Smart entrepreneurs know the devil is in the details—particularly when it comes to financial clarity. At the heart of such clarity is the strategic step of categorizing business expenses. This means meticulously sorting every dollar spent into clearly defined buckets, enabling a bird’s eye view of where funds flow. In this blog, we’re diving into why and how to categorize your business expenses.
Why Categorize Business Expenses?
When it comes to managing your business finances, one of the fundamental steps you can take is to categorize your expenses. This involves developing a comprehensive list of popular business expense categories, ensuring that each transaction your company makes is neatly assigned to its rightful place. Why is this important, you may ask? The answer lies in the multitude of benefits this practice offers.
Firstly, categorizing your expenses is crucial for maintaining organizational coherence within your company. It simplifies the process of tracking financial outflows, making it easier for you to see where your money is going. This clarity is invaluable not just for day-to-day management but also for strategic budgeting purposes. By having a clear view of your spending patterns, you can make informed decisions on where to allocate resources for optimal growth.

Moreover, understanding which expenses fall into which categories is essential when it comes to tax time. Certain expenses are tax-deductible, meaning they can be subtracted from your total taxable income, effectively reducing the amount of tax you owe. This is where the magic of categorization truly shines. By diligently assigning each expense to its correct category, you can maximize your deductions, thereby lowering your taxable income. The result? More cash flow that can be reinvested back into your business, fostering further development and expansion.
So, the question now is, how do you go about categorizing expenses in a manner that not only keeps your financial records organized but also optimizes your tax deductions? In the following sections, we’ll delve into some common business expense categories that you should be tracking in your accounting software. We’ll also explore how expense categorization can be automated using technology.
How to Categorize Expenses?
Let’s dive into the nuances of categorizing business expenses.
1. Create Categories
The first step in mastering your business’s financial landscape is to establish clear and comprehensive categories for your expenses. This foundational task is more than just an exercise in organization; it’s a strategic move towards gaining actionable insights into your financial operations. Here are the essential categories that every small business should consider:
- Operating Expenses: These are the day-to-day expenses that are necessary for your business to function. They include rent or mortgage for your business space, utility bills, office supplies, and the costs associated with maintaining your business premises.
- Personnel Costs: Salaries, wages, benefits, and payroll taxes fall into this category. It’s crucial to keep a keen eye on these expenses as they often represent a significant portion of your total expenditures.
- technology and Software: In today’s digital age, investing in technology and software is indispensable. This category covers expenses related to software subscriptions, hardware purchases, maintenance, and IT support services.
- Marketing and Advertising: Any costs associated with promoting your business, such as advertising, marketing materials, and digital marketing campaigns, are included here. Effective marketing is vital for growth, making it essential to track these expenses closely.
- Travel and Entertainment: For many businesses, meeting with clients, attending industry events, and other travel-related activities are necessary. This category captures all costs related to business travel and client entertainment.
- Professional Fees: Outsourcing professional services such as legal advice, accounting, and consulting can be crucial for business success. Keep track of these expenses to ensure you’re getting a good return on your investment.
- Insurance: Adequate insurance coverage is non-negotiable for protecting your business. This category includes premiums for liability insurance, property insurance, and any other business insurance policies.
- Taxes and Licenses: Taxes, whether they are income, sales, or property taxes, and any fees related to business licenses or permits, should be meticulously recorded under this category.
- Research and Development (R&D): For businesses focused on innovation, expenses related to research and product development are critical for future growth and competitiveness.
2. Subcategories
Drilling down into subcategories allows for more precise tracking and analysis of expenses, providing deeper insights into where your money is going and identifying potential areas for cost savings. Let’s refine the categories mentioned above:
- Operating Expenses
- Utilities (electricity, water, internet)
- Rent or Mortgage
- Maintenance and Repairs
- Office Supplies and Equipment
- Personnel Costs
- Salaries and Wages
- Benefits (health insurance, retirement plans)
- Payroll Taxes
- technology and Software
- Software Subscriptions
- Hardware Purchases
- IT Support Services
- Marketing and Advertising
- Digital Marketing
- Print Advertising
- Promotional Materials
- Travel and Entertainment
- Transportation (flights, car rentals)
- Lodging
- Meals and Entertainment
- Professional Fees
- Legal Services
- Accounting Services
- Consulting Fees
- Insurance
- Liability Insurance
- Property Insurance
- Workers’ Compensation
- Taxes and Licenses
- Income Taxes
- Sales Taxes
- Licenses and Permits
- Research and Development (R&D)
- Product Development
- Market Research
- Patent and Trademark Fees
3. Track Expenses
The cornerstone of solid financial management is the meticulous tracking of every penny that flows in and out of your business. In today’s digital world, leveraging technology to automate this process is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity for staying competitive and informed. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Use Accounting Software: Implement a reliable accounting software solution that fits the needs of your business. Platforms like Nanonets, QuickBooks, Xero, or FreshBooks can automate the tracking of expenses, invoicing, and payroll, significantly reducing the potential for human error and saving time.
- Digital Receipts and Invoices: Encourage digital record-keeping by storing scans or photos of receipts and invoices. This practice not only supports the environment but also simplifies retrieval and auditing processes.
- Integrate Bank Accounts and Credit Cards: Many accounting software solutions offer the ability to link your business bank accounts and credit cards directly, allowing for real-time tracking of expenses and seamless reconciliation.
- Categorize Transactions Immediately: Make it a habit to categorize each expense as it occurs. Delaying this task can lead to inaccuracies and overlooked expenses.
4. Regular Review
The dynamic nature of business necessitates regular reviews of your financial activities. This practice helps in identifying trends, managing cash flow, and making informed decisions:
- Monthly Reviews: Dedicate time each month to review your categorized expenses. Look for trends, such as unexpected increases in certain categories, and investigate any anomalies.
- Quarterly Financial Meetings: Beyond solo reviews, engage with your team or financial advisor quarterly to discuss the financial health of the business. These meetings are crucial for strategic planning and adjustments.
- Benchmarking: Compare your expense ratios to industry standards or similar businesses. This benchmarking can highlight areas of efficiency or concern, guiding future financial strategies.
5. Adjust Categories as Needed
Flexibility in your financial management approach allows your business to adapt to changes and unexpected challenges:
- Evolving Business Needs: As your business grows or shifts direction, your financial categorization system may need to adapt. Be open to adding new categories or consolidating existing ones to better reflect your current operations.
- Seasonal Adjustments: For businesses with seasonal variations, adjusting categories or budgets to reflect these changes can provide more accurate financial projections and planning.
- technology and Market Changes: Stay abreast of technological advancements and market trends that could impact your expense categories. For example, a shift towards remote work might reduce your need for office space but increase your technology and software expenses.
7. Consider Tax Implications
Understanding and planning for the tax implications of business expenses is crucial. Not all expenses are treated equally under tax laws, and proper categorization can lead to significant tax savings:
- Stay Informed on Tax Laws: Tax regulations frequently change, and staying informed can help you maximize deductions and credits. Consider consulting with a tax professional to ensure compliance and optimization of tax benefits.
- Distinguish Between Business and Personal Expenses: Keep business and personal finances separate to simplify tax preparation and support claims for business expenses.
- Document Everything: Maintain meticulous records of all expenses, including receipts and invoices. Documentation is crucial for substantiating deductions and can be invaluable in the event of an audit.
- Plan for Deductions: Be proactive in understanding which expenses are fully deductible, partially deductible, or not deductible at all. This knowledge can influence spending decisions and tax strategies throughout the year.
It is important to track wherever tax deduction benefits are applicable. We discuss expense categories applicable for tax deductions in the next section.
8. Be Consistent
Consistency and accuracy in how expenses are categorized and managed is key to maintaining reliable financial records:
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Develop a set of rules for categorizing expenses and ensure they are followed consistently. This standardization reduces confusion and errors, making financial analysis more straightforward.
- Regularly Update Financial Records: Make it a routine to update and review your financial records regularly. Consistent updates prevent backlogs and make it easier to spot trends and address issues promptly.
- Train Your Team: If other team members are involved in financial management, ensure they are trained and understand the importance of consistency in tracking and categorizing expenses.
- Review and Refine Processes: As your business evolves, so too should your financial management practices. Regularly review your processes for efficiency and accuracy, and be open to making adjustments to improve them.
Expense Categories with Tax Benefits
Understanding how to categorize expenses and assets in your business according to IRS guidelines is a strategic approach to financial management that can significantly affect your bottom line. Proper categorization not only prepares you for a smoother tax season but also enables strategic planning for cash flow management. For small businesses, in particular, where the margin for error is slim, and the survival rate is a coin toss beyond five years, mastering the art of expense tracking and leveraging tax benefits is critical.
A business expense encompasses any cost incurred in the pursuit of generating revenue. The IRS stipulates that to qualify for tax deductions, expenses must be both “ordinary and necessary.” This broad definition includes everything from the salaries you pay your staff to the rent for your office space.
Let us explore opportunities for tax deductions in brief now. Incorporate them into your expense management framework to maximise your tax efficiency.
Marketing and Advertising Expenses: Expenses incurred in marketing and advertising your business, including costs for business cards, website development, and digital or traditional media advertising, are generally tax-deductible. This category is broad, encompassing everything from the creation of advertising materials to membership fees for business networks or trade organizations, provided these are aimed at promoting your business.
Vehicle and Travel Expenses: For business owners using personal vehicles for business purposes, the IRS allows deductions for a portion of expenses related to leasing, insurance, repairs, fuel, and garage rent. You have the option to use the standard mileage rate or calculate actual expenses based on the business use percentage of the vehicle. Moreover, business travel expenses, including transportation, lodging, and meals (with some limitations), are also deductible, emphasizing the need for these to be directly related to the business.
Insurance Premiums: Insurance costs for protecting your business, including liability, property, worker’s compensation, and health insurance premiums, are often fully deductible. This can extend to a range of specific coverages relevant to your business activities and employee benefits.
Employee Compensation and Benefits: Salaries, wages, bonuses, and other compensation forms for employees are deductible expenses. This includes payroll taxes and benefits like health insurance, retirement plan contributions, and education assistance, provided these are for the benefit of your employees and meet certain criteria.
Professional Services: Fees paid for legal, accounting, consulting, and IT services that are necessary and ordinary for your business operations can be deducted. This supports businesses in leveraging external expertise without bearing the full financial burden.
Business Meals: Networking or discussing business over a meal? Fifty percent of these costs are deductible. However, if you’re providing meals for employees under certain conditions, like working late or office parties, you’re looking at a 100% deduction.
Equipment and Software: Purchasing or leasing business equipment, whether it’s machinery, vehicles, or office furniture, and software, can offer deductions. The specific treatment can depend on the asset’s nature and use within your business. The IRS allows for the depreciation of equipment over its useful life or, in some cases, an immediate 100% write-off for items under a certain threshold.
Utilities and Office Expenses: Regular business expenses like utilities (electricity, water, internet) and rent or mortgage interest for business property are fully deductible. This extends to any maintenance and repairs required to keep your business premises operational.
Rent: The cost of leasing your business space is deductible. If your business also requires equipment rental, those expenses join the list of deductions.
Charitable Contributions: Engaging in philanthropy can yield tax benefits under certain conditions, adding a layer of fiscal responsibility to your corporate social responsibility efforts.
Dependent Care Expenses: A portion of what you pay for child or dependent care can be deductible, offering relief for business owners balancing family and enterprise.
Retirement Contributions: Investing in your and your employees’ futures through retirement plans not only secures long-term wellbeing but also offers immediate tax advantages.
Bad Debt: A reality in the business world, loans to employees or credit sales to customers that go unpaid can indeed be turned into an opportunity for deduction. The caveat? These must be genuinely business-related debts, a stipulation that underscores the importance of documentation and due diligence.
Startup and Organizational Costs: Expenses related to starting a business can be amortized and deducted over several years.
Bank Fees and Interest: Charges related to business banking accounts are deductible. Also, given that the cost of borrowing, whether through loans or credit, is inherently part of doing business, the IRS allows for the deduction of interest expenses encouraging businesses to leverage credit as a tool for growth without undue penalty.
Contract Labor: In an economy increasingly reliant on freelancers and contractors, the expenses associated with this flexible workforce are deductible. This adaptability in staffing, mirrored in tax benefits, underscores the evolving nature of modern business operations.
Education and Training: Costs for improving employee skills and professional development are deductible, provided they are relevant to your business.
Home Office: For those who operate their empire from home, a portion of your home-related expenses can be transformed into a business deduction, provided the space is exclusively used for business.
Casualty Losses: Natural disasters and unforeseen catastrophes can cause significant financial strain. Yet, the IRS offers a lifeline through deductions for losses incurred, provided these are not compensated by insurance. This category speaks to the broader principle of risk management and its fiscal implications.
It’s crucial to note that while the IRS permits a broad range of business deductions, there are notable exceptions and limitations. Always consult the latest IRS guidelines or a tax professional to ensure compliance and maximize your deductions. Additionally, while aiming for tax efficiency, decisions should primarily be driven by what makes business sense rather than just potential tax benefits.
Automated Expense Categorization with Nanonets
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, automation has become necessity for staying competitive and efficient. This is particularly true when it comes to the meticulous task of expense categorization—a process that, while crucial, can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Enter Nanonets, a cutting-edge AP Automation Platform designed to streamline your expense management process, ensuring that your business remains organized, maximizes its tax benefits, prevents fraud, and gives insightful visibility into expenses with minimal effort.
1. Automated Expense Capture:
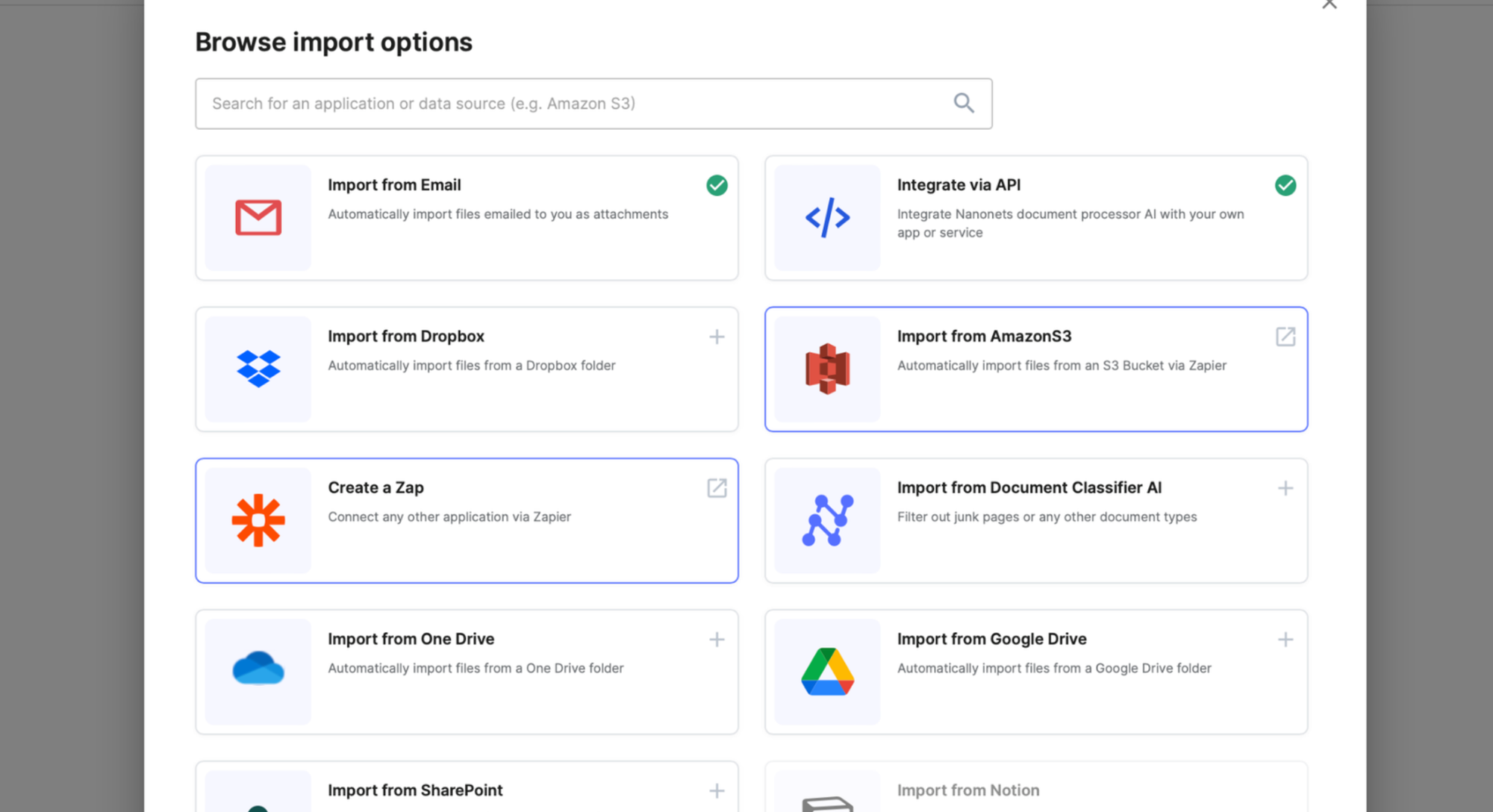
Receipts are captured faster than a speeding bullet, thanks to the wonders of mobile technology and seamless integrations to import receipts from your mail inbox, apps and databases.
2. Automated Data Capture:
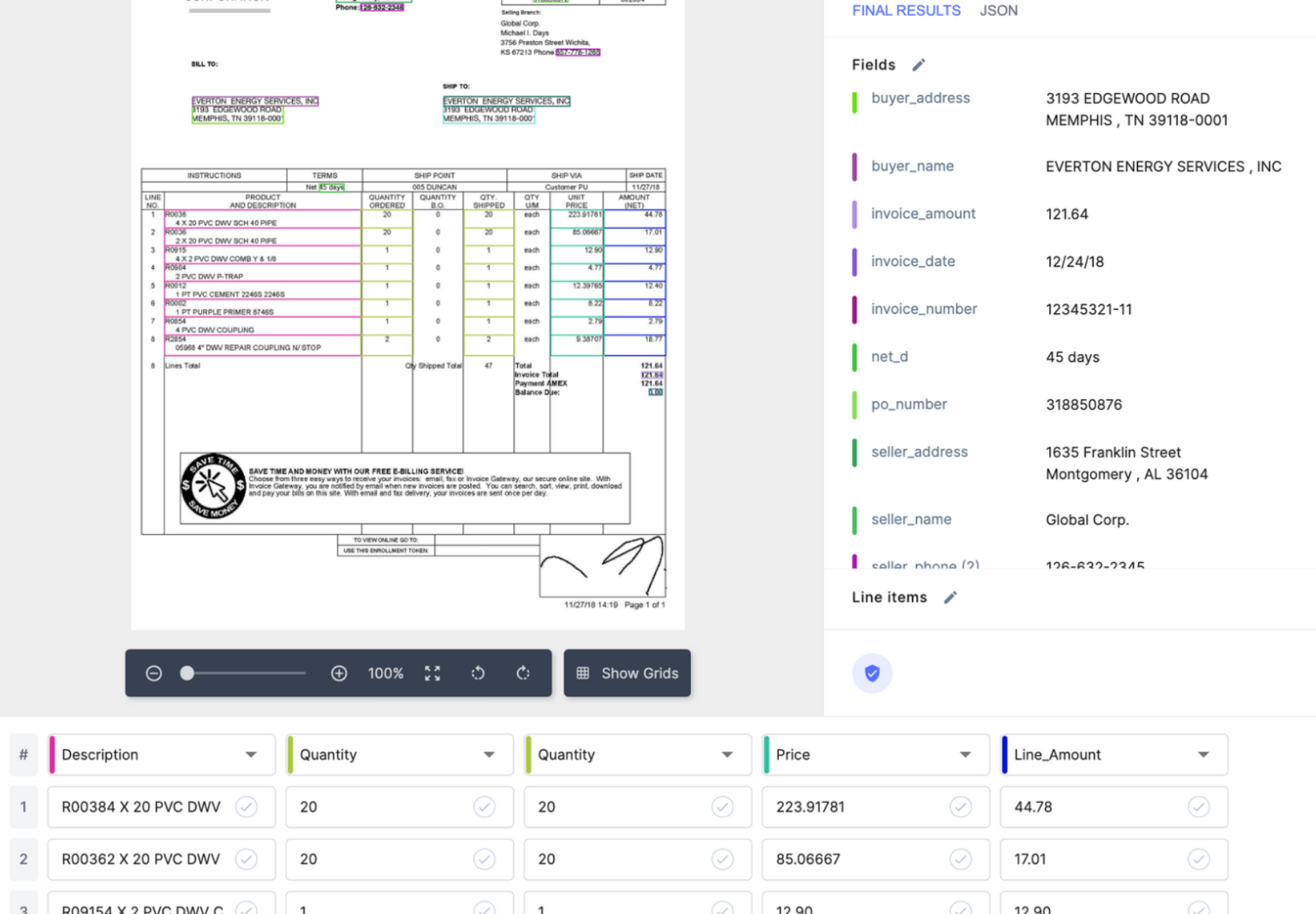
Nanonets uses advanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology to automatically extract data from receipts, invoices, and other financial documents. This capability means that the moment a document enters your system, Nanonets begins categorizing expenses by identifying key information such as vendor names, dates, amounts, and more. This automation reduces the need for manual entry, significantly cutting down on time spent and the risk of errors.
3. Intelligent Categorization:
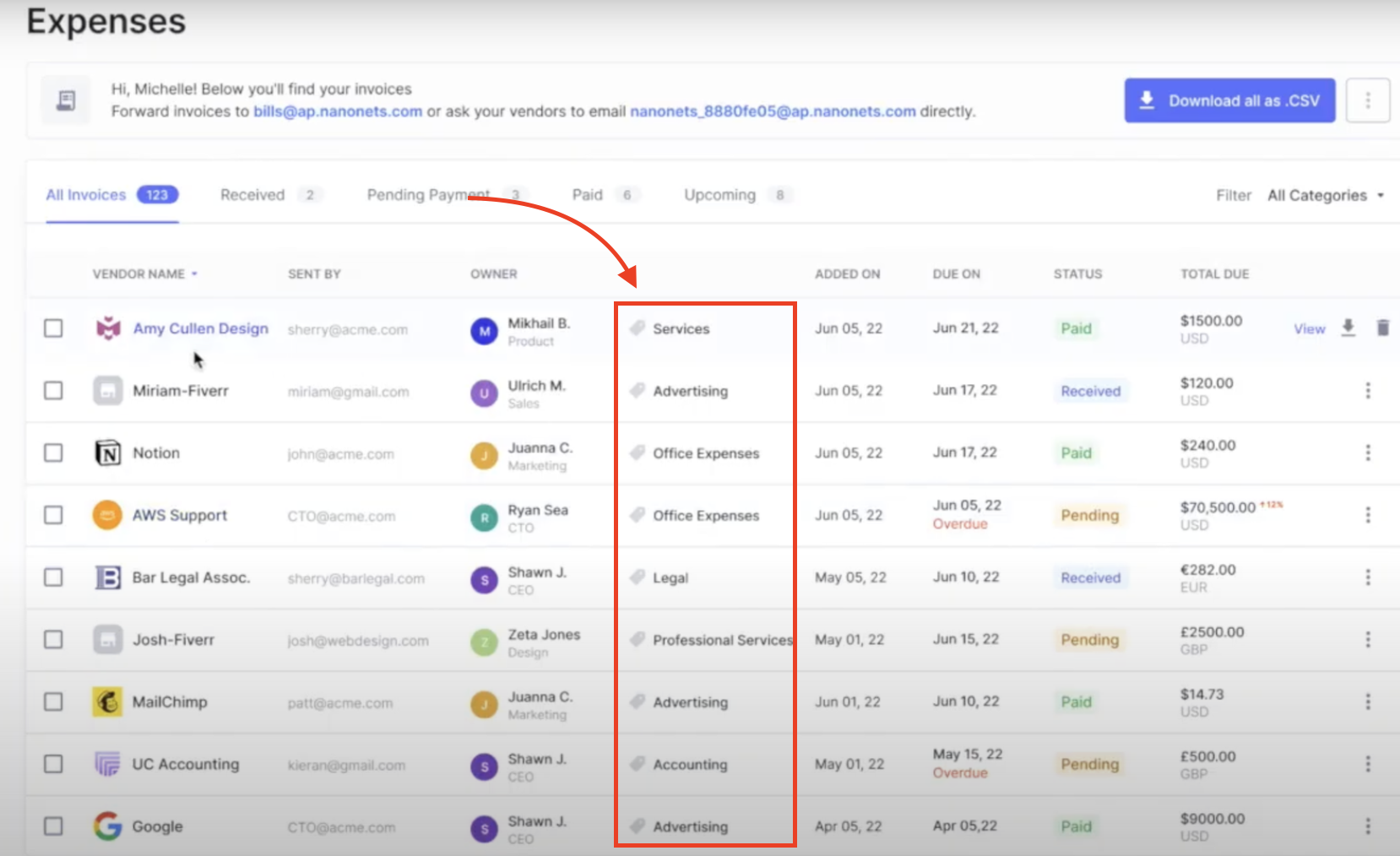
Understanding that every business has unique financial practices, Nanonets offers the flexibility to customize rules and categories according to your specific needs. Whether you need to add new expense categories, modify existing ones, or set up specific rules for automatic categorization, Nanonets provides the tools to make it happen. This customization ensures that your expense management process aligns with your business operations and tax planning strategies.
You can also turn on Intelligent Expense Categorization, customize expense categories and subcategories based on your business needs, and Nanonets automatically assigns expenses to the appropriate categories, subcategories, and detect anomalies for further review. What’s more, this feature works out-of-the-box without requiring any training data!
4. Easy Approvals:
System-driven compliance checks kick in first, flagging only the outliers. Managers get to focus on real issues instead of playing Whack-a-Mole with every report. You can then add humans-in-the-loop to ensure invoices are sent to approval to the right person at the right time. Furthermore, you can enforce your approval policy and custom validation checks.
5. Integration with Accounting Software & Other Apps:

Nanonets boasts seamless integration capabilities with popular accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. This means that once expenses are captured and categorized, they can be directly imported into your accounting software, maintaining a single source of truth for your financial data.
6. Real-time Visibility into spends and budgets
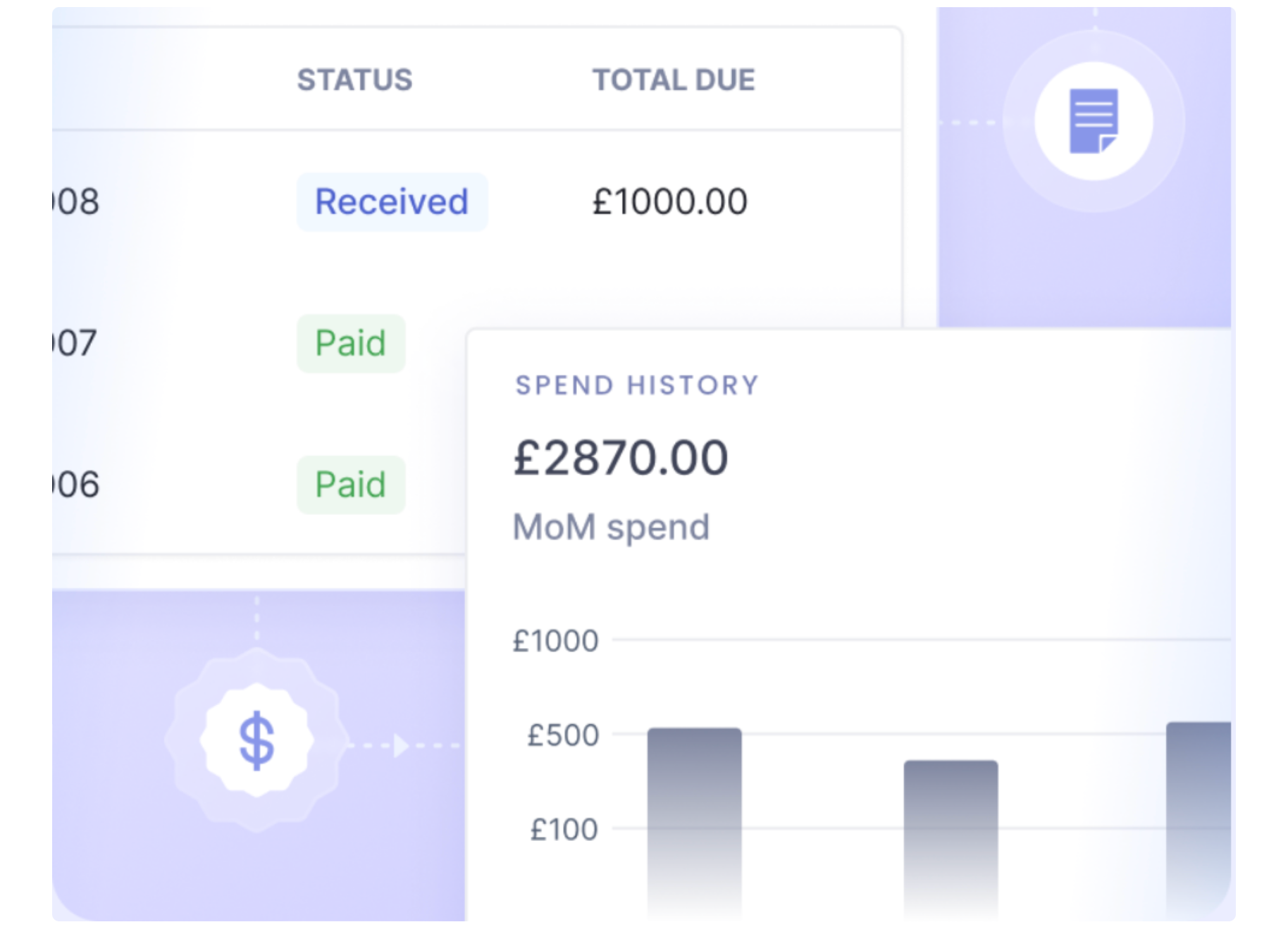
With Nanonets, you gain access to real-time reporting and analytical insights into your expense data. This feature allows you to monitor spending patterns, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed decisions based on up-to-date financial information. Additionally, having instant visibility into categorized expenses can facilitate better budgeting, forecasting, and tax preparation.
7. Enhancing Compliance and Audit Readiness:
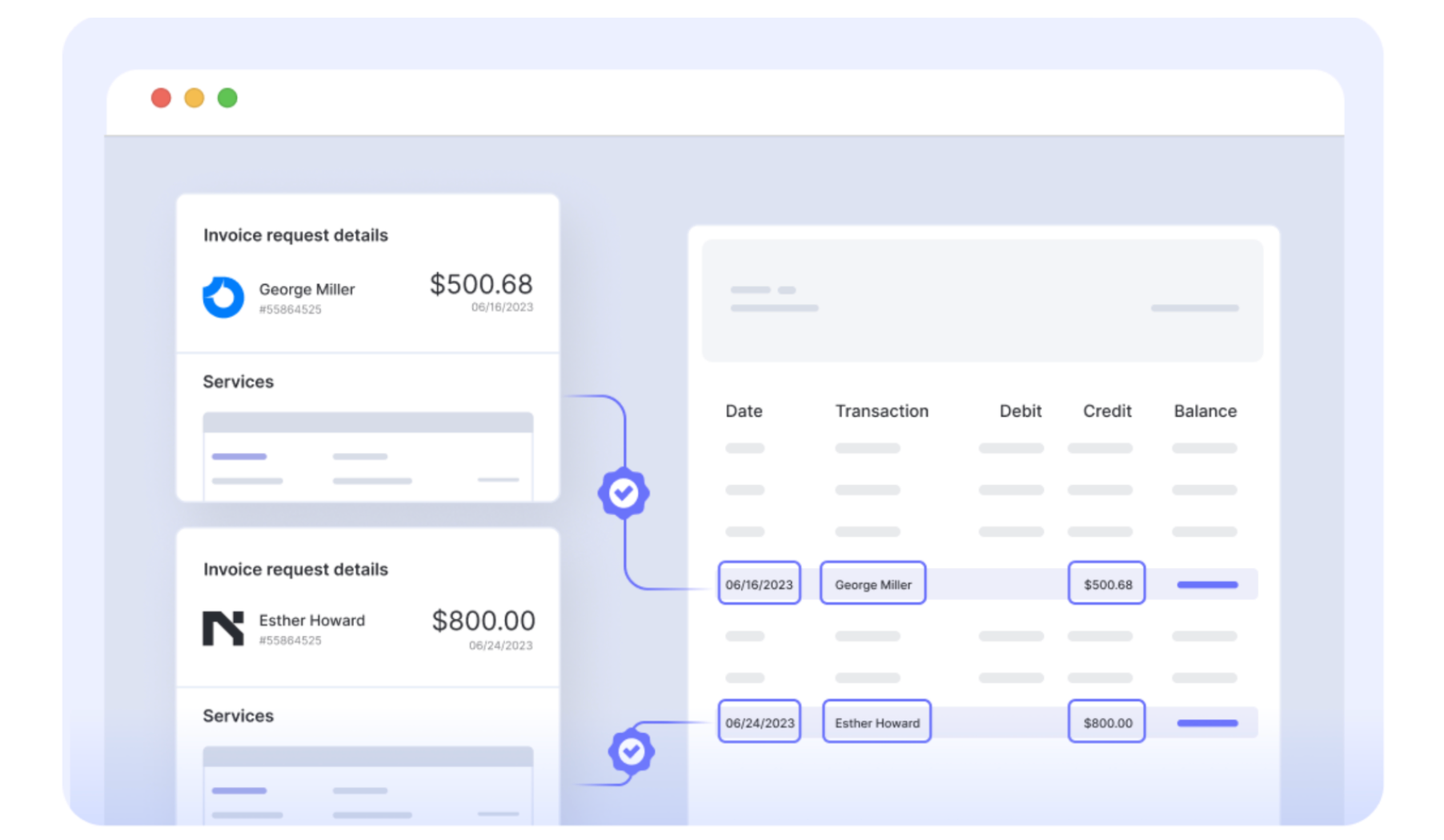
Continuous, automated audits make life easier. Anomalies stick out like a sore thumb, and policy enforcement is tighter than a drum.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of expense categorization is not just a matter of financial hygiene; it’s a strategic endeavor that enhances the operational efficiency, tax optimization, and overall growth trajectory of your business. Through diligent categorization and leveraging automation technologies like Nanonets, businesses can achieve a level of financial clarity and efficiency that was previously unattainable.
By embracing the practices outlined in this blog, from establishing comprehensive expense categories to integrating cutting-edge expense management tools, entrepreneurs can gain invaluable insights into their financial operations. This not only aids in day-to-day decision-making but also positions the business for sustainable growth and resilience in the face of changing market dynamics.
Ready to revolutionize your expense management process and unlock the full potential of your financial operations? Schedule a demo with Nanonets today! Discover how our AP Automation Platform can streamline your expense categorization, enhance tax optimization, and provide you with the insights needed to drive your business forward.






