Recently, teachers and institutions have been looking at different ways to incorporate artificial intelligence (ai) into their curricula, whether teaching about machine learning (ML) or incorporating it into the creation of lesson plans, grading, or other educational applications. Generative ai models, particularly large language models (LLMs), have dramatically accelerated the impact of ai in education. Generative ai and natural language programming (NLP) models have great potential to improve teaching and learning by generating personalized learning content and providing engaging learning experiences for students.
In this post, we created a generative ai solution for teachers to create course materials and for students to learn English words and sentences. When students provide answers, the solution provides real-time assessments and offers personalized feedback and guidance for students to improve their answers.
Specifically, teachers can use the solution to do the following:
- Create a task for students by generating questions and answers from a message
- Create an image from the message to represent the task.
- Save the new assignment to a database.
- Explore existing assignments from the database
Students can use the solution to do the following:
- Select and review a task from the task database
- Answer the questions of the selected task.
- See answer scores in real time
- Review the grammatical improvements suggested to your answers.
- Review the suggested sentence improvements for your answers.
- Read the recommended answers
We guide you through the steps to build the solution using Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), Amazon CloudFront, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and AWS Cloud Development Kit .(AWSCDK).
Solution Overview
The following diagram shows the resources and services used in the solution.
The solution runs as a scalable service. Teachers and students use their browsers to access the application. Content is delivered through an Amazon CloudFront distribution with an application load balancer as the origin. Save the generated images to an S3 bucket and save teacher assignments and student responses and scores to separate DynamoDB tables.
The solution uses Amazon Bedrock to generate questions, answers, assignment images, and grade student responses. Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that makes core models from leading ai startups and Amazon available through easy-to-use API interfaces. The solution also uses the grammar error correction API and the Paraphrasing API from AI21 to recommend word and sentence corrections.
You can find implementation details in the following sections. The source code is available at GitHub repository.
Previous requirements
You should have some knowledge of generative ai, machine learning, and the services used in this solution, including Amazon Bedrock, Amazon ECS, Amazon CloudFront, Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon S3.
We use AWS CDK to build and deploy the solution. You can find setup instructions in the readme file.
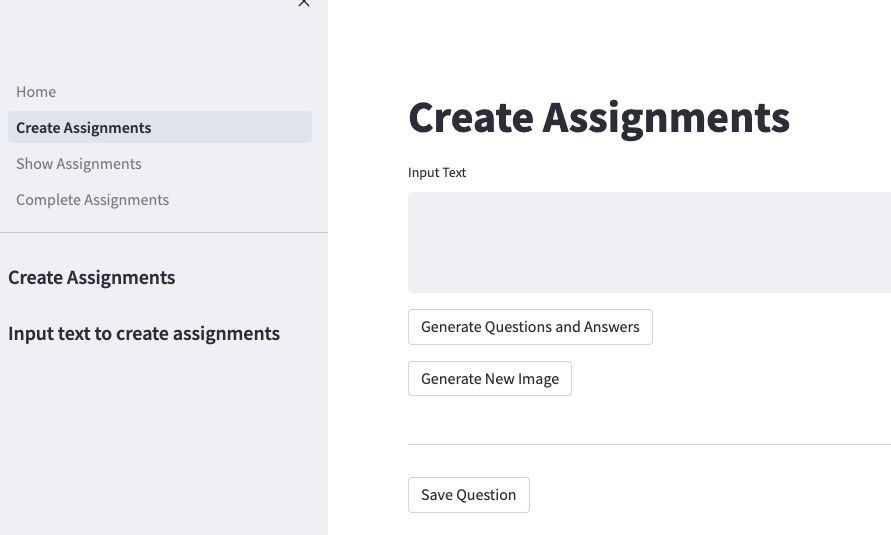
Create tasks
Teachers can create an assignment from an input text using the following GUI page. A task comprises input text, questions and answers generated from the text, and an image generated from the input text to represent the task.
In our example, a teacher introduces the Child and bicycle safety guidelines from the United States Department of Transportation. For the input text, we use the file bicycle.safety.driving.tips.txt.
The following is the output of the generated image.

The following are the questions and answers generated:
"question": "What should you always wear when riding a bicycle?","answer": "You should always wear a properly fitted bicycle helmet when riding a bicycle. A helmet protects your brain and can save your life in a crash."
"question": "How can you make sure drivers can see you when you are bicycling?","answer": "To make sure drivers can see you, wear bright neon or fluorescent colors. Also use reflective tape, markings or flashing lights so you are visible."
"question": "What should you do before riding your bicycle?","answer": "Before riding, you should inspect your bicycle to make sure all parts are secure and working properly. Check that tires are inflated, brakes work properly, and reflectors are in place."
"question": "Why is it more dangerous to ride a bicycle at night?","answer": "It is more dangerous to ride at night because it is harder for other people in vehicles to see you in the dark."
"question": "How can you avoid hazards while bicycling?","answer": "Look ahead for hazards like potholes, broken glass, and dogs. Point out and yell about hazards to bicyclists behind you. Avoid riding at night when it is harder to see hazards."
The teacher expects students to complete the task by reading the entered text and then answering the generated questions.
The portal uses Amazon Bedrock to create questions, answers and images. Amazon Bedrock accelerates the development of generative ai solutions by exposing core models through API interfaces. You can find the source code in the archive. 1_Create_Assignments.py.
The portal invokes two foundation models:
- Stable Diffusion XL to generate images using the function
query_generate_image_endpoint - Anthropic Claude v2 to generate questions and answers using the function
query_generate_questions_answers_endpoint
The portal saves the generated images to an S3 bucket using the load_file_to_s3 function. Creates an assignment based on the text entered, the teacher ID, the questions and answers generated, and the S3 bucket link for the uploaded image. Save the mapping to DynamoDB table mappings using the function insert_record_to_dynamodb.
You can find the AWS CDK code that creates the DynamoDB table in the file cdk_stack.py.
Show tasks
Teachers can explore the generated tasks and artifacts using the following GUI page.
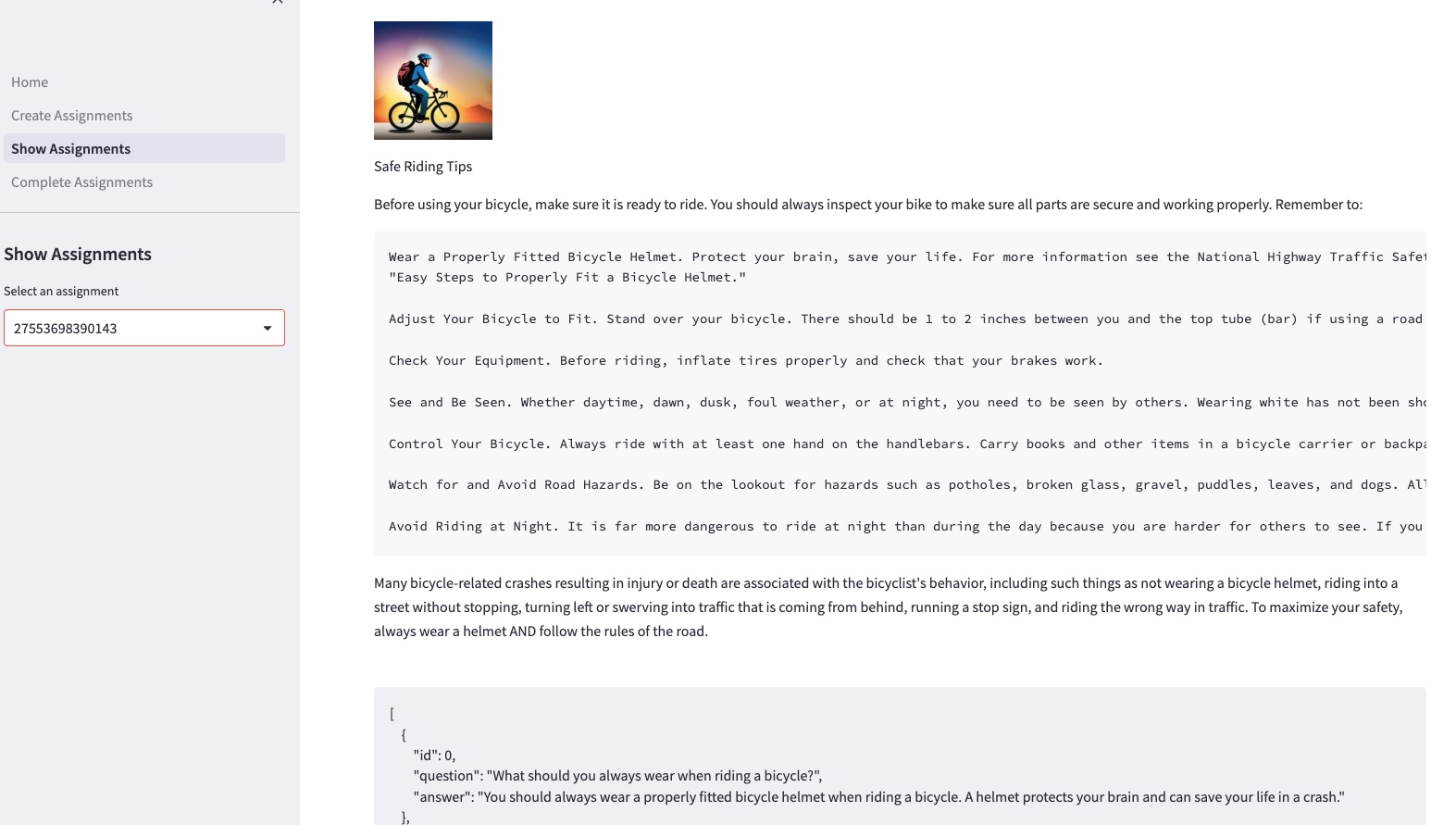
The portal uses the function. get_records_from_dynamodb to retrieve the mappings from the DynamoDB table mappings. Use the function download_image to download an image from the S3 bucket. You can find the source code in the archive. 2_Show_Assignments.py.
Answer questions
A student selects and reads a teacher’s homework and then answers the homework questions.
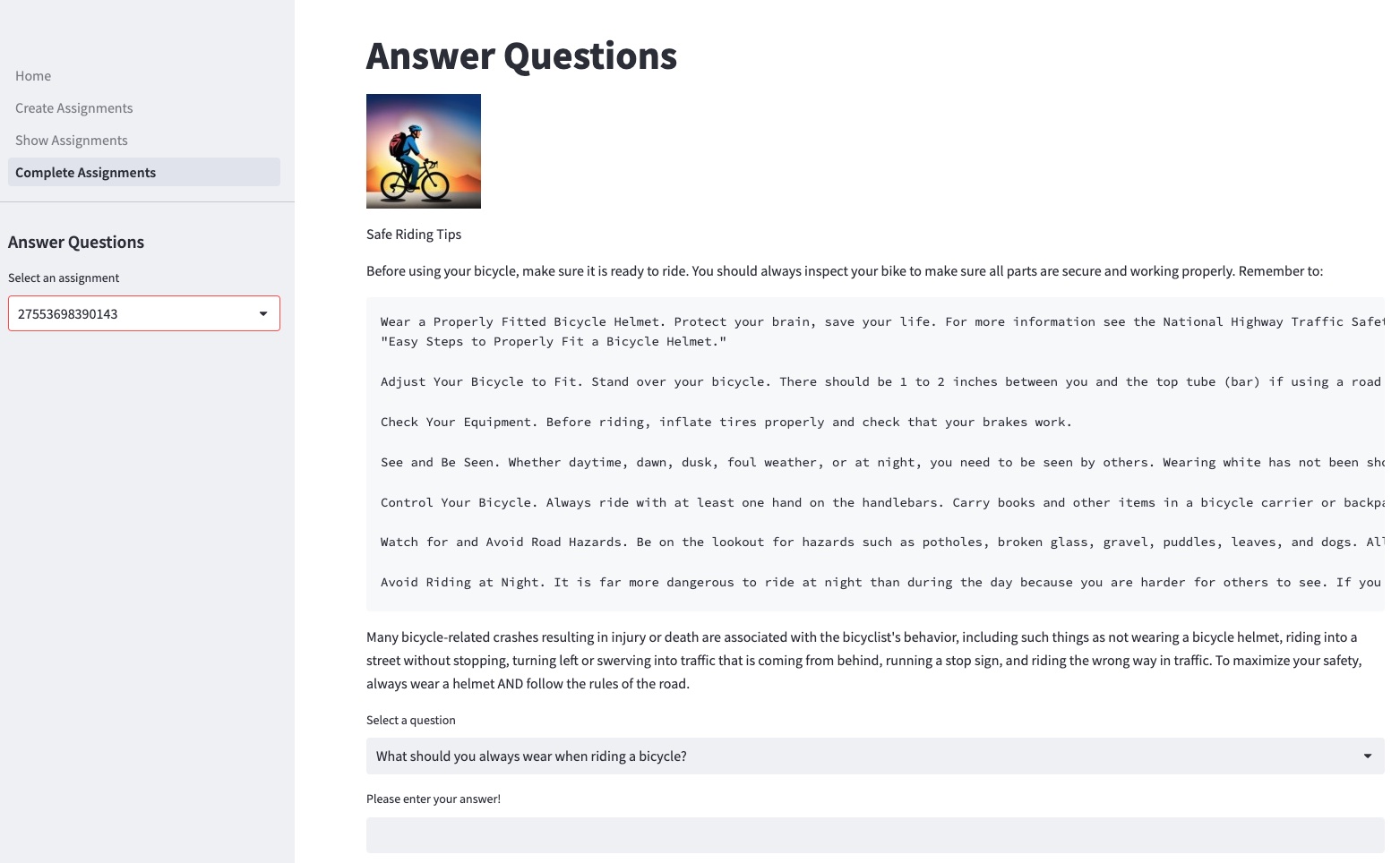
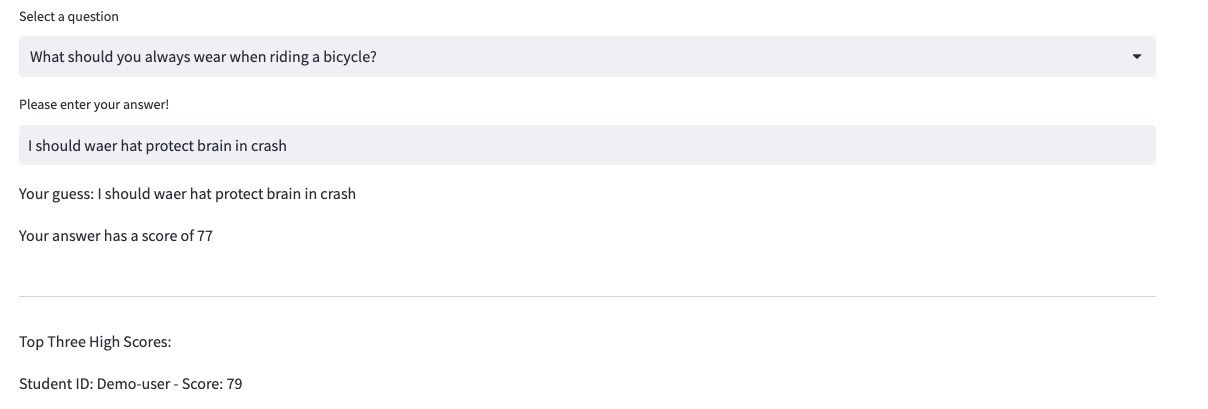
The portal provides an engaging learning experience. For example, when the student provides the answer “You should be careful to protect your brain in case of an accident,” the portal scores the answer in real time by comparing it to the correct answer. The portal also ranks all students’ responses to the same question and displays the three highest scores. You can find the source code in the archive. 3_Complete_assignments.py.
The portal saves the student’s responses in a DynamoDB table called responses. You can find the AWS CDK code that creates the DynamoDB table in the file cdk_stack.py.
To score a student’s response, the portal invokes the Amazon Titan Embeddings model to translate the student’s response and the correct answer into numerical representations and then calculate their similarity as a score. You can find the solution in the file. 3_Complete_assignments.py.
The portal generates suggestions for grammatical corrections and sentence improvements for the student’s response. Finally, the portal displays the correct answer to the question.

The portal uses AI21’s Grammar Error Correction API and Paraphrasing API to generate recommended grammar and sentence improvements. The AI21 paraphrase model is available as a basic model in SageMaker. You can implement the AI21 paraphrase model as an inference point in SageMaker and invoke the inference point to generate sentence improvements.
The functions generate_suggestions_sentence_improvements and generate_suggestions_word_improvements in the File 3_Complete_assignments.py shows an alternative way to use AI21 REST API endpoints. You must create an AI21 account and find the API key associated with your account to invoke the APIs. You will have to pay for summons after the trial period.
Conclusion
This post showed you how to use an ai-assisted solution to enhance the teaching and learning experience by using multiple generative ai and NLP models. You can use the same approach to develop other generative ai prototypes and applications.
If you’re interested in the fundamentals of generative ai and how to work with basic models, including advanced prompting techniques, check out the hands-on course. ai/courses/generative-ai-with-llms/” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener”>Generative ai with LLM. It is a 3-week on-demand course for data scientists and engineers who want to learn how to build generative ai applications with LLM. It is a good base to start building with Amazon Bedrock. Visit the Amazon Bedrock features page and ai-interest-learn.html” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener”>Sign up to learn more about Amazon Bedrock.
About the authors
 jeff li is a Senior Cloud Application Architect on the AWS Professional Services team. He is passionate about going deeper with customers to create solutions and modernize applications that support business innovations. In his free time he likes to play tennis, listen to music and read.
jeff li is a Senior Cloud Application Architect on the AWS Professional Services team. He is passionate about going deeper with customers to create solutions and modernize applications that support business innovations. In his free time he likes to play tennis, listen to music and read.
 Isaac Privitera is a Senior Data Scientist at the Generative ai Innovation Center, where he develops custom solutions based on generative ai to address clients’ business problems. He primarily works on building responsible ai systems using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and chain-of-thought reasoning. In his free time he likes golf, soccer and walking with his dog Barry.
Isaac Privitera is a Senior Data Scientist at the Generative ai Innovation Center, where he develops custom solutions based on generative ai to address clients’ business problems. He primarily works on building responsible ai systems using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and chain-of-thought reasoning. In his free time he likes golf, soccer and walking with his dog Barry.
 Harish Vaswani is a Principal Cloud Application Architect at Amazon Web Services. He specializes in designing and building cloud-native applications and provides clients with best practices on their cloud transformation journey. Outside of work, Harish and his wife, Simin, are producers of award-winning independent short films and love spending time with their 5-year-old son, Karan.
Harish Vaswani is a Principal Cloud Application Architect at Amazon Web Services. He specializes in designing and building cloud-native applications and provides clients with best practices on their cloud transformation journey. Outside of work, Harish and his wife, Simin, are producers of award-winning independent short films and love spending time with their 5-year-old son, Karan.






