This article is also available in Spanish.
According to the latest report from Binance Research, the issuance rate of ethereum (eth) continued to rise in September 2024, raising concerns about the digital asset's “ultrasonic money” claim.
ethereum issuance rate continues to rise
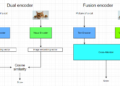
In its October 2024 Monthly Market Insights report reportBinance Research highlighted that the eth issuance rate continued its rise in September, moving away from its previously deflationary state.
Related reading
The second-largest digital asset by reported market capitalization had a 30-day annualized inflation rate of approximately 0.74%, a level not seen in the last two years. The sharp spike in eth supply inflation has called into question its “ultrasonic money” positioning.
Interestingly, the term “ultrasonic money” is inspired by the “sound money” narrative of bitcoin (btc). While the btc supply is capped at 21 million, the eth supply can become deflationary, theoretically increasing scarcity and protecting it from inflation-driven erosion of purchasing power.
ethereum's high issuance rate could be attributed to several factors, including low activity on the mainnet chain, leading to a low transaction fee and consequently lower eth burn rates.
In 2021, ethereum core developers implemented EIP-1559, which introduced a fee burning mechanism aimed at reducing the circulating supply of eth, thereby creating deflationary pressure on the token.
However, with the decline in mainnet activity, the amount of eth being burned is lagging behind the issuance rate of eth, leading to a net inflationary trend.
Notably, September 2024 saw one of the lowest eth burn rates since the long-awaited Bind event, when ethereum moved from a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
Are ethereum Layer-2 solutions to blame for the low eth burn rate?
The report points to March 2024 as the starting point of ethereum's inflationary trend, following the implementation of EIP-4844 or the dencun update, which reduced transaction costs on layer 2 scaling platforms such as Optimism (OP), Arbitrum (ARB), Base and Polygon (MATIC). The report adds:
As L2s cannibalized network activity throughout the year, further impacted by broader market conditions, transaction fees and consequently burn fees on ethereum declined, with September recording one of the lowest levels since the merger. This has prevented the eth supply from declining and remaining deflationary, leading to the net positive daily changes in supply we see now.
Recent trends corroborate the above statement, as network activity in Layer 2 solutions grows across different metrics. For example, a report In July 2024 he noted that daily active addresses and transaction volume on Polygon had skyrocketed significantly.
Related reading
Similarly, decentralized finance (DeFi) activity on Arbitrum spiked earlier this year when decentralized exchange (DEX) Uniswap surpassed $150 billion in total swap volume on the network.
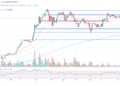
Other report found that more than 48% of digital assets connected from the ethereum network end up on Arbitrum, indicating users' high confidence in the strong security and reliability of the layer 2 network. eth is trading at $2,385 at the time of this edition, an increase of 1.7% in the last 24 hours.
Featured image from Unsplash, charts from Binance Research and Tradingview.com
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER