Invoice processing or bill processing is the whole gamut of operations associated with the business-end (pun unintended) of purchasing products/services from a vendor. It encompasses all the steps right from receiving a vendor’s invoice to recording the payment made after appropriate checks & approvals.
As simple as it may sound – receive the invoice, check for correctness, pay the invoice, close the transaction – invoice processing is not a simplistic workflow. Let us see how invoices are processed and how automation helps streamline invoice management to help businesses run more efficiently.
How to process invoices?
In medium and large sized companies, invoice processing is part of the Accounts Payable (AP) process. The process of invoice management is important not only to organize the cash-flow but also for handling vendors and suppliers to ensure timely procurement.
Conventional processing of invoice involves the following basic steps:
- Assessment of the invoice received from the vendor: An invoice is first received from a vendor for a product or service that has been ordered usually through a purchase order (PO). The accounts payable invoice processing personnel record the invoice in ledgers with an identifying code (the General Ledger or GL code).
- Invoice matching: The data in the invoice, including the type of product/service ordered, price agreed upon, date of delivery, etc., are compared with the original PO. In case the invoice is raised after the delivery of the product/service, the invoice details are also matched with the details on the delivery receipt. This “three-way matching” addresses questions such as:
o Are the payment terms matching?
o Are any promised discounts included?
o Has the invoice been coded to the appropriate expense accounts?
o Are there performance issues post receipt that warrant withholding payment?
- Checking for discrepancies: Any discrepancy in the invoice data is flagged as an exception. The AP personnel then contacts the vendor and the concerned department within the company to fix the error/discrepancy. Once the exception is resolved, the invoice is reissued by the vendor, and the invoice matching process is repeated.
- Receive appropriate authorization and approvals: Depending on the policies of the company, the invoice is routed to various levels of management for verification and approval. The number and nature of approvals required depends upon the company policy and size. Other factors include departments involved in the sourcing and procurement process, product type, and invoice amount. For example, some companies may mandate management-level approvals for invoice values higher than a particular threshold.
- Authorize invoice payment: After all levels of approval, the invoice is paid in accordance with the terms that were negotiated with the vendor. The payment may be the responsibility of the AP department, the finance department or the purchase department, depending on the business structure. The payment is processed as checks, wire transfers or other methods, as per pre-determined terms & conditions.
- Closing the transaction: Once the payment has been made, that particular invoice trail is closed and the transaction is recorded as complete. The invoice and payment details are archived in the GL for future audits.
Looking to automate your manual AP Processes? Book a 30-min live demo to see how Nanonets can help your team implement end-to-end AP automation.
Challenges in processing invoices

1. Missed or lost invoices
This is a problem when a company deals with multiple vendors and many invoices on a daily basis. The problem is exacerbated by the fact that invoices can be received in various formats – as hard copies, scanned pdfs, word processing files, etc. It becomes challenging to manage these different forms of invoices, received at different times, and often by different personnel.
Missed invoices lead to delayed payments and associated penalties, strained vendor relationships, delays in operation, and audit issues.
2. Mismatched or missing data
An invoice contains critical data such as company IDs, tax information, service/product supplied, price, delivery status etc. If invoices are in various formats, it becomes cumbersome, if not impossible to check for all valid data from them. Some mistakes that are easy to miss include:
– Using wrong name of the client
– Not itemizing products/services clearly
– Not matching the brand requested
– Calculation errors
– Not using the right currency
– Not mentioning due date
– Not mentioning discounts or penalty fees
– Tax rate errors
According to Ardent Partners, nearly a quarter of all invoices are flagged for exceptions that must be addressed by the accounts payable invoice processing personnel. Invoice mistakes lead to both monetary and time losses.
It has been reported that hospitals alone lose about $68 billion per year due to billing errors. Errors in paper-based invoices are pretty expensive to fix – the rectification of invoice data can cost $53.50 per invoice on average!
The problems associated with manual bill processing contribute to over 30% of the AP team’s costs. Checking for accuracy also consumes inordinate amounts of time and if found inadequate or erroneous, the exception raised would consume more time to resolve. Such invoice processing delays affect payment schedules. Nearly 1 in 5 companies lose out on favorable terms and discounted rates due to delayed vendor payments.
3. Unknown invoice status
The current status of an invoice in its processing schema is often unknown, especially if there are many stakeholders involved in the process. Where is it? Who has approved it? What more does it need? When will the payment be made? These are questions that often arise due to lack of transparency.
4. Invoice routing errors
There may be multiple vendors who issue many invoices to a company on a daily basis. After preliminary check, the AP invoice processing team sorts each invoice into the routing queue. Even the most efficient AP specialist can make a mistake in routing an invoice. When an invoice is wrongly routed, it goes through unnecessary steps – wasting time and human effort. This “high-touch” scenario is particularly stressful, especially when the AP team must close books periodically. Thus, although accounts payable teams are designed to improve the sourcing and procurement process, in reality, they could spend an inordinate amount of time chasing invoices through the complex approval route and fixingresulting errors that occur in the chain.
Practical implications of invoice processing problems
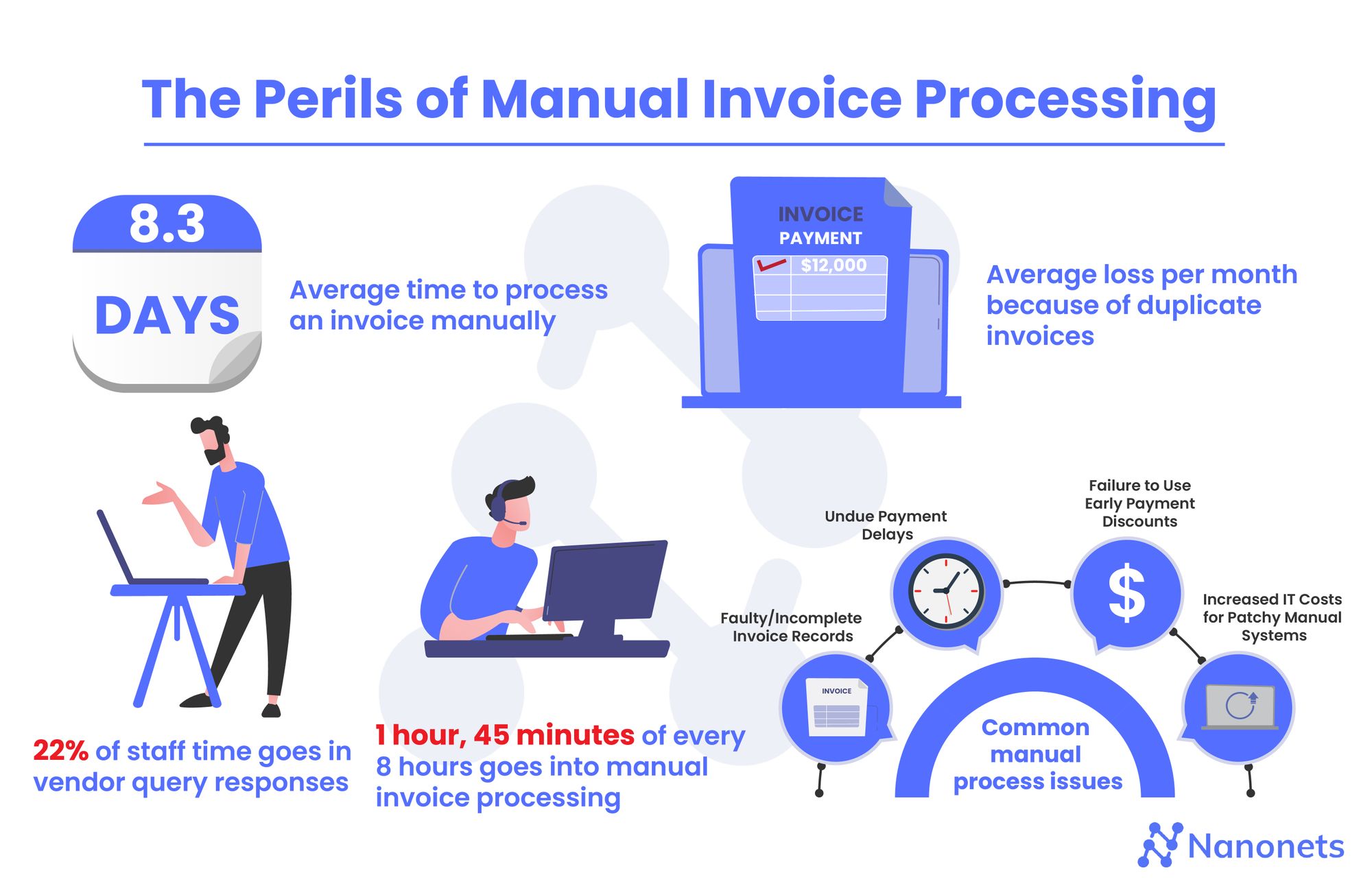
The problems of the traditional process of invoice management, listed in the previous section, can have serious implications on the productivity and profitability of a company:
- Loss in efficiency and productivity: Checking an invoice, handling errors and exceptions, tracking its course, getting approvals, and paying the invoice are time-consuming processes. The time “wasted” on such tasks would be better spent on tasks that contribute to enterprise value. The repetitive tasks associated with bill processing can stifle the productivity of an organization.
- Employee morale and culture: 60% of AP personnel reportedly find invoice processing the most detested chore of their job – dissatisfaction with more than half their jobs leads to loss of morale and enthusiasm among workers. It is natural that employees find time spent on interesting aspects of their jobs rewarding. Thus, minimizing mundane chores of the invoice processing process and increasing time spent on challenging and interesting aspects of an employee’s job can enhance job satisfaction and thereby employee retention.
- Escalating liabilities: Delays caused in the invoice processing workflow can result in unactionable invoices. This can lead to accrued liabilities over time, escalating pressure at audit periods, and non-compliance. All of these affect the bottomline.
- Fraud vulnerability: Some frauds that occur in the invoice process include third-party frauds, labor mischarging, duplicate payments and other internal errors. Invoice frauds may manifest as abnormal invoice volume, mismatch between product/service delivered and invoice specifications, discrepancies between PO and invoice, and dubious employee behaviour. Manual invoice processing tasks can be boring and result in mental lethargy. This may result in frauds being missed when checking invoices for errors and data problems. This is especially true during times of crisis. For example, the Covid-19 pandemic reportedly increased the incidence of invoice fraud in 2020. Invoice fraud is difficult to be manually detected, especially when the business volume is high.
- Decentralized invoice processing: The absence of a consistent or cohesive invoice management workflow can lead to fragmented processes, which in turn can hamper centralized visibility and governance.
- Obstacles to scaling up: As the company grows, manual bill processing becomes unwieldy. Thus, continuing to hold on to what presumably works for a small setup hinders expansion and potential to scale. The ultimate aim of any business is not to maintain status-quo but to grow!
Set up touchless AP workflows and streamline the Accounts Payable process in seconds. Book a 30-min live demo now.
Automated invoice processing
The automation of invoice processing offers a clear solution to most, if not all the problems associated with this manual process. The caveat of “if not all” arises due to the minor need of manual intervention at some stages. Nevertheless, automating many of the repetitive tasks of the process can conserve time, save money, preserve employee morale, and maintain good vendor relationships.
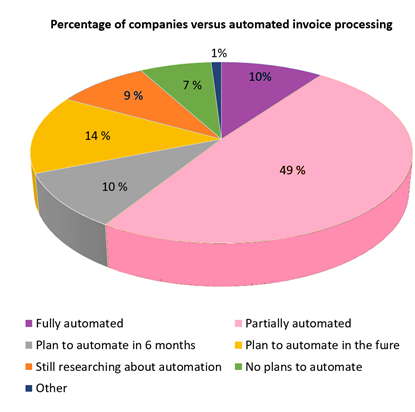
Completely touchless invoice routing – automatically processing invoices from receipt to closure, without manual intervention – is still rare. A survey conducted among personnel involved in AP processes shows an overwhelming support for automating a majority of the manual tasks.
Some specific advantages of the automation of some or most tasks of the invoice processing workflow are:
- Data coherence: Automated invoice processing tools often include automated data Extraction tools that can extract relevant data from invoices and save them in a standardized format that would assist subsequent checks and approvals. Many invoice processing tools come with built-in OCR modules that can extract relevant data from invoices. AI-enabled invoice management tools such as Nanonets can be trained to extract specific data from a variety of formats of invoices.
- Faster three-way matching: Automated three-way comparisons of the invoice with the PO and receipt are faster than manual validations since all data pertinent to the transaction are digitally stored in the same place and can be easily compared either visually or through AI-based software. Automated invoice processing workflows can be integrated with databases and other accounting systems for automatic matching without human intervention.
- Streamlined approvals: Automatic passage of the invoice from one stage to the next and setting up of reminders for approval can avoid delays in the processing of the invoice. The inclusion of contingencies and reminders into the workflow can eliminate bottlenecks. The integration of electronic signatures and digital forms can enable on-the-go approvals from different participants of the process so that physical absence from office would not delay the approval process.
- Process transparency: Multi-level access to data and centralized data storage can allow for transparency. The automation of invoice processing also creates an audit trail for tracking the progress of the invoice along the checkpoints.
- Data security: Digitization of invoice data can prevent loss of information commonly associated with physically moving the document for validation and approval. Automation can also enable integration of the invoice management workflow with the company’s document management system and other bookkeeping tools for audit and archiving purposes. It also helps with regulatory compliance.
- Better business intelligence: Automated invoice management can enable easy access and assessment of purchase data and spending, thereby allowing better analytics and decision making.
- Maintenance of vendor relationships: The absence of delays and organized management of invoices results in timely payments, better vendor communication and thus productive relationships with vendors.
- Elimination of fraud: Automating invoice approval workflows can eliminate fraud by placing checks across the workflow and increasing visibility. Irregularities can be automatically flagged during the automated three-way match. And electronic signature verification can prevent both internal/external frauds and associated losses.
💡
AP processes that are a good fit for automation
Some of the invoice processing steps that would benefit from automation are:
- Invoice receipt: Given that various formats of invoices are received from different vendors, automatic detection of the various relevant fields in the invoice would help in digitization of the invoice and better management of data. OCR tools come in handy here.
- Invoice validation: It is easy to set up rules to check for data integrity and completeness in invoices. Populating the various custom-made fields in the invoice database can help in detecting incomplete or missing information.
- Three-way matching: Invoices are often raised in response to a PO and are often associated with a receipt. These three documents would be connected by a common PO number. Automated matching of invoices, POs and receipts will hasten the validation process and move the invoice to the next level without delays.
- Exception handling: Exceptions and edge cases are not uncommon in invoice management. Edge cases may arise due to time zone changes, multiple recurring charges, retrospective price adjustments, and variable month lengths. Some software, especially those powered by AI, like Nanonets, can handle these edge cases, while some require differing levels of human intervention.
- The approval process: Digital invoices can be moved along the management hierarchy automatically for approvals. The setting up of reminders can also help in hastening the invoice process.
- Payment: Digital payments (wire-transfer etc.) can be built into the software to enable automatic payment to the vendor once all approvals have been received.
- Analytics: Automation can enable assessment and analyses of spend patterns and vendor relationships, which could help in course corrections and productive business decisions. AI-based systems would allow better analytics with more training with invoices.
Book this 30-min live demo to make this the last time that you’ll ever have to manually key in data from invoices or receipts into ERP software.
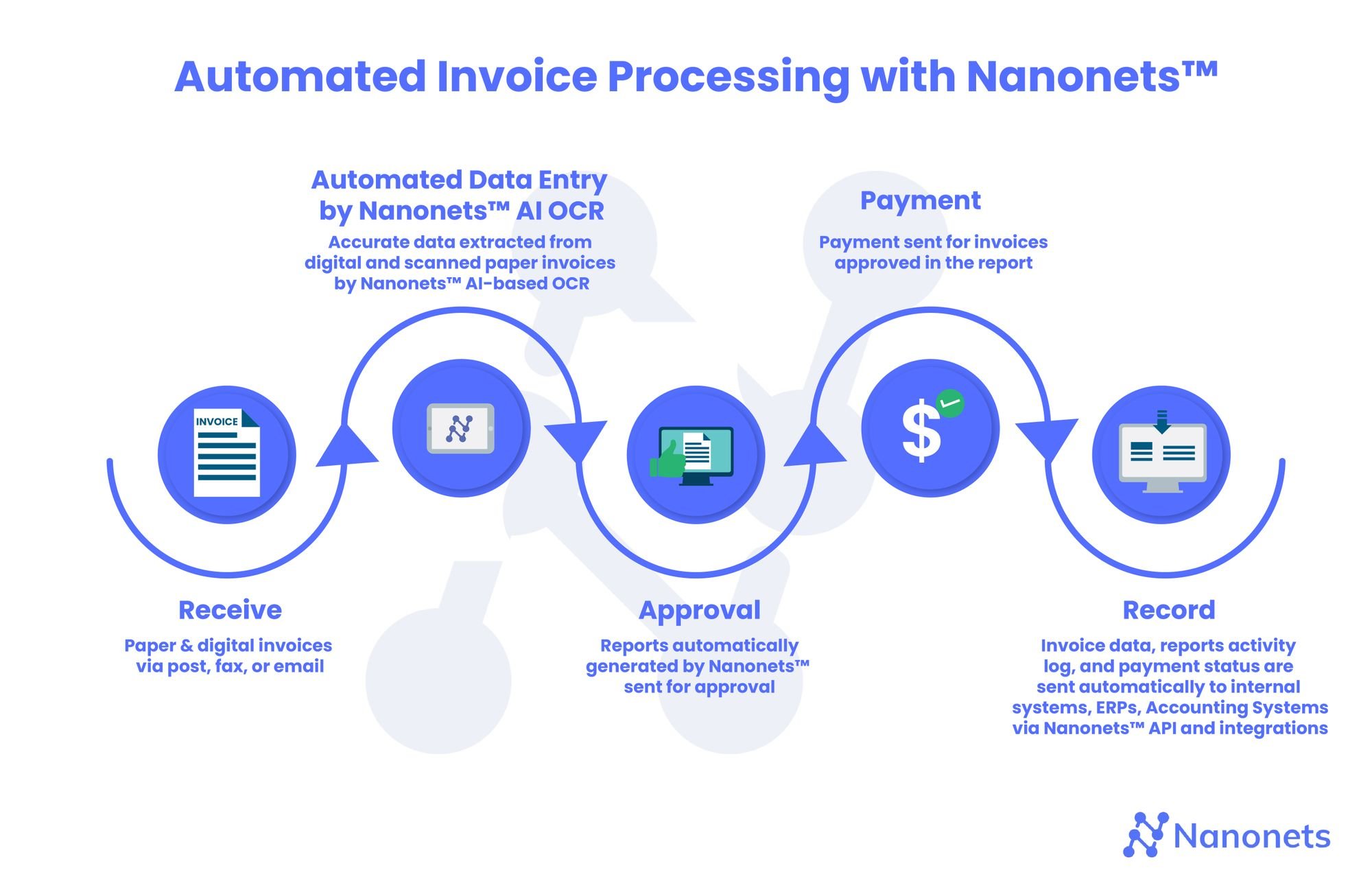
Nanonets for intelligent invoice processing
Nanonets is an AI-based software that can be used to automate and streamline the invoice processing steps of your business.
Data can be captured error-free from a variety of invoice file types. The AI engine of Nanonets can be trained with actual invoices, without the need for coding, which makes it customizable to the company.
It also has built-in state-of-art algorithms and a strong infrastructure for multi-step approvals. The Nanonets invoice processing software can be integrated with other systems such as the Mysql database, QuickBooks, or Salesforce and is platform agnostic. It is accurate and scalable, saves time and money for your Accounts Payable Invoice processing team and enhances productivity.
Takeaway
The automation of invoice processing streamlines the purchase process, enhances transparency of the invoice route, saves time and money, increases employee productivity, and improves vendor relationships. Invoice flow automation allows human employees to concentrate on less mundane, higher-value activities such as planning and strategizing. These can, in turn, lead to improved overall efficiency and profitability of the business.






