Automation has become a cheat code in recent years, with each business function improving efficiency and moving away from manual, repetitive roles to more strategic roles.
Imagine a world where your procurement process runs like a well-oiled machine—no more delays, no more errors, and no more endless paperwork. Sounds too good to be true? Well, it’s not. Procurement automation today is indeed capable of automating and streamlining each step of your procurement workflow.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through four practical steps to implement automation in your procurement process.
Whether you’re a small business looking to cut costs or a large enterprise aiming to enhance efficiency, this guide will provide you with the actionable insights you need.
What is Procurement Automation?
Procurement automation is the use of software to streamline the procurement process by automating tasks such as creating purchase orders, approvals, invoice processing, and communicating with suppliers.
Procurement automation today basically covers the following aspects –
- automated purchase order creation
- pre-defined approval checks
- streamlined approvals with notifications and tracking
- invoice data entry and matching
- integration with procurement portal
- integration with ERP / accounting software
- automated reconciliation
This is how an automated procurement workflow looks like when integrated with a P2P automation software like Nanonets.
The process starts with the need of a new purchase.
1. Purchase Request:
An employee logs into the Nanonets portal to submit a purchase request digitally.
2. Purchase Order Creation:
Nanonets automatically creates a Purchase Order (PO) based on the details provided in the request.
3. Purchase Order Approval:
The PO undergoes an automated approval process within Nanonets.
You can set predefined rules and conditions to ensure consistency across procurement activities, minimizing errors and preventing unauthorized expenditures.

Approval notifications are sent and managed easily through popular communication tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams, featuring direct Call To Actions (CTAs) for quick decision-making.
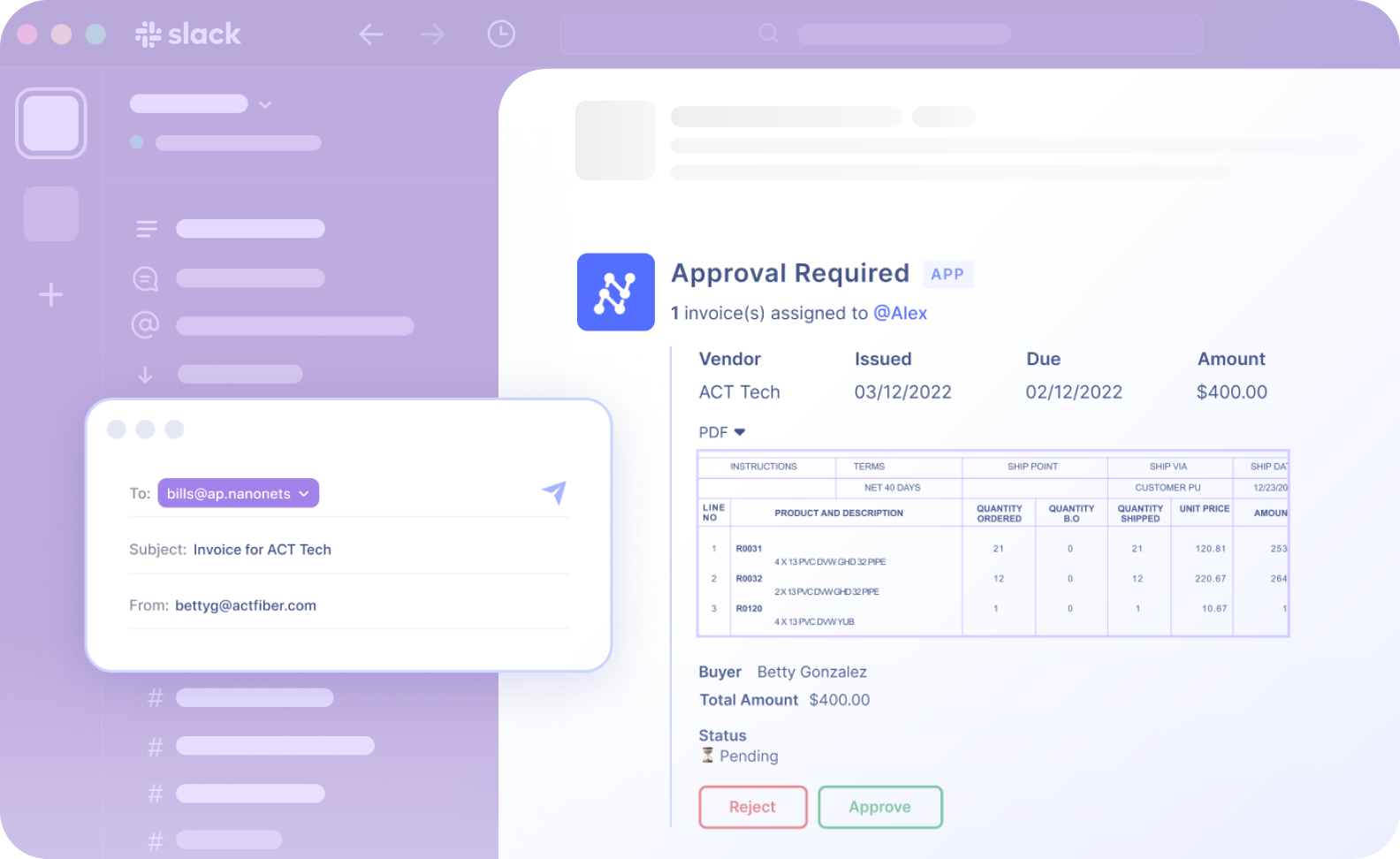
4. Purchase Order Dispatch:
Once approved, the system automatically sends the PO to the supplier via integrated email or supplier portals such as SAP Ariba or Coupa.
5. Goods or Services Delivery:
The supplier processes the order and updates the delivery status in the supplier portal, which syncs with Nanonets.
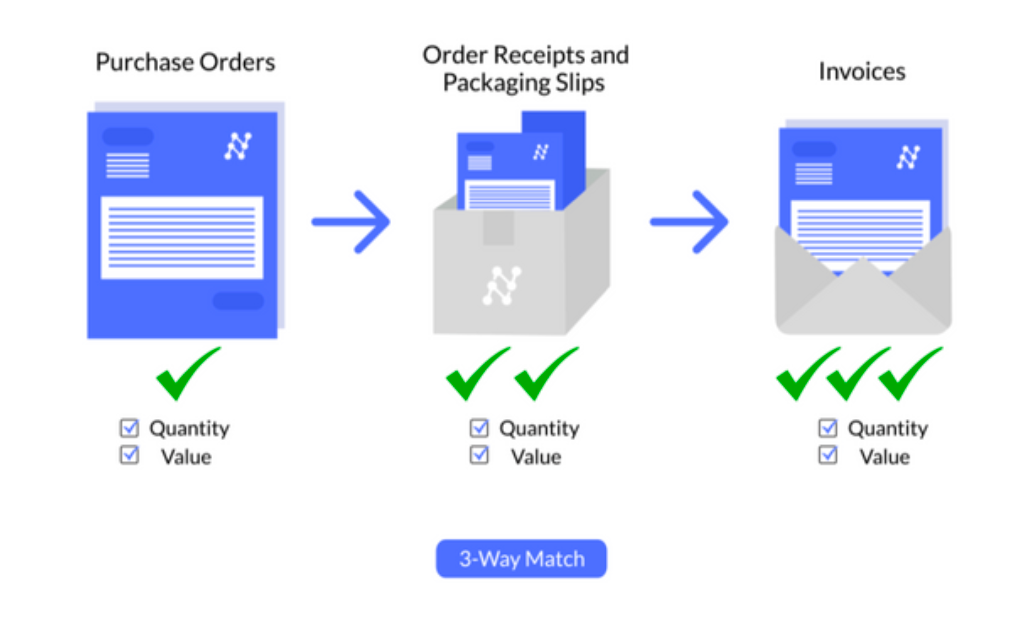
6. Invoice Data Capture and Matching:
Nanonets automatically extracts data from invoices, purchase orders, and delivery notes, reducing manual entry and errors.
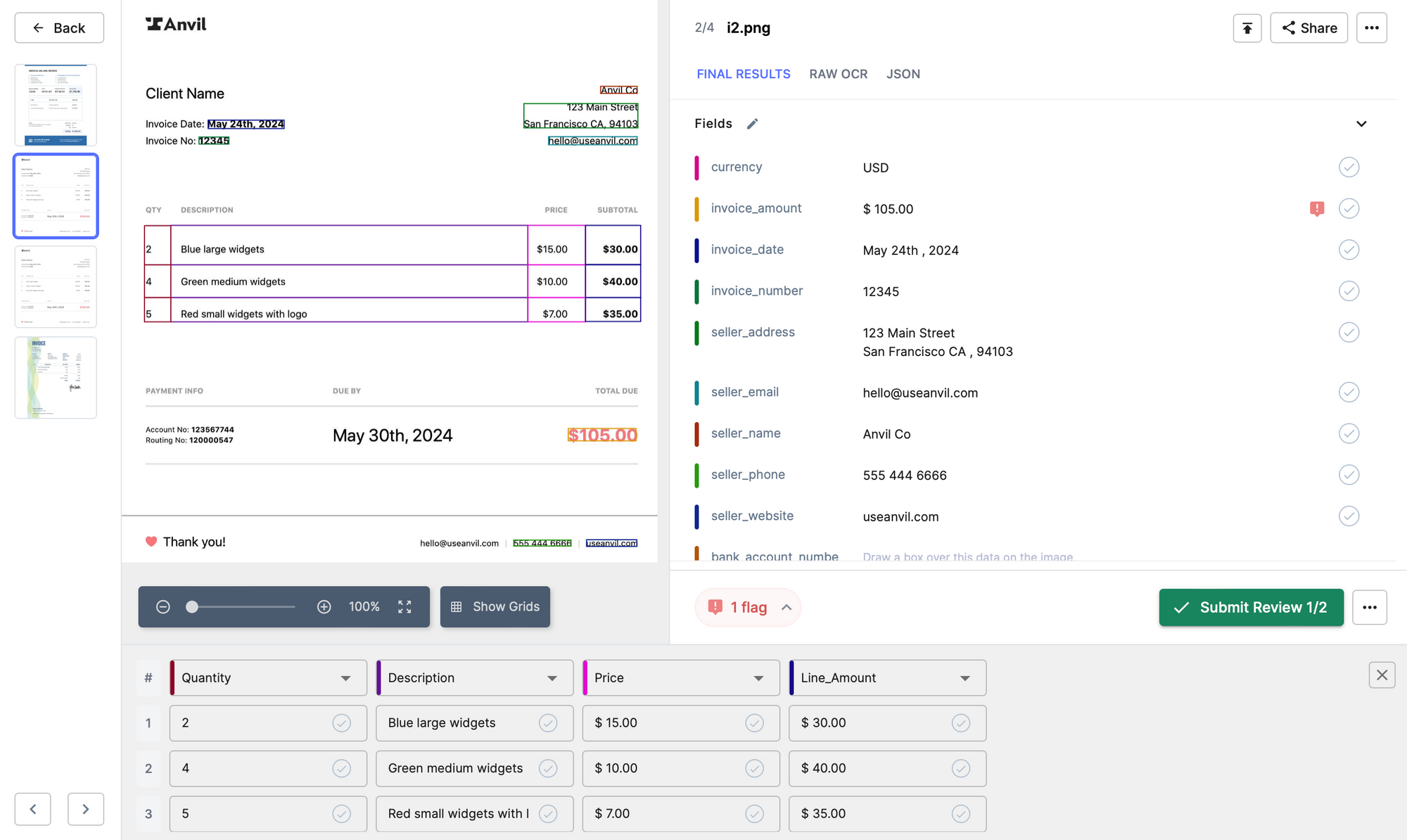
Automated three-way matching ensures accuracy by verifying the alignment of invoices, purchase orders, and delivery notes before payment processing.
7. Payment Processing:
Nanonets streamlines the payment process, ensuring all transactions are completed efficiently and on time.
This helps maintain good relationships with suppliers and avoid late payment penalties.

8. Integration with ERP/Accounting Software:
Nanonets integrates seamlessly with various ERP and accounting systems, providing a unified experience for procurement and financial data management.
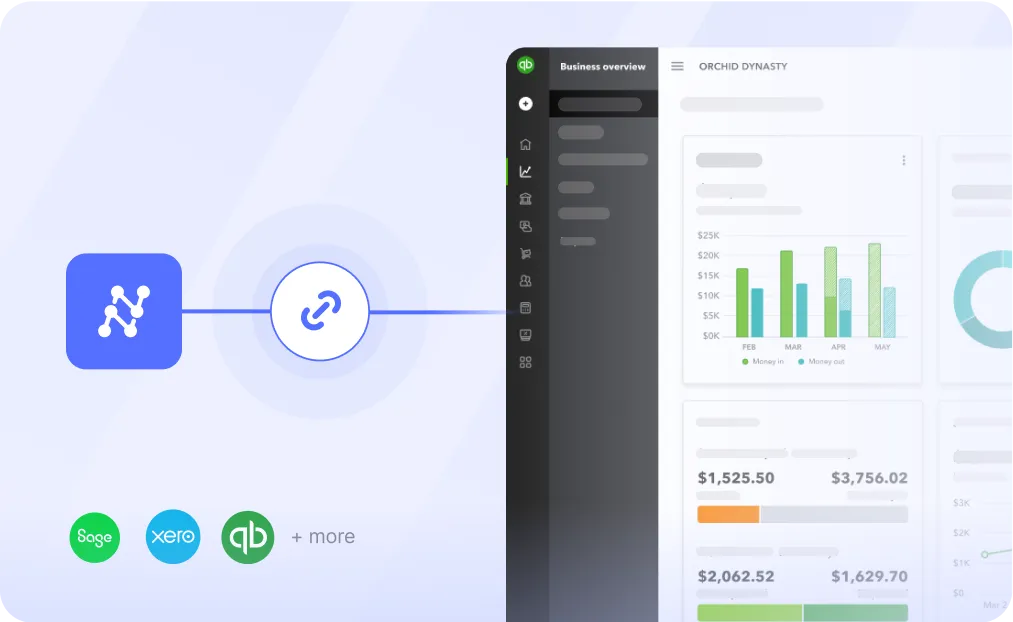
Thus, it is clear that procurement automation streamlines the purchase process and enhances the performance of your business function.
Here are some commonly seen benefits of automation in the procurement process:
- Cost Reduction: Automate repetitive tasks to reduce labor costs and minimize errors.
- Efficiency Gains: Streamline approval and invoice processing workflows to speed up the procurement process.
- Compliance Improvement: Ensure adherence to procurement policies and standards through automated checks and balances.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Enhance communication and coordination with suppliers through automated systems.
Now let’s take a step-by-step look at how businesses can go about automating their procurement workflow.
Step 1: Map your Current Procurement Process
The first step should be to map out your current workflow. This will help you localize inefficiencies, set clear objectives based on them, and then choose the right tools for automation.
- Break down each task into smaller components.
- Identify who is responsible for each step.
- Note any dependencies between tasks.
Once you have a clear map of your current process, the next step is to pinpoint where things are going wrong.
Within each step, look for areas where delays occur, errors are common, or resources are wasted.
These bottlenecks are often prime candidates for automation. Common bottlenecks seen frequently are –
- Manual data entry errors.
- Time-consuming approval processes.
- Poor supplier communication and coordination.
- Delays in invoice processing and payment.
You can also compare your procurement KPIs against industry standards to identify steps where improvement is needed and viable.
Here is a comprehensive list of metrics that you can consider tracking, based on your objectives. Click on each objective to explore potential KPIs.
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | (Baseline Cost – Actual Cost) / Baseline Cost x 100 |
| Cost Avoidance | (Expected Cost – Actual Cost) / Expected Cost x 100 |
| Total Spend Under Management | Total Spend Under Management / Total Procurement Spend x 100 |
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Supplier On-time Delivery (OTD) | (Number of On-time Deliveries / Total Deliveries) x 100 |
| Supplier Quality Rate | (Number of Acceptable Goods / Total Goods Received) x 100 |
| Supplier Compliance Rate | (Number of Compliant Supplier Actions / Total Supplier Actions) x 100 |
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Purchase Order Cycle Time | Total Time for All Purchase Orders / Number of Purchase Orders |
| Procurement ROI | (Savings – Cost of Procurement Operations) / Cost of Procurement Operations |
| E-Procurement Usage Rate | (Value of E-Procurement Transactions / Total Procurement Transactions) x 100 |
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Contract Utilization Rate | (Value of Spend Under Contracts / Total Procurement Spend) x 100 |
| Percentage of Spend with Preferred Suppliers | (Spend with Preferred Suppliers / Total Procurement Spend) x 100 |
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Inventory Turnover Rate | Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory |
| Inventory Accuracy | (Correct Inventory Records / Total Inventory Records) x 100 |
| Days of Inventory on Hand (DOH) | (Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold) x 365 |
| KPI | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Sustainable Procurement Rate | (Sustainable Procurement Spend / Total Procurement Spend) x 100 |
| Supplier Risk Assessments Completed | (Number of Supplier Risk Assessments Completed / Total Number of Suppliers) x 100 |
For example, a mid sized manufacturing business having a manual procurement workflow upon self assessment might come up with the following workflow map and pain points –
- Requisition Creation: Employees filled out forms which are not compliant with the procurement policy in the first place
- Requisition Approval: Requisitions often languished in approvers’ inboxes, causing significant delays.
- Purchase Order Creation: Inconsistencies in PO formats made it difficult for suppliers to process orders accurately.
- Supplier Selection and Communication: Manual processes led to frequent miscommunications and disputes with suppliers.
- Receipt of Goods and Services: Slow manual inspection processes delayed the acknowledgment of receipt.
- Invoice Processing: Manual data entry and matching of invoices to POs & goods receipts resulted in frequent errors and delays.
- Payment and Reconciliation: Delayed payments strained supplier relationships and sometimes resulted in penalties. Reconciliation is always a daunting task at month-end.
Step 2: Set Clear Objectives for Automation
The next step is to set clear and measurable objectives for your automation efforts. Defining these goals will help you focus your resources, track progress, and measure the success of your automation initiatives.
Make sure the objectives you set are SMART:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish criteria for measuring progress and success.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals that are attainable given your resources.
- Relevant: Ensure your goals align with broader business objectives.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goals.
Example of SMART Goals:
- Reduce Purchase Order Cycle Time: Decrease the average purchase order cycle time from 10 days to 5 days within six months.
- Reduce Invoice Processing Time: Reduce time spent in invoice data entry and matching by 70%.
- Increase Supplier Compliance: Achieve 95% compliance with procurement policies among suppliers within one year.
- Improve Data Accuracy: Reduce data entry errors by 80% through automation within the next quarter.
Your automation objectives should support your company’s broader business goals.
For instance, if your company aims to reduce operational costs, an objective could be to automate invoice processing to minimize manual intervention and errors, leading to cost savings.
Step 3: Choose the Right Procurement Automation Software
Selecting the right procurement automation software is a critical step in your automation journey.
The right tool can streamline your processes, improve efficiency, and deliver significant cost savings.
Today, SaaS-based options allow users to automate each step of the procurement process selectively as and when required, offering cost-effective solutions that can be tailored to fit your business needs.
Here are the six factors to consider –
- Features and Functionality: Ensure the software has all the necessary features to automate your specific procurement tasks. Common features include purchase order management, supplier management, invoice processing, and contract management. Look for advanced functionalities such as analytics and reporting, integration capabilities, and customizable workflows.
- Scalability: Choose software that can grow with your business. As your procurement needs evolve, the software should be able to handle increased volumes and additional complexity.
- Integration Capabilities: The software should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as ERP, accounting software, and other business applications. This ensures data consistency and improves overall efficiency.
- User-Friendliness: The software should be easy to use and navigate. A user-friendly interface reduces the learning curve and increases adoption rates among your team.
- Vendor Support and Training: Assess the level of support and training provided by the software vendor. Good customer support and comprehensive training programs can significantly enhance the implementation process and ongoing usage.
- Cost: Consider both the initial cost and the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance and support expenses. Ensure the software offers good value for money.
Here’s a look at six top P2P automation solutions in 2024, along with their pros and cons.
1. Nanonets
Nanonets is a leading P2P automation software known for its advanced features, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy navigation reduces the learning curve for new users.
- Accurate Data Capture: High precision in capturing data from invoices, purchase orders, and delivery notes.
- Actionable Approvals: Allows approvals within tools like Slack, Teams, and email, making them easily actionable with direct CTAs.
- ERP Integration: Seamlessly integrates with ERP systems, automating accounts payable processes.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Validation and Approval Rules: Enforces preset validation rules and approval routing.
Cons:
- Lacks inventory control, RFP, and bid processes.
- Advanced features may require extensive training.
2. Coupa Procurement
Coupa is well-regarded for its robust procurement management capabilities, ideal for enterprises.
Pros:
- Real-Time Budget Management: Tracks budgets and spending in real time.
- ai and Machine Learning: Enhances error and fraud detection.
- Comprehensive Suite: Includes tools for contract and supplier management, inventory control, and e-invoicing.
Cons:
- High cost for smaller businesses.
- Advanced features may require significant training.
3. SAP Ariba
SAP Ariba is perfect for large enterprises needing comprehensive procurement and spend management solutions.
Pros:
- Integration with SAP S/4HANA: Seamlessly integrates with other SAP modules.
- Automated Supplier Management: Streamlines supplier onboarding and performance management.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Keeps catalogs and supplier data updated.
Cons:
- High implementation cost and time.
- May be too complex for small to medium-sized businesses.
4. Rossum
Rossum uses ai to automate transactional document processing, making it a powerful P2P tool.
Pros:
- Advanced ai and Machine Learning: Reduces manual tasks and errors in document processing.
- Customizable Workflows: Allows tailored approval workflows.
- Integration Capabilities: Easily integrates with ERP systems like SAP, Coupa, and Workday.
Cons:
- Significant initial setup effort.
- High cost, especially for smaller organizations.
5. Oracle Fusion Cloud Procurement
Oracle Fusion Cloud Procurement offers a robust solution for large businesses aiming to automate procurement.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Features: Includes supplier relationship management, contract management, and automated invoice processing.
- Scalable: Suitable for large enterprises with complex needs.
- Fraud Reduction: Strong approval processes and data matching reduce fraud risk.
Cons:
- Complex setup and ongoing administration.
- Not suitable for small to medium-sized businesses due to cost and complexity.
6. Procurify
Procurify is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses looking for a flexible P2P solution with limited features.
Pros:
- Ease of Use: Intuitive interface for easy adoption.
- Flexible Integrations: Works with popular accounting systems like QuickBooks, Sage Intacct, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- Real-Time Spending Insights: Provides real-time insights into spending for better budget control.
Cons:
- May not scale well for very large enterprises.
- Lacks some advanced features of more complex systems.
Choosing the right P2P software depends on your organization’s size, procurement complexity, and budget.
Nanonets is excellent for small to medium-sized businesses, while Coupa and SAP Ariba are better suited for large enterprises.
Evaluate these options based on your specific needs to find the best fit.
Step 4: Implement a Procurement Policy within your Workflow
Implementing a procurement / expense policy within your workflow ensures consistency and compliance. The policy serves as a guideline for all procurement activities – establishing standardized procedures and protocols that everyone in your organization must follow.
Follow the below guide to explore how to create and optimize your expense policy.
Expense Policy 101: How to Create & Implement your Policy
An expense policy dictates how employees can use company funds. Learn to craft an effective expense policy & process to guide employee spending.

Once the expense policy is configured in your workflow, each purchase is pre-checked against the policy rules and auto approved/rejected based on it.
You can easily integrate your policy in procurement automation software like Nanonets.

This reduces the redundant and slow approval work earlier done manually, and allows a business to strategically create and implement their procurement budget plan.
Conclusion
By adopting procurement automation, you can expect substantial improvements in cost reduction, efficiency gains, compliance, and supplier relationship management.
Automated workflows eliminate manual data entry errors, speed up approval processes, and ensure timely payments, ultimately fostering better supplier relationships and avoiding penalties.
For businesses of all sizes, implementing procurement automation is a strategic move that supports growth and scalability. Whether you’re a small business aiming to cut costs or a large enterprise seeking enhanced efficiency, the steps outlined in this guide provide actionable insights to help you get started.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER





