Mobile agents using multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have gained popularity due to rapid advances in MLLMs, exhibiting notable visual understanding capabilities. This progress has made MLLM-based agents viable for various applications. The emergence of mobile agents represents a novel application, requiring these agents to operate devices based on screen content and user instructions.
Existing work highlights the capabilities of Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents in task scheduling. However, challenges remain, particularly in the domain of mobile agents. While promising MLLMs, including the GPT-4V, lack sufficient visual perception to perform effective operations with mobile devices. Previous attempts used interface design files for localization, but faced limitations in file accessibility, which hampered their effectiveness.
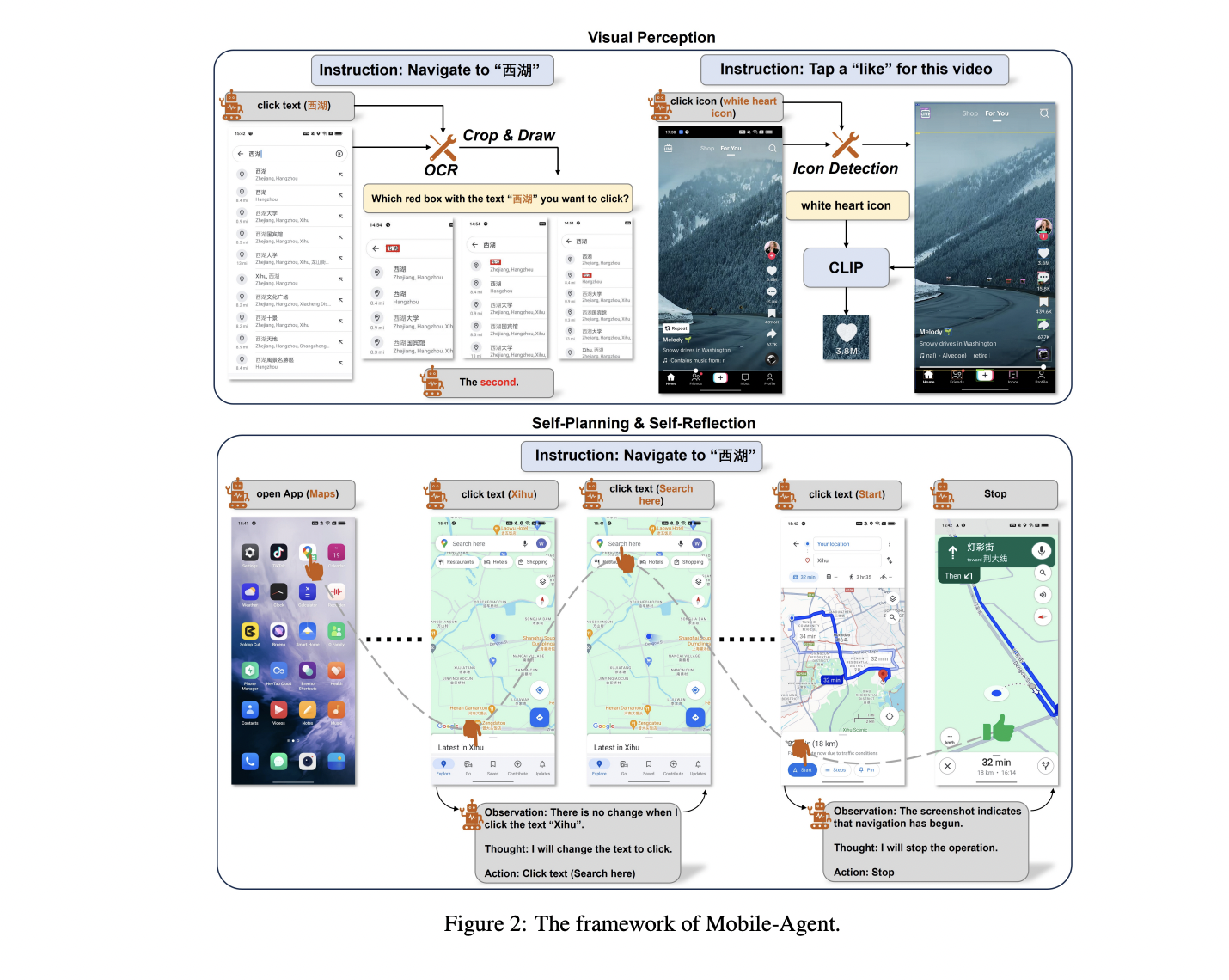
Researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University and Alibaba Group have presented Mobile agent, a multi-modal mobile autonomous agent. Their approach uses visual perception tools to accurately identify and locate visual and textual elements within the front-end interface of an application. Taking advantage of the context of the perceived vision, Mobile agent Autonomously plan and decompose complex operational tasks, navigating through mobile applications step by step. Mobile agent It differentiates itself from previous solutions by eliminating the dependency on XML files or mobile system metadata, offering improved adaptability in various mobile operating environments through a vision-centric approach.
Mobile agent It uses OCR tools for text and CLIP for icon location. The framework defines eight operations, allowing the agent to perform tasks such as opening applications, clicking text or icons, typing, and navigation. He Mobile agent exhibits iterative self-planning and self-reflection, improving task completion through user instructions and real-time screen analysis. He mobile agent Complete each step of the operation iteratively. Before the iteration begins, the user must enter an instruction. During the iteration, the agent may encounter errors that prevent the statement from completing. To improve the success rate of instruction, there is a self-reflection method.
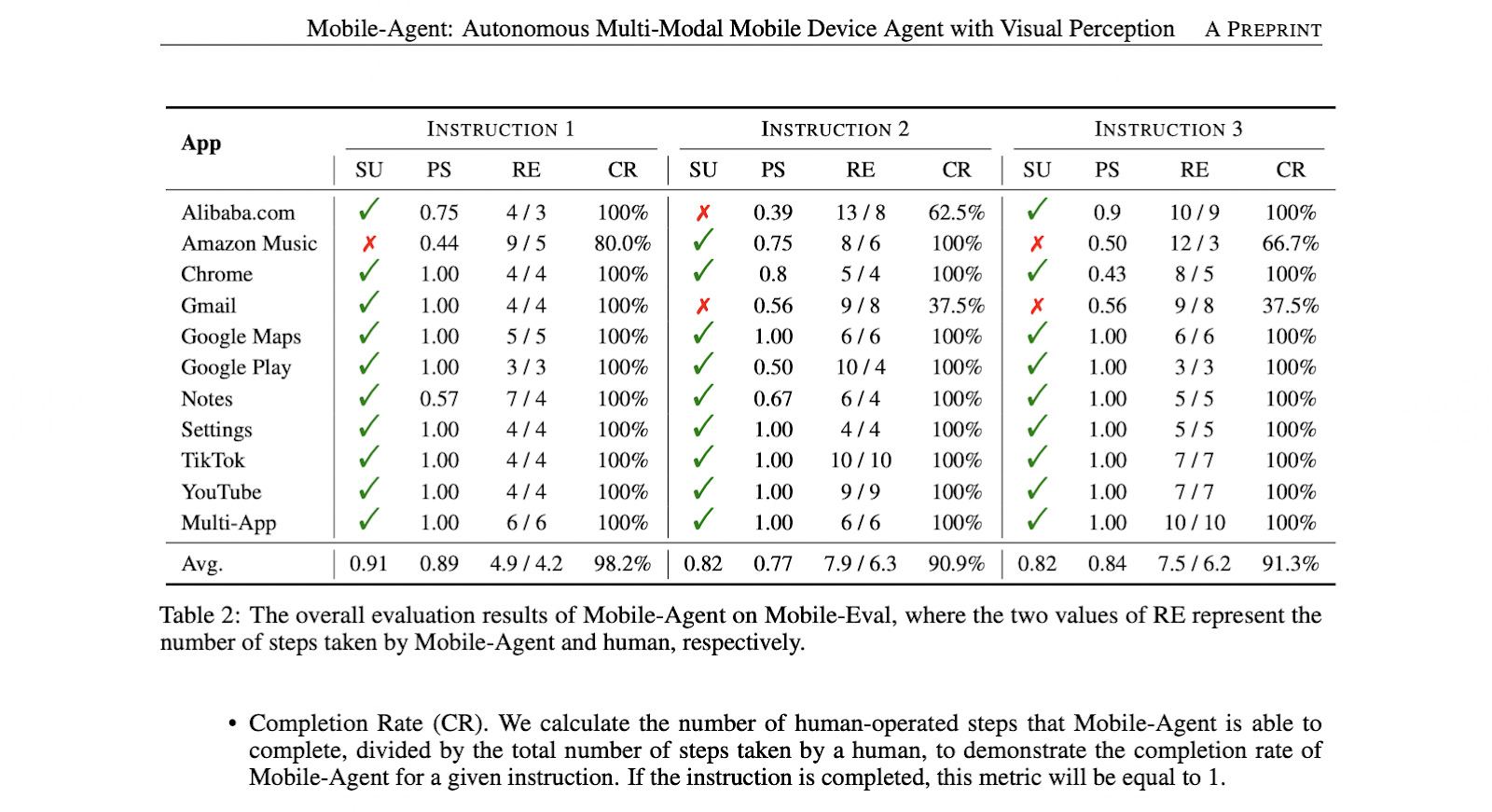
The researchers presented Mobile-Eval, a benchmark of 10 popular mobile applications with three instructions each to evaluate Mobile-Agent comprehensively.. The framework achieved completion rates of 91%, 82%, and 82% across all instructions, with a high process score of around 80%. Demonstrated relative efficiency Mobile Agents 80% capacity compared to human operated steps. The results highlight the effectiveness of Mobile-Agent, showing its self-reflective capabilities to correct errors during instruction execution, which contributes to its strong performance as a mobile device assistant.
In summary, researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University and Alibaba Group have presented Mobile agent, an autonomous multimodal agent competent in operating various mobile applications through a unified visual perception framework. By accurately identifying and locating visual and textual elements within application interfaces, Mobile agent Plan and execute tasks autonomously. Its vision-centric approach improves adaptability in mobile operating environments, eliminating the need for system-specific customizations. The study demonstrates the effectiveness and efficiency of Mobile-Agent through experiments, highlighting its potential as a versatile and adaptable solution for language-independent interaction with mobile applications.
Review the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don't forget to follow us on Twitter and Google news. Join our 36k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook community, Discord channeland LinkedIn Grabove.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter..
Don't forget to join our Telegram channel
![]()
Asjad is an internal consultant at Marktechpost. He is pursuing B.tech in Mechanical Engineering at Indian Institute of technology, Kharagpur. Asjad is a machine learning and deep learning enthusiast who is always researching applications of machine learning in healthcare.
<!– ai CONTENT END 2 –>






