For too long, the world of natural language processing has been dominated by models that primarily serve the English language. This inherent bias has left a significant portion of the world's population feeling underrepresented and ignored. However, an innovative new development will challenge this status quo and usher in a more inclusive era of language models: the Chinese Tiny LLM (CT-LLM).
Imagine a world where language barriers are no longer an obstacle to accessing cutting-edge ai technologies. That is precisely what the researchers behind CT-LLM have set out to achieve by prioritizing the Chinese language, one of the most spoken in the world. This 2 billion parameter model departs from the conventional approach of training language models primarily on English datasets and then adapting them to other languages.
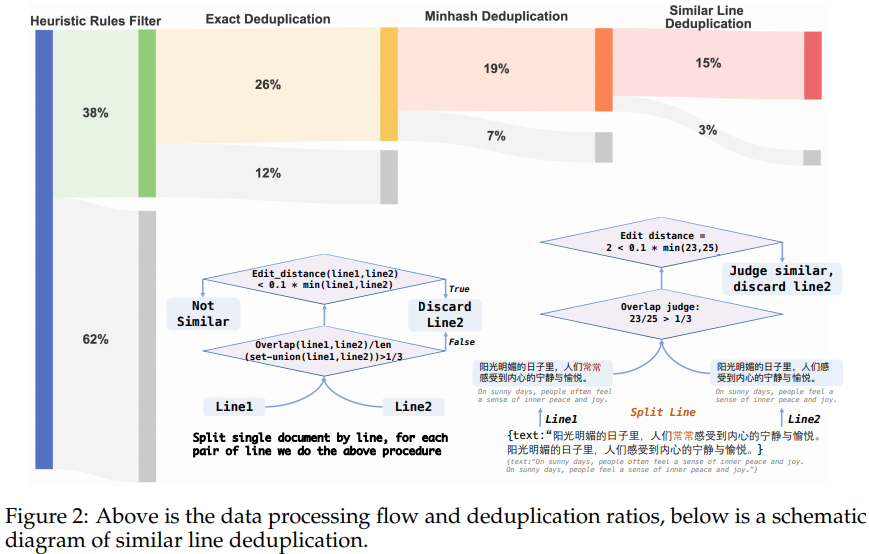
Instead, CT-LLM has been meticulously pre-trained on a staggering 1.2 trillion tokens, with a strategic emphasis on Chinese data. The pre-training corpus comprises an impressive 840.48 billion Chinese tokens, complemented by 314.88 billion English tokens and 99.3 billion code tokens. This strategic composition not only endows the model with exceptional proficiency in understanding and processing Chinese, but also enhances its multilingual adaptability, ensuring that it can easily navigate the linguistic landscapes of diverse cultures.
But that's not all: CT-LLM incorporates cutting-edge techniques that contribute to its exceptional performance. One such innovation is supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which strengthens the model's prowess in Chinese language tasks while improving its versatility in understanding and generating English text. Additionally, researchers have employed preference optimization techniques, such as DPO (Direct Preference Optimization), to align CT-LLM with human preferences, ensuring that its results are not only accurate but also harmless and useful.
To test the capabilities of CT-LLM, the researchers developed the Chinese Hard Case Benchmark (CHC-Bench), a multidisciplinary set of challenging problems designed to assess the model's instruction understanding and monitoring skills in the Chinese language. Surprisingly, CT-LLM demonstrated outstanding performance on this benchmark, excelling in tasks related to social comprehension and writing, showing its strong understanding of Chinese cultural contexts.
The development of CT-LLM represents a significant step towards creating inclusive linguistic models that reflect the linguistic diversity of our global society. By prioritizing the Chinese language from the beginning, this innovative model challenges the predominant English-centric paradigm and paves the way for future innovations in NLP that cater to a broader range of languages and cultures. With its exceptional performance, innovative techniques, and open source training process, CT-LLM stands as a ray of hope for a more equitable and representative future in the field of natural language processing. In the future, language barriers will no longer be an impediment to accessing cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies.
Review the Paper and HF Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on twitter.com/Marktechpost”>twitter. Join our Telegram channel, Discord channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our SubReddit over 40,000ml
![]()
Vibhanshu Patidar is a Consulting Intern at MarktechPost. He is currently pursuing a bachelor's degree at the Indian Institute of technology (IIT) Kanpur. He is a robotics and machine learning enthusiast with a knack for unraveling the complexities of algorithms that bridge theory and practical applications.
<script async src="//platform.twitter.com/widgets.js” charset=”utf-8″>
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





