information about frequencies. Frequencies simply tell us how many times a certain event has occurred.
For example, the following table shows how many items a particular store sold in a week based on the price of the item:


This type of table is known as a frequency table. In one column we have the “class” and in the other column we have the frequency of the class.
We often use frequency histograms to visualize values in a frequency table, as it is usually easier to understand the data when we can visualize the numbers.
What are density curves? (Explanation and examples)
A density curve is a curve on a graph that represents the distribution of values in a set of data. It is useful for three reasons:
- A density curve gives us a good idea of the “shape” of a distribution, including whether a distribution has one or more “peaks” of values that occur frequently and whether the distribution is skewed to the left or the right.
- A density curve allows us to visually see where the mean and median of a distribution lie.
- A density curve allows us to visually see what percentage of observations in a data set fall between different values.
For more content like this, keep checking back at Statology and sign up for their weekly newsletter to make sure you don't miss a thing.
Matthew May (twitter.com/mattmayo13″ rel=”noopener”>@mattmayo13) holds a master's degree in computer science and a postgraduate diploma in data mining. As editor-in-chief of KDnuggets & Statologyand contributing editor at Mastering Machine LearningMatthew aims to make complex data science concepts accessible. His professional interests include natural language processing, language models, machine learning algorithms, and exploring emerging ai. His mission is to democratize knowledge in the data science community. Matthew has been coding since he was 6 years old.
<script async src="//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js” charset=”utf-8″>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





